We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +47 80010068 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Value Management is a crucial process that organisations undertake to optimise the value they deliver to their customers while minimising costs and resources. By strategically analysing and evaluating their operations, businesses can identify areas for improvement, enhance efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction. This blog will explore the different Stages of Value Management and how they contribute to achieving organisational success.
Table of Contents
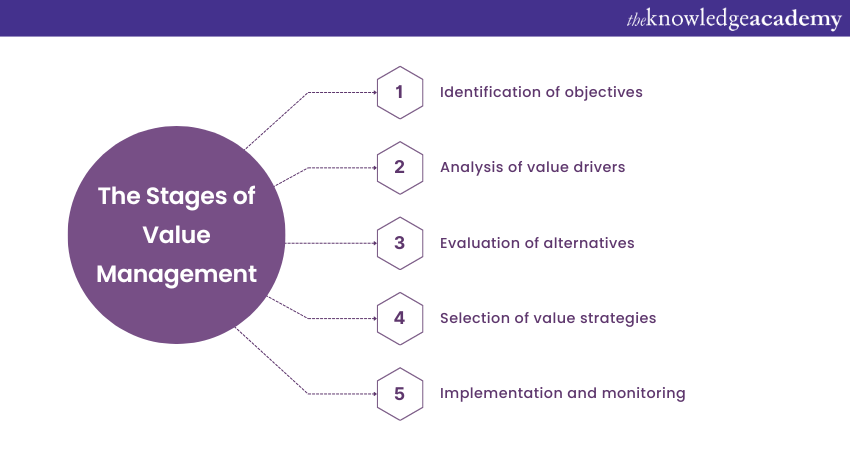
1) The Stages of Value Management
a) Identification of objectives
b) Analysis of value drivers
c) Evaluation of alternatives
d) Selection of value strategies
e) Implementation and monitoring
2) Conclusion
The Stages of Value Management
This blog section will elaborate on the different stages in the Value Management process.
Identification of objectives
The first stage in the Value Management process is the identification of objectives. This step involves setting measurable and clear goals aligning with the organisation's vision and mission. By clearly defining objectives, businesses can provide a sense of direction and purpose for their Value Management initiatives.
During the identification phase, organisations need to assess their current position and determine what they want to achieve through Value Management. This involves conducting a thorough market analysis, customer needs, and internal capabilities. By understanding the external environment and internal strengths and weaknesses, companies can identify areas where value can be enhanced.
Organisations should involve key Stakeholders like senior management, department heads, and customer representatives to identify objectives effectively. This collaborative approach ensures that diverse perspectives and insights are considered when setting goals.
When defining objectives, it is crucial to ensure they are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Specific objectives provide clarity and focus, while Measurable objectives enable progress tracking. Achievable objectives ensure that they are realistic and within the organisation's capabilities. Relevant objectives should align with the organisation's overall strategy and priorities. Lastly, Time-bound objectives should be trackable, time-oriented, time-limited, time-sensitive and achievable within a time frame.
Unlock your potential in managing successful projects with our MoV Foundation course - sign up now!
Analysis of value drivers
The analysis of value drivers is a crucial stage in the Value Management process, allowing organisations to comprehensively understand the factors that contribute to creating value. By conducting a thorough analysis of these drivers, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement and optimisation.
During the analysis phase, organisations delve into various aspects that impact value creation, such as quality, cost, innovation, customer experience, and efficiency. Each of these value drivers plays a unique role in shaping the overall value proposition of a product, service, or process.
Quality is a pivotal value driver that directly influences customer satisfaction and loyalty. By maintaining high standards of quality throughout their operations, businesses can enhance the perceived value of their offerings.
Cost is another critical value driver that organisations need to assess. By closely evaluating and managing costs, businesses can improve profitability and competitiveness. This involves identifying cost-saving opportunities, optimising resource allocation, and implementing efficient processes.
Innovation serves as a critical value driver that drives continuous improvement and differentiation. By fostering a culture of innovation and exploring new ideas, organisations can stay ahead of the competition and deliver unique value to customers.
Customer experience is a vital value driver that focuses on meeting and exceeding customer expectations. By understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points, businesses can design products and services that provide a superior experience, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Efficiency is a value driver that aims to streamline processes and eliminate waste. By optimising workflows, reducing bottlenecks, and enhancing productivity, organisations can achieve operational excellence and deliver value more efficiently. By leveraging data-driven insights, organisations can gain an exhaustive understanding of the current state of their value drivers and identify areas for improvement.
Enhance your project management knowledge to the next level with our combined MoV Foundation & Practitioner course - sign up now and become a certified expert!
Evaluation of alternatives
The evaluation of alternatives is a critical stage within the Value Management process that allows organisations to assess and compare various options for achieving their objectives and maximising value. This stage involves carefully considering different alternatives and selecting the most effective strategies.
During the evaluation phase, businesses analyse and weigh the advantages, disadvantages, risks, and feasibility of each alternative. They consider factors such as cost-effectiveness, return on investment, alignment with organisational goals, market potential, competitive advantage, and sustainability.
To conduct a thorough evaluation, organisations establish clear criteria and benchmarks against which each alternative is assessed. These criteria ensure a consistent and objective evaluation process. Involving relevant stakeholders, such as cross-functional teams and decision-makers, provides diverse perspectives and expertise, enabling comprehensive evaluations.
Organisations employ various evaluation techniques and tools, such as cost-benefit analysis, risk assessment, market research, feasibility studies, pilot projects, and scenario planning. These methods generate valuable insights and data to support the decision-making process.
Organisations critically assess each alternative against the established criteria throughout the iterative evaluation. They consider potential benefits and drawbacks, short-term and long-term implications, resource requirements, and potential risks. This careful evaluation enables informed decision-making and selection of the most viable alternatives.
By conducting a comprehensive evaluation of alternatives, organisations can make strategic choices that align with their objectives and have the highest potential for value creation. This stage paves the way for effective decision-making in subsequent phases, ultimately driving value maximisation and organisational success.
Selection of value strategies
The selection of value strategies is a crucial stage in the Value Management process, where organisations determine the most effective approaches to optimise value creation and achieve their objectives. This stage involves evaluating different strategies and choosing the ones that align with the organisation's goals and have the most significant potential for value enhancement.
During the selection phase, businesses assess various value strategies based on their ability to leverage identified value drivers and address specific objectives. These strategies may encompass areas such as product development, process improvement, customer engagement, cost optimisation, innovation, or market expansion.
Organisations consider a range of factors when evaluating value strategies to make informed decisions. These factors include market dynamics, competitive landscape, resource availability, risk tolerance, customer insights, and alignment with the organisation's vision and values.
The selection process often involves cross-functional collaboration and input from key stakeholders, including senior management, department heads, and subject matter experts. Engaging these stakeholders ensures diverse perspectives, encourages buy-in, and increases the chances of successful strategy implementation.
Organisations may use various evaluation methods, such as cost-benefit analysis, scenario planning, risk assessment, and market research, to assess the potential impact and feasibility of each strategy. These techniques provide valuable insights into the potential risks, benefits, resource requirements, and long-term implications of the selected strategies.
Once the evaluation is complete, organisations can confidently choose the most appropriate value strategies that align with their objectives and have the highest likelihood of success. The selected strategies serve as a roadmap for subsequent actions and initiatives.
By carefully selecting value strategies, organisations can direct their efforts towards value optimisation, ensuring that resources are allocated to areas that will generate the greatest impact. This stage sets the foundation for effective implementation and execution, driving the organisation closer to its desired outcomes and maximising overall value creation.

Implementation and monitoring
The stage of implementation and monitoring is a critical phase in the Value Management process, where organisations put their selected strategies into action and continuously monitor their progress towards achieving value optimisation. This stage involves translating plans into practical actions, allocating resources effectively, and actively tracking performance.
During the implementation phase, organisations focus on executing the chosen value strategies. This may involve deploying new processes, introducing product enhancements, improving customer service, or implementing cost-saving measures. Clear communication and coordination among various teams and departments are essential to ensure smooth execution.
Effective implementation requires assigning responsibilities, setting timelines, and providing the necessary resources and support to accomplish the planned activities. It is essential to involve and engage employees at all levels, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment to the implementation process.
Simultaneously, organisations establish monitoring mechanisms to track the progress and effectiveness of the implemented strategies. This involves collecting relevant data, setting performance indicators, and regularly assessing the outcomes against predefined targets and benchmarks.
Continuous monitoring allows organisations to identify any deviations, challenges, or gaps that may arise during implementation. It provides important insights into the effectiveness of the strategies and helps in making timely adjustments or refinements as needed. Regular reviews and evaluations ensure that the Value Management process remains dynamic and responsive to changing circumstances.
Organisations can proactively identify and address any issues hindering value optimisation by implementing strategies and closely monitoring their progress. This stage ensures that the Value Management process remains on track and enables organisations to make data-driven decisions to refine their strategies and actions. Successful implementation and diligent monitoring lead to improved performance, enhanced customer satisfaction, and long-term success.
Conclusion
All in all, Value Management is vital for organisations to optimise value creation and achieve their objectives. The abovementioned systematic approach ensures informed decision-making, effective execution, and continuous improvement. By adhering to the different Stages of Value Management, organisations can maximise value, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and achieve long-term success.
Accelerate your career in project management. Register for our comprehensive MoV Training courses today and gain the skills to excel!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 MoV® Foundation
MoV® Foundation
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


