We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +31 208081674 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
What is Management? It’s a term we often hear, but have you ever paused to consider its true essence? Management isn’t just about delegating tasks or maintaining smooth operations. It’s an art, a science, and a dynamic practice that drives organisations toward their goals.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the multifaceted world of Management, exploring its evolution, core principles, essential functions, and the skills required to excel. By understanding What is Management, you’ll uncover valuable insights to navigate its complexities and unlock its potential to create lasting impact within any organisation.
Table of Contents
1) Evolution of Management
2) Key Principles of Management
3) Types of Management
4) Functions of Management
5) Skills Required for Effective Management
6) The Future of Management
7) What are the Different Levels of Management Within an Organisation?
8) What are the Various Management Styles?
9) Conclusion
Evolution of Management
The evolution of Management spans civilisations and centuries. In ancient times, informal Management structures were evident in organising collective efforts. The Industrial Revolution brought the need for more structured Management, leading to Frederick Taylor's scientific Management principles, which focused on efficiency.
Further, Henri Fayol's administrative Management introduced crucial functions like planning and organising. Moreover, Peter Drucker emphasised human-centred approaches and organisational behaviour in the 20th century.
As organisations globalised, new Management Theories emerged, including the Contingency Theory and Total Quality Management. Additionally, technology and the digital age brought agile Management and remote coordination to the forefront.
Today, Management adapts to challenges with data-driven decision-making, sustainability, and ethical leadership. Understanding this evolution provides insights to optimise processes, boost productivity, and foster success in modern organisations. By building on past wisdom, effective Management practices continue to evolve and shape the future of business.
Key Principles of Management
Before learning about What is Management, it’s time to understand its core principles. The Principles of Management serve as the building blocks for effective organisational control and success.
Each principle is crucial in ensuring that an organisation operates efficiently, achieves its objectives, and maintains a positive work environment. Here is each Principle of Management explained in detail:
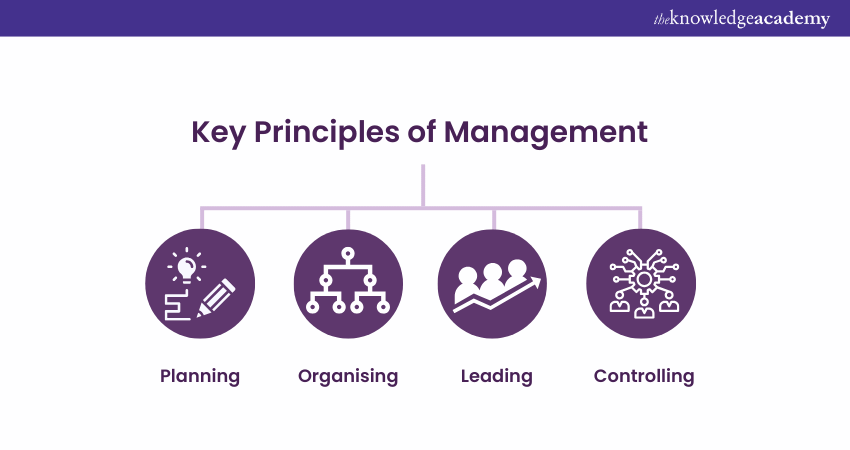
Planning
Planning is the first and foremost principle of Management. It involves setting clear, achievable objectives and developing a detailed strategy to accomplish them. A well-crafted plan outlines the tasks, resources, and timelines required to achieve the desired goals.
Further, effective planning provides direction to the organisation and helps in avoiding haphazard decision-making. It allows Managers and employees to align their efforts towards a common purpose. As a result, it helps maximise productivity and reduce wastage of resources.
Organising
Organising is the process of arranging and allocating resources, tasks, and responsibilities to different individuals or departments within the organisation. A well-organised structure ensures that every member of the organisation understands their roles and contributions to the overall success.
It establishes clear lines of communication and authority, facilitating smooth coordination and collaboration among employees. Additionally, organising optimises the allocation of resources and helps streamline workflows. As a result, it leads to increased efficiency and reduced conflicts.
Leading
Leading is a critical principle that focuses on inspiring and guiding employees to work towards the organisation's objectives. Effective leaders motivate and empower their teams, providing a sense of direction and purpose.
They lead by example, exhibiting the desired values and behaviours that influence others positively. Leadership is not solely about Management positions; it can be displayed at all levels of an organisation. Inspiring leadership fosters a positive work culture, boosts employee morale, and encourages innovation and creativity.
Controlling
Controlling is the process of monitoring, measuring, and evaluating the organisation's performance against established standards and goals. It involves comparing actual results with planned outcomes and taking corrective actions if deviations occur.
Through effective control, Managers can identify potential issues and address them promptly. They can also ensure that the organisation stays on course. Therefore, controlling helps in maintaining efficiency, quality, and consistency in operations, contributing to the overall success of the organisation.
Learn about the roles and responsibilities of a Manager with our Introduction to Management Course - join now!
Types of Management
Management is a diverse field that encompasses various specialised areas, each designed to serve distinct purposes within an organisation. Let's explore the different Types of Management in detail:
General Management
General Management is the broadest and most encompassing type of Management. General Managers are often responsible for the following:
a) Overseeing the overall performance of an organisation
b) Setting strategic goals and objectives
c) Formulating policies and guidelines
d) Making high-level decisions that impact the entire organisation
e) Working closely with department heads and team leads
By fulfilling these responsibilities, Managers ensure effective coordination and alignment of efforts towards achieving organisational goals. Moreover, they are skilled communicators and leaders who provide vision and direction to the organisation as a whole.
Operations Management
Operations Management focuses on the efficient Management of production processes and day-to-day operations within an organisation. Operations managers have the following duties:
a) Ensuring smooth and efficient production of goods or services
b) Planning production schedules
c) Managing inventory
d) Optimising resource allocation
e) Implementing quality control measures
Operations Management plays an important role in improving productivity, reducing costs, thus enhancing the overall efficiency of the organisation.
Project Management
Project Management involves planning, organising, and executing specific projects from initiation to completion. Project Managers are responsible for performing the following:
a) Establishing and defining the project objectives
b) Setting milestones
c) Creating detailed project plans
d) Leading project teams
e) Allocating resources
f) Managing risks
g) Ensuring the timely delivery of projects within the allocated budget
Project Management is essential for organisations that undertake various initiatives, as it ensures efficient project execution and successful achievement of project goals.
Strategic Management
Strategic Management is concerned with long-term planning and guiding the organisation in adapting to changing external environments. Strategic Managers analyse market trends, competitors, and internal strengths and weaknesses to formulate effective strategies.
These strategies align the organisation's resources and capabilities to create a sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management, guided by a well-defined Management Model, involves making critical decisions related to diversification, expansion, mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships, with a focus on achieving the organisation's long-term vision and objectives.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
HRM is responsible for managing the organisation's workforce. HR Managers handle various functions, including the following:
a) Recruitments
b) Candidate selections
c) Employee training
d) Performance evaluations
e) Handling compensation
Employee development
Creating and implementing HR policies and practices
Attracting and retaining a motivated and skilled workforce
By performing these activities, HR Managers promote a positive work environment and talent retention. As a result, HRM plays a pivotal role in an organisation's success.
Financial Management
Financial Management deals with the effective Management of an organisation's financial resources. Financial Managers are responsible for the following:
a) Budgeting
b) Financial analysis
c) Financial reporting
d) Making investment decisions
e) Ensuring the organisation's financial health
f) Optimally allocating financial resources
Therefore, Financial Management is essential for financial planning, Risk Management, and ensuring the organisation's stability and sustainability.
Learn how to bring the best out of people with our Introduction to Managing People Course - sign up today!
Functions of Management
The Management process entails several critical functions that are important in ensuring the smooth operation and success of an organisation. Let's explore each function in detail:
Setting Clear Goals and Objectives
One of the primary Functions of Management is to define clear and achievable goals and objectives for the organisation. These goals provide direction and purpose to employees. They direct their efforts towards a common vision.
Moreover, well-defined objectives help align the organisation's activities and resources. As a result, it ensures that everyone is working towards the same desired outcomes.
Decision-making
Decision-making is a pivotal function that Managers perform on a regular basis. Managers are faced with numerous choices and alternatives that impact the organisation's direction and performance. Effective decision-making involves evaluating options, analysing risks and benefits and selecting the best course of action to achieve the desired results.
Effective Communication
Communication is often considered the lifeblood of an organisation. It is crucial for conveying information, ideas, and instructions across all levels and departments.
Managers need to ensure that communication flows smoothly and efficiently, both vertically (from top to bottom) and horizontally (among different teams and departments). Clear and effective communication fosters understanding, collaboration, and a sense of unity within the organisation.
Motivation and Team Building
Managers are critical in motivating employees to give their best. Motivation involves inspiring individuals to be proactive, dedicated, and committed to their work. Effective Managers understand the needs and aspirations of their team members. They also create an environment that encourages personal growth and professional development.
Team building is another essential function. As Managers must foster a sense of camaraderie and collaboration among team members, they promote a positive work environment and enhance productivity.
Master verbal and non-verbal communication with our Senior Management Training - join today!
Skills Required for Effective Management
Effective Management requires a diverse skill set that empowers managers to navigate various challenges and drive organisational success. Let's explore the key Management Skills:
Technical Skills
Technical skills refer to the specific set of knowledge and expertise required to perform tasks related to the organisation's industry or field. For example, in a manufacturing setting, technical skills may include proficiency in operating machinery, understanding production processes, and implementing quality control measures. Similarly, in the business world, technical skills may encompass financial analysis, data interpretation, or marketing strategies. Additionally, Test Management Tools are essential for ensuring the proper execution of tasks in software development, as they help manage test cases, track defects, and improve overall process efficiency.
These skills provide Managers with the ability to understand and address the technical aspects of their roles. As a result, it ensures that they can make informed decisions and contribute efficiently to the organisation's operations.
Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are crucial for building positive relationships and effective communication with team members, colleagues, clients, and stakeholders. These skills involve the following:
a) Active listening
b) Empathy
c) Conflict resolution
d) Collaboration
Effective Managers are skilled communicators who can articulate ideas clearly, motivate their teams and foster a sense of trust and respect among different members of the team. Moreover, strong interpersonal skills enable Managers to create a supportive work environment where employees feel valued and motivated to contribute their best efforts.
Conceptual skills
Conceptual skills are the ability to think critically and understand the broader picture of the organisation and its industry. Effective managers possess the capacity to analyse complex situations, identify patterns, and conceptualise solutions.
They can see how various elements within the organisation are interconnected and how external factors can impact the business. Additionally, conceptual skills enable Managers to make strategic decisions, envision the organisation's future, and adapt to changing environments.
Learn how to bring structure and order to events with our Event Management Course – sign up now!
The Future of Management
In today's constantly changing landscape of technology and society, the future of Management is poised for significant transformation. As organizations adapt to the dynamic environment, new trends and practices will shape the way they are approached. These evolving approaches will likely build upon established Management Concepts. Here are some key aspects that will define the future of Management:
Focus on Diversity
The future of Management will place greater emphasis on diversity and inclusion in the workforce. Organisations will recognise the value of diverse perspectives, experiences, and backgrounds in fostering creativity and innovation.
Further, inclusive leadership will be essential for building diverse teams. It will be helpful in creating an environment where every individual feels valued, appreciated and empowered to contribute their best.
Flexible Work
The rise of remote work and flexible work environments will continue to shape Management practices. Managers will need to adapt to leading virtual teams. As a result, they will ensure effective communication and maintain team cohesion in a digital workspace. Moreover, flexibility in work arrangements will be key in attracting and retaining top talent.
Employee Well-being
Employee well-being and work-life balance will be at the forefront of Management concerns. Organisations will invest in programs and initiatives that promote mental and physical health. They will also recognise that a healthy and happy workforce leads to higher productivity and reduced employee turnover.
Adaptive Leadership
The future of Management will demand agile and adaptive leadership. Managers will need to be responsive to rapid changes, navigate uncertainty, and make data-driven decisions. They will be required to inspire and motivate teams in times of transformation and complexity.
Unlock new sets of Managerial skills with our courses in Management Courses - join now!
What are the Different Levels of Management Within an Organisation?
Organisations typically have three levels of Management:
1) Top (strategic decisions)
2) Middle (implementation and coordination)
3) Lower (supervising operations and employees)
What are the Various Management Styles?
Common Management styles include autocratic leadership, democratic, laissez-faire, and transformational. They differ in decision making approaches, employee involvement, and focus on achieving organisational goals effectively.
Unlock the Benefits of Management Training in our blog and enhance your career!
Conclusion
As we conclude this What is Management blog, we hope you understand that it is an exciting journey of transformation and adaptation. Embracing innovation and continuous learning will define the future of the managerial process, shaping organisations for success in a dynamic world. Management will continue to evolve, guided by forward-thinking leaders and responsive strategies.
New to the Management process? Try our Management Training for New Managers Course - now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Four Key Management Practices?

Four Key Management Practices are:
a) Setting clear goals and expectations
b) Effective communication and feedback
c) Employee development and training
d) Performance monitoring and continuous improvement
What is the Difference Between Management and Leadership?

Management focuses on planning, organising, and controlling resources to achieve goals. Leadership inspires, motivates, and guides people toward a vision, emphasising influence over authority.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including Introduction To Management, Management Training For New Managers, Introduction To Managing People and Personal & Organisational Development. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Principles of Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Management
Introduction to Management
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


