We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +47 80010068 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

All businesses, regardless of their industry, must have a strong online presence to expand and reach a wider global market. The most effective way to achieve this is by creating a website and directing potential customers to it. If you're unfamiliar with this concept, you may be wondering, "What is a website?"
A website is a digital space that explicitly provides information about a company or individual, along with other features and elements that define the brand's identity. In this blog, we will discuss what a website is, it's different types, essential characteristics, and categories to help you build a website that aligns with your niche.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Website?
2) Types of Websites
3) Website categories
4) Elements of a Website
5) Conclusion
What is a Website?
A Website is a digital platform accessible via the internet, serving as a virtual space where individuals, businesses, or organisations can create an online presence. It allows them to share information, offer various products or services, and connect globally. Websites come in multiple types and categories, each tailored to specific purposes and consisting of essential elements contributing to their functionality and design.
Types of Websites
To help you understand more about Websites, let us have a look here at the types of Websites:
1) Static Website
A static Website is a straightforward and essential form where the content remains fixed and unchanging. It typically consists of web pages with content that doesn't require frequent updates. Static Websites are easy to create and cost-effective to host since they don't rely on databases or Content Management Systems (CMS).
These Websites are suitable for displaying company brochures, personal portfolios, or simple informational pages. While they lack the interactive features and dynamic content found in more complex Websites, static sites are reliable and serve as a stable online presence for those who need a web presence without frequent updates or user engagement. Understanding static vs dynamic website differences can help in choosing the right type for your needs.
2) Dynamic Website
A dynamic Website is a more complex and interactive form with content that can be updated regularly. Unlike static Websites, active sites are designed to adapt and change frequently. They are well-suited for businesses, news outlets, or e-commerce platforms that require continuous updates and user interaction.
Dynamic Websites often use CMS like WordPress, which allows users to easily create, modify, and publish content without extensive technical knowledge. This flexibility makes dynamic Websites ideal for delivering fresh information, engaging users with interactive features, and offering a personalised experience, making them a versatile choice for a wide range of online endeavours.
Website categories
Here, we have discussed some different Website categories. Let’s have a look:
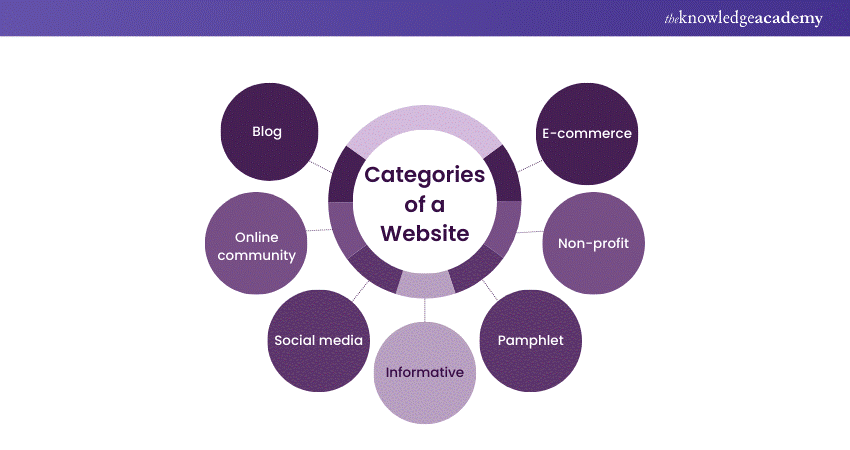
1) Blog
A blog is a dynamic Website primarily focused on sharing written content in the form of articles or blog posts. Blogs serve various purposes, from personal journals and creative writing to professional commentary and niche-specific topics. They provide a platform for individuals, businesses, and organisations to express their ideas, share knowledge, and engage with an audience. Blogs often encourage reader interaction through comments, fostering a sense of community and enabling discussions around the posted content.
2) Online community
Online communities are dynamic Websites designed to facilitate social interaction and discussions among members. These communities include forums, discussion boards, and social networking platforms where people with shared interests or goals can connect and engage. Online communities provide a virtual space for networking, information exchange, and support. They often revolve around niche-specific topics, hobbies, or professional interests, allowing members to collaborate, seek advice, or engage in discussions with like-minded individuals.
3) Social media
Social media platforms are dynamic Websites created for people who want to connect, share, and communicate with others on a global scale. Popular examples include Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn. These platforms enable user-generated content, real-time interaction, and networking. Users can share text, images, videos, and links, fostering engagement with friends, family, colleagues, and even broader communities. Social media has become integral to modern communication, influencing social trends, news dissemination, and online marketing strategies.
4) Informative
Informative Websites serve as valuable educational information resources on various topics. These dynamic sites can include the web pages of educational institutions, government websites, and news portals. They prioritise providing accurate and reliable information to visitors, offering in-depth coverage of subjects such as news, research findings, or educational content. Informative Websites often feature a dynamic structure, with regularly updated articles, reports, or multimedia content to keep the audience informed and engaged with the new developments in their respective fields.
5) Pamphlet
Pamphlet Websites are concise and straightforward, serving as online brochures that provide essential information about a business or service. These dynamic sites offer key details, including contact information, services or products, and brief descriptions. Their design emphasises simplicity, making them easy to navigate and ideal for quick reference. Pamphlet Websites are commonly used by small businesses, local service providers, or professionals who want to establish an essential online presence without complex features or extensive user engagement. Effective website design tips can enhance pamphlet websites, improving functionality and presentation.
6) Non-profit
Non-profit Websites are dynamic platforms dedicated to organisations with charitable or philanthropic missions. These sites aim to raise awareness, attract volunteers, and facilitate donations to support their causes. Non-profit Websites often include detailed information about the organisation's mission, projects, and initiatives, along with compelling stories and visual content to connect with visitors emotionally.
They serve as vital tools for fundraising, volunteer recruitment, and sharing the impact of charitable efforts. Dynamic features such as event listings, donation portals, and volunteer registration forms are commonly integrated to support their goals.
7) E-commerce
E-commerce Websites are dynamic platforms designed for buying and selling products or services online. These sites feature product listings, shopping carts, secure payment processing, and often extensive product catalogues. Examples include popular online marketplaces like Amason and eBay and dedicated e-commerce stores powered by platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
E-commerce Websites prioritise user-friendly navigation, product search, and seamless checkout experiences. They cater to online shoppers, offering convenience, product reviews, and various payment options. Dynamic inventory management, real-time pricing updates, and order tracking are essential to successful e-commerce Websites.
Are you interested in learning more about how to develop an app or a Website? Register now for our App & Web Development Training!
Elements of a Website
There are several elements and aspects of a Website that you need to maintain. These are as follows:

1) Web host
A web host is the backbone of any Website, serving as the infrastructure that makes a website accessible on the internet. Web hosting providers store all the Website's files, databases, and content on their servers, allowing users to access these resources through a web browser. Selecting the right web host is crucial, as it directly influences a Website's performance, uptime, and security.
Web hosting comes in several forms: shared hosting, Virtual Private Servers (VPS), dedicated hosting, and cloud hosting. Each type has distinct features and resources, catering to different Website needs. Shared hosting, for example, is cost-effective but may have limited resources, making it suitable for small Websites. On the contrary, dedicated hosting provides exclusive resources for more extensive, high-traffic sites.
A reliable web host ensures minimal downtime, high-speed access, and robust security measures. Factors to consider when choosing a web host include server reliability, customer support, bandwidth, storage, and scalability. The hosting choice depends on the Website's size, traffic, and specific requirements.
2) Address
The address, also known as a domain name, is a unique web address that people use to enter in their web browsers to access a website. It plays a pivotal role in a Website's branding, identity, and accessibility. Domain names have two main parts: the Top-level Domain (TLD) and the Second-level Domain (SLD).
The TLD comes after the last dot in the domain name, such as .com, .org, or country-code extensions like .uk or .ca. It often reflects the Website's purpose, geographic location, or nature. The SLD, which precedes the TLD, represents the core part of the domain name and typically reflects the Website's name, brand, or subject matter. For example, on www.example.com, "example" is the SLD.
Selecting a suitable domain name is crucial for a Website's success. It should align with the Website's content or business, be memorable, and be easy to type. The chosen domain name also impacts Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) and brand recognition. Domain registration services facilitate the purchase and management of domain names.
Users typically pay an annual fee to register and retain ownership of their chosen domain names. Some domain registrars protect domain privacy by keeping personal information from the public WHOIS database.
3) Homepage
The website's homepage serves as the initial landing page visitors encounter when they enter the Website's domain address. It plays a vital role in creating the first impression and guiding users through the site's content and navigation. Homepage design typically includes critical elements such as a site logo or branding, a navigation menu, and a hero section that may feature eye-catching visuals or concise messaging about the Website's purpose.
It should provide a clear and concise overview of the site's content, guiding users to the sections or pages that interest them the most. Navigation menus on the homepage enable visitors to explore the Website further by clicking links to other pages or areas. These menus should be user-friendly, organised logically, and include essential pages like About Us, Contact, Services, or Products.
The design and layout of the homepage should align with the Website's overall aesthetics and brand identity. It should be responsive, ensuring it looks and functions well on numerous devices, including desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones. Effective homepage content is concise and engaging. It also offers a glimpse of what the Website has to offer.
It should capture the audience's attention, provide clear Calls To Action (CTAs), and guide visitors to explore more. Homepage content often includes headlines, subheadings, brief descriptions, and links to featured or popular sections.
4) Design
Website design involves the visual and structural aspects that shape a Website's appearance and User Experience. Effective design is critical to a successful Website, as it significantly influences user engagement, trust, and overall satisfaction. Design elements include layout, colour scheme, typography, images, graphics, and interactive features. A cohesive and visually appealing design enhances brand identity and communicates professionalism.
Layout means the arrangement of various elements on web pages. It should prioritise user-friendly navigation, ensuring that visitors can easily find information. Well-structured layouts improve readability and guide users through the content. Colour schemes should align with the Website's branding and create a harmonious visual experience.
Colour psychology can be leveraged to evoke specific emotions or associations. Typography involves selecting fonts and text formatting. Readable and accessible fonts are essential for conveying content effectively. Images and graphics must be high-quality and relevant to the content. Visual elements enhance engagement and break up text-heavy pages.
Interactive features like buttons, forms, and sliders enhance user engagement and functionality. They should be intuitive and responsive across different devices. Responsive design ensures that the Website looks and functions well on various screen sizes and devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Using the right website design tools can enhance these elements and improve user experience.
5) Content
Content is the heart and soul of a Website, which includes all text, images, videos, and interactive elements that convey information, engage users, and deliver value. High-quality and relevant content is important for attracting and retaining visitors, achieving search engine visibility, and accomplishing the Website's goals. Text content includes articles, blog posts, product descriptions, and other written materials.
It should be well-researched, informative, and tailored to the target audience. Content should also be organised with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance readability. Images and graphics should be visually appealing, relevant, and optimised for web use to prevent slow loading times. Alt text should be provided for images and graphics to improve accessibility and SEO.
Videos can engage and inform visitors effectively. They should be high-quality, relevant, and optimised for web streaming. Interactive elements like forms, buttons, and navigation menus should be user-friendly and intuitive, enhancing the user experience. Content should align with the Website's goals and target audience. For e-commerce sites, product information and descriptions are critical. Blogs offer valuable information and engage readers.
Service-based businesses should highlight their offerings and expertise. Regularly updating and maintaining content is essential to keep it accurate and relevant. Fresh content can improve SEO rankings and encourage repeat visits.
Enhance your knowledge about WordPress with our WordPress Essentials Course. Join now!
Conclusion
We hope that you learnt "What is a Website?" This blog also discussed vital elements, including web hosting, domain name, homepage, design, and content, collectively defining its online presence. Each element is vital in user experience, brand identity, and functionality. A well-structured Website prioritising these elements can effectively engage users and achieve its intended goals in the digital market.
Learn more about Website Design with our Website Design Course – join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

A domain name and a Uniform Resource Locator (URL)of a Website serve different purposes in web addressing. A domain name like "example.com" is a human-readable, user-friendly web address representing a website's identity. On the other hand, a URL is a complete web address that includes the domain name along with the protocol (e.g., https://) and specific page or resource (e.g., /about) needed to access a particular webpage on that website.

Responsive web design is crucial because it ensures that a website adapts and displays effectively on various devices and screen sizes, such as desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones. This adaptability enhances the user experience, making it easy for visitors to navigate and interact with the site, regardless of the device they use. Responsive design not only accommodates diverse user preferences but also contributes to improved search engine rankings, as search engines like Google prioritise mobile-friendly websites in search results.

Web hosting provides server space and infrastructure where a website's files, data, and content are stored and made accessible to users via the internet. Web hosting is necessary for a website because it ensures it is available and accessible 24/7. When someone enters a website's domain name in a web browser, the web hosting server delivers the requested web pages, images, and other resources to the user's device, allowing them to view and interact with the site.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Website Design courses, including WordPress Essentials, Web Development Training With TypeScript, and Web Development Using Python And Web2py. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into App and Web Development methodologies.
Our App and Web Development blogs cover a range of topics related to Website Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills in Website development, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Website Design Course
Website Design Course
Thu 30th Jan 2025
Thu 27th Mar 2025
Thu 29th May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


