We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +47 80010068 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
If you are looking to explore the financial sectors to make sensible financial decisions, then you need to learn the distinctions between Mortgage vs. Loan. While both involve borrowing money, they have different purposes and distinct characteristics. A Mortgage is a specific type of Loan used to purchase real estate secured by the property itself.
In contrast, a Loan is a broader term encompassing various forms of borrowing, such as personal, car, and business, often without collateral. Are you intrigued to learn more about these types of financial products? Read further into this blog to learn more about the distinctions between Mortgage vs. Loan.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Mortgage?
2) What is a Loan?
3) Differences between Mortgage and Loan
4) Mortgage vs Loan: Collateral requirement
5) Mortgage vs Loan: Interest rates
6) Mortgage vs Loan: Loan amounts and repayment terms
7) What are the types of Mortgages?
8) What are the types of Loans?
9) Conclusion
What is a Mortgage?
A Mortgage is a Loan where a home or the piece of property an individual owns is offered as security. When you obtain a Mortgage, the Loan company gains the rights to your house by legally putting a claim on the property, referred to as a lien. This lien allows the lending institution to seize or sell your property if you fail to pay your bills.
Mortgages are often used to purchase or refinance homes or other properties. Due to the value of Real Estate being expensive, many buyers need a Loan to help them instead of buying property in full. During Loan processing, the following factors are considered: Credit score and history, income, and debt-to-income ratio, among others. An appraisal is commonly required to determine the value of the property, which in turn determines the loan amount you qualify for. Also, they enable individuals to access other sources of funds through home equity, which in most cases is a Mortgage.
What is a Loan?
Loans are credit agreements that involve a borrower receiving cash from a lender, with agreed terms regarding the size of the principal amount of money borrowed and the interest to be charged and paid.
There are numerous Loans for personal and business financing with different rates of security, which certain valuable items may secure. Every type of Loan has its advantages and disadvantages, and it remains best suited for different fiscal circumstances.
Borrowing denotes obtaining a Loan with the understanding that it shall be reimbursed by a certain amount plus interest within some stipulated period. In the case of term Loans, this entails paying the entire amount of the borrowed money before the specified period elapses, although it is done a little at a time in the form of instalments.
On the other hand, revolving credit means that a specified amount of money is available at a particular time, and a client can repay and borrow again without limitations, thus giving variable usage of the given funds.
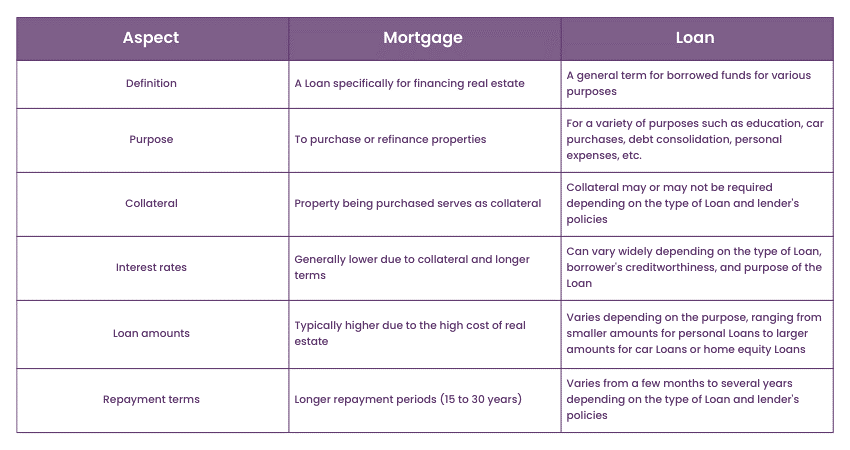
Differences between Mortgage and Loan
The table showing the aspects of Mortgage and Loan will help you understand the distinctions between them:
Embark on a rewarding journey in Mortgage advice, gain industry knowledge, and become a certified Mortgage professional with our comprehensive CeMAP Training.
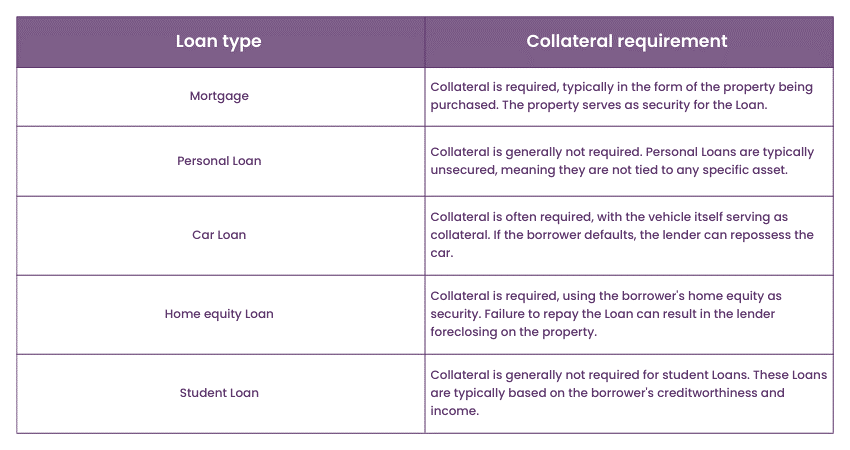
Mortgage vs. Loan: Collateral requirement
Mortgages and Loans differ in some ways, one of which is in terms of collateral. A Mortgage is a type of secured Loan because it is offered as security against the house or property that is purchased. The actual deed or title of the property is pledged and acts as security for the money advanced to the borrower.
In case the borrower is unable to pay the Loan, the lender can seize the property and use the proceeds from the sale to recover the balance. This collateral requirement also provides a certain level of comfort to the lender, as the borrower stands to lose their house, giving the lender a measure of security.
Mortgages, which are kinds of actual security, generally incur lower interest rates than those for unsecured Loans. Because the property secures the money lender, they are willing to pay more lenient interest rates for the borrowers. This is because the default rate risk is considerably lower since the property can be seized if there is a default.
On the other hand, when borrowing capital in the form of Loans, there is always an option of providing security for the Loan or not, depending on the nature of the Loan. Other Loans, like automobile Loans or second Loans, might be collateralised by the re-credited Asset being purchased.
In these cases, the lender can regain their money by repossessing the asset if the borrower defaults. However, most Loans, including personal or credit cards, are considered unsecured, meaning they do not call for an asset’s backing. As their name suggests, these Loans depend on the borrower’s credit ratings and income to get credit approval, and they attract higher interest rates to cover the higher risk of default as seen by the Lender.
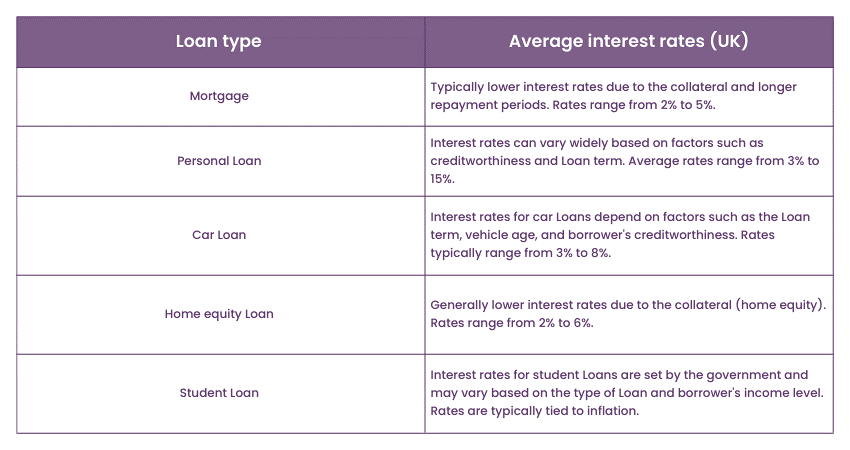
Mortgage vs. Loan: Interest rates
The following differential feature between Mortgages and Loans focuses on interest rates. Again, interest rates associated with Mortgages are lower than most other Loans extended to consumers in the market. This is mainly because of the security offered by the property and the longer tenures compared to different types of securities, such as car and personal Loans, usually endorsed by Mortgages.
Mortgage interest rates are often fixed, which means that the indicated type of interest stays unchanged during a specific period necessary for the full repayment of the Loan amount. Regularity and grace period make this type of Loan favorably helpful to borrowers.
This allows them to have a fixed monthly payment where planning for the future is not a game of risks. Concerning Mortgages, in particular, it would be relevant to conclude that lower interest rates make definite savings during the entire term of the Loan.
On the contrary, Loans may have a fixed or a floating rate depending on the kind of Loan being taken and the terms given. Another example is that the interest rate is higher than that of Mortgages when taking out personal Loans or buying on credit cards. As the name suggests, unsecured Loans do not demand any form of security and, therefore, pose a higher risk to lending institutions, attracting higher interest rates on Loans.
Moreover, some of the fundamental features of Loans include that student Loans may be either fixed or variable. The stated monthly payment may also alter the market situation of the financial instrument, which influences the variable interest rate.
A borrower can benefit when interest rates vary, in this case between a Mortgage and a Loan, by evaluating whether interest rates should or should not have an impact. Mortgages can be helpful, too, because lower interest levels and homeownership are possible. So, individuals can invest in increasing their equity of a home.
However, when the interest on Loans is raised, the cost of borrowing increases. This may lessen the borrower's capacity to clear the Loan within the required time.
When preparing to take any Loan or Mortgage, it is important to review the various interest rates and policies. If you are a borrower, you need to also recognise the guidelines involved and estimate the overall financial outcome.
Appraising the interest rates of lending institutions and the various Loan products available in the market enables you to access the best deals and avoid the congestion of extra expenses during the borrowing period.
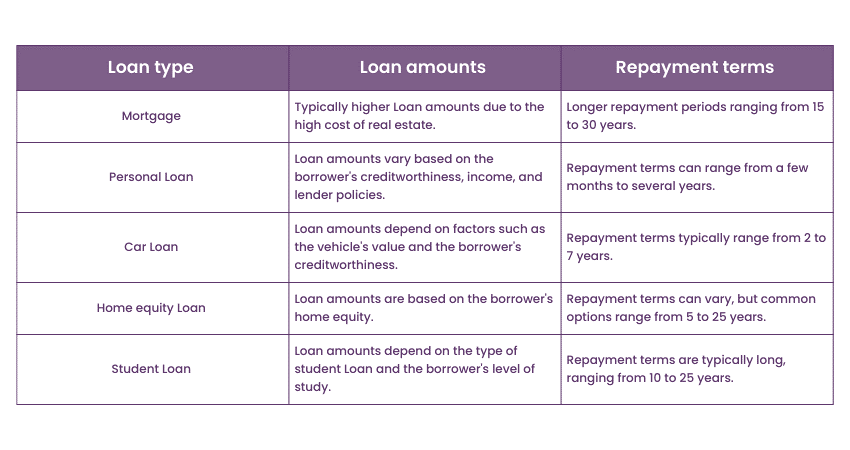
Mortgage vs. Loan: Loan amounts and repayment terms
Mortgages and Loans are two distinct categories with different amounts and repayment terms. Such facilities usually require higher Loans since Real Estate is rather expensive. It depends upon the property's value and the borrower's creditworthiness.
These huge Loan amounts allow people to buy houses and real estate, which they would not be able to afford otherwise, with long-term Loans. Mortgages are a unique type of Loan where the Repayment period is longer than that of other Loans. The repayment span usually falls between 15 and 30 years, thus giving a borrower ample time to repay the Loan.
The longer time frame for repayment ensures that the monthly instalments are relatively low, thus making it easier for borrowers to manage their finances towards acquiring their homes. However, more extended terms often mean the total interest you pay over the entire Loan duration will also increase.
However, Loans other than Mortgage Loans may be highly diversified in Loan sizes and repayments. Loan amounts for these purposes are generally smaller than Mortgages. The repayment period for Loans can range from a few months to several years based on certain factors like the lender, the borrower's creditworthiness, and the Loan's specific use. Shorter repayment periods may be suitable for candidates who want to pay back the funds promptly or have some timeline in mind.
Lenders should also ensure that Loan amounts and repayment terms suit the borrower’s financial capacity, demands, and desires. Knowing how much you need to pay each month and the total cost of financing is crucial. You should always compare different Loan offers, review the repayment conditions, and select the most suitable solution based on your individual needs and budget.
What are the types of Mortgages?
There are various kinds of Mortgages through which the Loan amount varies depending on the rate of interest, the size of term, and much more. Let us look at a few of them to gain clarity:
Fixed-rate Mortgages
Home Loans are mainly of two types: fixed-rate Mortgages and adjustable-rate Mortgages. A third type of fixed-rate Mortgage is known as a ‘hybrid’ Mortgage. These big Loans are paid gradually over a long term, which may span as long as 10 to 50 years or an early term if possible.
Fixed-rate Mortgages feature a rate of interest set when the Loan is issued, and changing this rate is possible only through refinancing the Loan. Interests are also fixed for the entire Loan period, and borrowers can make additional payments for a shorter repayment term. In these Loan programs, repayment of the amount reduces the interest amount first and then the principal amount.
FHA Mortgage Loans
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) is an agency that provides insurance for Mortgage Loans from FHA-sanctioned creditors to borrowers with risky credit status. The government does not fund these Loans; instead, they are offered by private entities like banks, though the government acts as a guarantor for up to a particular value of the Loan.
FHA Loans are primarily offered to first-time home-buying households and those with low—and moderate-income earners who cannot afford a 20% down payment. These include people with bad credit and a history of bankruptcy, among other cases. As mentioned earlier, FHA Loans enable high-risk borrowers to buy a home without putting down a 20% down payment, but they need to pay private Mortgage insurance.
VA Loans for veterans
VA Loans work similarly to FHA Loans, where the government does not lend the money but rather provides insurance or a guarantee for Loans provided by any other third-party lender. A veteran's performance in paying the Loan is crucial because if a veteran cannot pay the Loan in due time, the government refunds the Lender not less than twenty-five percent of the amount of the Loan.
The unique features of VA Loans include the fact that veterans are not expected to make any down payments and that no private Mortgage insurance (PMI) is required. So, certain single veterans might have poorly documented civilian work records and income, which would make them part of the high-risk segment that can be turned away from Mortgage Loans in the conventional lending market.
There are currently different Types of Mortgages, including interest-only, adjustable-rate (ARM), and reverse Mortgages. Although non-adjustable Mortgages are the most common kind, fixed-rate Mortgages have continued to enjoy wide acceptance. Housing finance agencies use different types of fixed-rate Mortgages, but the 30-year fixed-rate program is the most popular.
With our comprehensive training, you can unlock your full potential in Mortgage advice, advance through all levels of expertise, and achieve your CeMAP Level 1, 2, and 3 certifications.
What are the types of Loans?
Let us look at a few types of Loans to gain clarity on which are suitable for your needs:
Open-end vs closed-end Loans
There are two primary types of Loan credit: open-end credit, which is also referred to as revolving credit, and closed-end credit. Open-end credit is like a credit card, which can be borrowed multiple times. It has a credit limit that may be borrowed and repaid as often as desired if the borrower pays off the card monthly and does not exceed their credit limit.
Each time the card balance rebounds to zero, the borrower can borrow the total amount of the credit limit again. On the other hand, closed-end credit, also referred to as a term Loan, is when an individual is permitted to borrow a specific amount of money under the understanding that they will have to repay the total amount at a certain period.
But what if the borrower partially repaid the Loan? This means that they can apply for this amount once again. For example, if you have a closed-end Mortgage Loan of 150,000, a person who has already paid back 70,000 cannot borrow another 70,000 for the same Loan. However, they would have to apply for a new Loan to borrow some more money.
Secured vs. Unsecured
Loans can be simplified into two types: A secured Loan is one in which the borrower must provide collateral, while an unsecured Loan is one in which the borrower does not provide any security. Unsecured Loans do not have any security for collateral in the event of non-payment or in situations where the borrower is insolvent.
In this case, it is difficult for the creditor to recover the dues. The amount and terms of unsecured Loan applications are determined by the borrower’s income, credit report, and credit rating. Since unsecured Loans involve a higher risk exposure to the lenders' exposures, the interest rate on such Loans is normally high, and the amount of money given is normally small compared to secured Loans. Examples of unsecured Loans are personal Loans, bank overdrafts, credit cards, and others.
Secured Loans are known as collateral Loans. These Loans are availed by using an asset, such as a property or vehicle. Examples include Mortgages, auto Loans, and others. These Loans require the borrower to offer an asset against an amount of money as security to receive the cash.
Using secured Loans as an alternative, lenders are likely to lend larger sums of money at relatively lower interest rates than unsecured Loans, though they are deemed to have less risk. Lastly, it lays out some of the conditions governing the Loan agreement and whether the lenders can seize all or part of the asset in the case of the borrower defaulting on the Loan.
Learn how to become a Mortgage Broker with the help of our Mortgage Interview Questions blog today!
Conclusion
Understanding the comparison between Mortgage vs. Loan will help you to make better financial decisions in your future. If you want to make any kind of significant investment, then you need to evaluate both Mortgage and Loan based on their collateral, interest rates, Loan amounts, etc. We hope this blog can provide you with the insight to ensure your long-term financial success.
Embark on a rewarding career in financial advice, acquire in-depth knowledge and skills, and earn your CeMAP Courses.
Frequently Asked Questions

If you want to choose between a Mortgage and a home Loan, it will depend on the interest rates, Loan rates, and your own individual financial goals.

A reMortgage can often be cheaper than a personal Loan due to typically lower interest rates, as it is secured against your property.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various CeMAP Courses, including the CeMAP Course (Level 1,2 And 3). These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Mortgage Life Cycle.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Mortgage, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Mortgage Advisory skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CeMAP Course (Level 1,2 and 3)
CeMAP Course (Level 1,2 and 3)
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


