We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
AI in Manufacturing has emerged as a game-changer, welcoming a new era of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. The fusion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies with manufacturing processes has unlocked unprecedented potential for businesses across the globe.
This synergy has enabled manufacturers to enhance their operations, optimise resource utilisation, and deliver higher-quality products while maintaining cost-effectiveness. You will learn about how AI in manufacturing refers to the integration of Artificial Intelligence technologies and applications into various aspects of the manufacturing process.
Table of Contents
1) What is AI in Manufacturing?
2) AI in Manufacturing
a) Artificial Intelligence in Logistics
b) AI Autonomous Vehicles
c) AI for IT operations
d) Design and Production with AI
e) AI for Factory Automation
f) AI Robots - Robotic Process Automation
g) Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence
h) AI in Warehouse Management
i) AI for Purchasing Price Variance
3) Conclusion
What is AI in Manufacturing?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in manufacturing represents a revolutionary integration of cutting-edge technology into the industrial landscape. It encompasses the application of AI and machine learning algorithms to various aspects of the manufacturing process, with the primary goal of optimising efficiency, quality, and overall productivity.
At its core, AI in manufacturing involves the utilisation of advanced algorithms and data analytics to automate and enhance decision-making processes within the production environment. This technology leverages massive amounts of data collected from sensors, machinery, and other sources to make real-time predictions, identify patterns, and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
One of the important applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance, where AI algorithms analyse equipment data to forecast when machines might fail or require maintenance. This proactive approach helps prevent costly downtime and minimise disruptions in production.
Quality control and inspection have also seen significant advancements through AI-powered vision systems that can detect defects, ensuring that products meet stringent quality standards. Furthermore, AI plays a pivotal role in optimising manufacturing processes, from supply chain management to resource allocation, resulting in cost reductions and improved resource utilisation.
AI in manufacturing is not just about automation but also about fostering smarter, more sustainable, and efficient production methods. As technology continues to evolve, the idea of AI in manufacturing promises to reshape the industry by enabling smart factories and driving innovation that benefits both manufacturers and consumers alike.
AI in Manufacturing
AI in Manufacturing is the application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to enhance production processes. It includes predictive maintenance, quality control, process optimisation, and supply chain management, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring product quality. AI transforms factories into smart, data-driven environments, revolutionising the manufacturing industry. Below are the various applications of AI in the Manufacturing industry:
1) Artificial Intelligence in Logistics
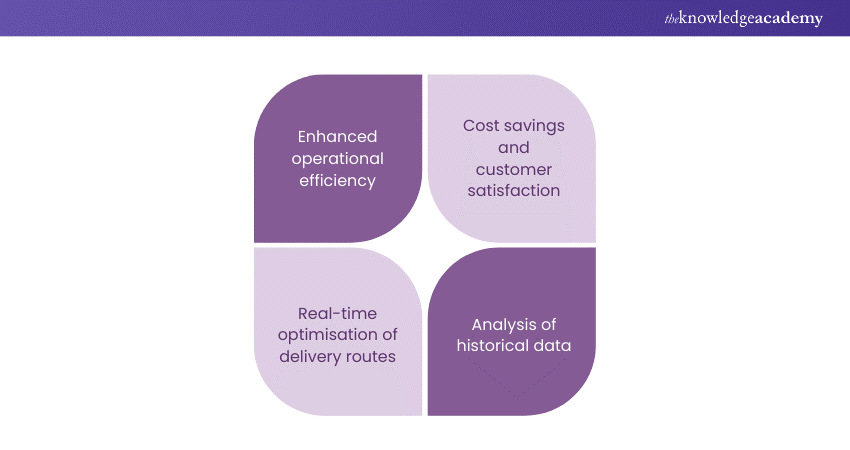
AI-driven logistics not only enhances operational efficiency but also leads to cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a more sustainable supply chain. As technology continues to advance, AI's application in logistics is set to grow, reshaping the way goods are transported, managed, and delivered worldwide:
a) Demand forecasting: AI algorithms analyse historical data and market trends for providing accurate demand forecasts, helping companies optimise inventory levels and reduce excess stock.
b) Route optimisation: AI optimises delivery routes in real-time, considering traffic, weather, and other factors, reducing transportation costs and delivery times.
c) Warehouse automation: AI-powered robots and drones streamline order picking, packing, and inventory management, increasing warehouse efficiency and accuracy.
d) Predictive maintenance: Sensors and AI predict equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimising downtime in transportation fleets and warehouses.
e) Inventory management: AI systems manage inventory levels efficiently, ensuring the right products are in stock when needed while minimising carrying costs.
f) Last-mile delivery: AI enhances last-mile delivery logistics, optimising delivery routes, and providing real-time tracking and delivery notifications to customers.
g) Supply chain visibility: AI provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, enabling companies to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
h) Risk management: AI assesses supply chain risks and offers contingency plans in case of disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
i) Customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer inquiries, order tracking, and issue resolution, improving customer service efficiency.
j) Sustainability: AI helps reduce the carbon footprint by optimising transportation routes, minimising empty truckloads, and promoting eco-friendly practices within the logistics industry.
2) AI Autonomous Vehicles
AI-driven autonomous vehicles hold the promise of safer roads, reduction in traffic congestion, and increased mobility for people who cannot drive. As technology advances and regulations evolve, the integration of AI in autonomous vehicles will play a pivotal role in reshaping the future of transportation:
a) Sensory perception: AI equips autonomous vehicles with sensors like lidar, radar, and cameras, enabling them to perceive their surroundings, detect obstacles, and make informed decisions.
b) Object detection and recognition: AI algorithms identify and classify objects, pedestrians, road signs, and other vehicles, ensuring safe navigation.
c) Mapping and localisation: AI combines GPS data with high-definition maps to accurately locate the vehicle and plan routes with centimetre-level precision.
d) Path planning: AI calculates optimal routes, considering factors like traffic conditions, road rules, and real-time data, ensuring safe and efficient travel.
e) Predictive analysis: AI anticipates the behaviour of other road users, predicting their movements to make proactive decisions.
f) Adaptive cruise control: AI controls vehicle speed and distance from other vehicles, ensuring smooth traffic flow while maintaining safety.
g) Lane keeping assist: AI keeps the vehicle within the correct lane, preventing unintended drifting.
h) Emergency handling: AI responds to sudden obstacles or adverse conditions, taking evasive actions to avoid accidents.
i) Human-machine interaction: AI interfaces with passengers through voice recognition and touchscreen controls, enhancing the user experience.
j) Data analysis and improvement: AI collects and analyses vast amounts of data from sensors and real-world driving scenarios to continually refine autonomous driving algorithms, making vehicles safer and more reliable.
Acquire in-depth understanding of data by signing up for our Big Data Analysis Course now!
3) AI for IT operations
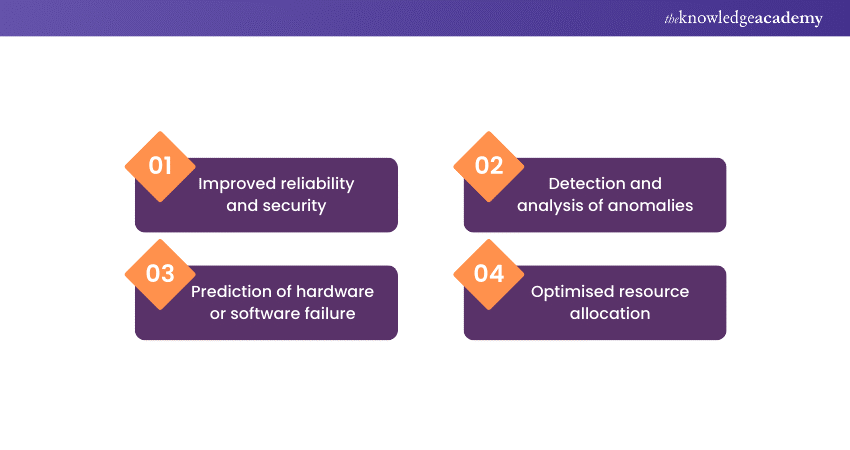
AI for IT operations not only improves efficiency but also enhances reliability and security, making it a valuable tool for managing complex IT environments. As AI technologies continue to evolve, their contribution in IT operations will become even more critical in ensuring the smooth operation of modern businesses and services:
a) Anomaly detection: AI analyses vast amounts of data from IT systems and networks to identify unusual patterns and anomalies, helping detect potential issues early.
b) Predictive maintenance: AI predicts when hardware or software components are likely to fail, enabling proactive maintenance and minimising downtime.
c) Automated remediation: AI can automatically resolve common IT problems, such as restarting services or reallocating resources, reducing the need for manual intervention.
d) Performance optimisation: AI optimises resource allocation, ensuring that IT systems and applications run efficiently and cost-effectively.
e) Security monitoring: AI continuously monitors for security threats, detecting suspicious activities and responding quickly to potential breaches.
f) Capacity planning: AI helps IT teams plan for future resource needs by analysing historical data and forecasting requirements accurately.
g) Root cause analysis: AI identifies the underlying causes of IT incidents, streamlining troubleshooting and reducing mean time to resolution.
h) Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots provide IT support, handling routine inquiries and freeing up IT staff for more complex tasks.
i) Network management: AI optimises network performance by identifying bottlenecks, prioritising traffic, and ensuring a seamless user experience.
j) Cost optimisation: AI helps organisations reduce IT costs by identifying opportunities to streamline operations, consolidate resources, and eliminate waste.
4) Design and production with AI
AI in design and production offers the potential to revolutionise manufacturing by accelerating design iterations, reducing costs, and improving product quality. It enables businesses to respond more flexibly to market demands and opens the door to innovative product concepts that were previously challenging to realise.
As AI technologies continue to advance, their integration into design and production processes will become increasingly vital for staying competitive in the modern marketplace:
a) Generative design: AI algorithms assist in generating innovative design concepts by exploring countless possibilities and optimising for specific criteria, leading to more efficient and creative solutions.
b) CAD enhancement: AI-powered tools within Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software automate repetitive tasks, such as drawing generation, reducing design time and errors.
c) Prototyping and simulation: AI-driven simulations enable designers to test and refine prototypes virtually, saving time and resources in the product development cycle.
d) Supply chain optimisation: AI analyses supply chain data to optimise sourcing, procurement, and logistics, ensuring materials are available when needed and minimising production delays.
e) Quality control: AI-based vision systems inspect products for defects during manufacturing, ensuring higher quality and reducing waste.
f) Predictive maintenance: AI monitors machinery and equipment conditions in real-time, predicting maintenance needs and minimising downtime.
g) Inventory management: AI algorithms optimise inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring that the right materials are available for production.
h) Personalisation: AI enables mass customisation by tailoring products to individual customer preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
i) Resource efficiency: AI helps minimise resource consumption, such as energy and raw materials, by optimising production processes.
j) Workflow automation: AI automates administrative and repetitive tasks in the production process, freeing up human workers to focus on more creative and value-added tasks.
5) AI for factory automation
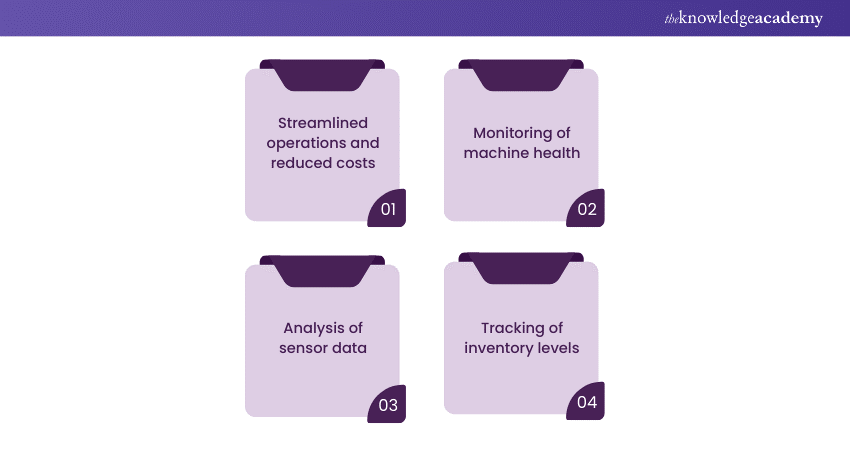
AI for factory automation drives efficiency, quality, and safety in manufacturing environments. It empowers manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce costs, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry. As AI technologies continue to advance, their role in factory automation will become even more critical in shaping the future of manufacturing:
a) Robotic control: AI guides industrial robots to perform complex tasks, such as assembly, welding, and packaging, with precision and adaptability.
b) Quality assurance: AI-based vision systems inspect products in real-time, identifying defects and ensuring consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process.
c) Predictive maintenance: AI monitors machinery health, analysing sensor data to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime.
d) Process optimisation: AI optimises manufacturing processes by adjusting parameters in real-time, enhancing efficiency and minimising waste.
e) Supply chain management: AI tracks inventory levels, manages supplier relationships, and predicts demand, ensuring timely access to materials and reducing production disruptions.
f) Energy efficiency: AI controls and monitors energy consumption, optimising usage and reducing environmental impact.
g) Safety monitoring: AI enhances workplace safety by detecting unsafe conditions or behaviours and taking immediate corrective actions.
h) Inventory management: AI optimises inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring that materials are available for production.
i) Human-machine collaboration: AI enables human workers to collaborate seamlessly with machines, enhancing productivity and safety on the factory floor.
j) Data analytics: AI analyses vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing processes, providing insights for continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
Automate your routine tasks by signing up for our Duet AI for Workspace Training now!
6) AI Robots - Robotic Process Automation
AI robots and RPA have the potential to revolutionise industries by automating routine tasks, increasing efficiency, and reducing operational costs. They provide organisations with the agility to respond to changing business needs and emerging challenges while enhancing the overall quality of their services and products. As technology continues to advance, AI robots and RPA will play an increasingly vital role in streamlining workflows across various sectors:
a) Task automation: AI robots automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, freeing human workers from mundane activities and allowing them to focus on higher-value tasks.
b) Data entry and extraction: AI robots can process and extract data from various sources, such as documents, emails, and forms, with high accuracy and speed.
c) Error reduction: AI-powered RPA reduces human errors in data handling and processing, leading to improved data quality and reliability.
d) Workflow integration: RPA seamlessly integrates with existing software and systems, allowing for the automation of end-to-end business processes.
e) Scalability: AI robots can handle an increasing volume of tasks without the need for additional human resources, making them adaptable to growing business needs.
f) Cost savings: RPA reduces operational costs by eliminating the need for manual labour and minimising resource-intensive tasks.
g) Enhanced customer service: AI robots can be used for chatbots and virtual assistants, providing immediate responses to customer inquiries and improving user experiences.
h) Compliance and auditing: RPA ensures that tasks are performed consistently, helping businesses maintain compliance with regulations and facilitating auditing processes.
i) Data analytics: AI robots can analyse large datasets and generate insights, aiding in decision-making and strategy development.
j) 24/7 operations: RPA robots operate round-the-clock, ensuring uninterrupted workflow execution and increased productivity.
7) Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence
AI and IoT complement each other by enabling the efficient collection, analysis, and utilisation of data from interconnected devices. This synergy results in smarter and more responsive systems across various domains, from healthcare and agriculture to transportation and smart cities. As AI and IoT technologies continue to evolve, their combined potential to transform industries and improve our daily lives will only grow stronger:
a) Data analytics: AI processes vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, extracting valuable insights and patterns for informed decision-making.
b) Predictive maintenance: AI predicts equipment failures in IoT-connected machinery, reducing downtime and optimising maintenance schedules.
c) Energy efficiency: AI optimises energy usage in IoT-enabled smart buildings, helping reduce costs and environmental impact.
d) Security enhancement: AI identifies anomalies and potential threats within IoT networks, enhancing the cybersecurity of connected devices and systems.
e) Healthcare monitoring: IoT sensors collect patient data, while AI analyses it in real-time to enable remote patient monitoring and early disease detection.
f) Supply chain optimisation: AI and IoT together provide end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, ensuring timely deliveries and minimising disruptions.
g) Smart agriculture: AI analyses data from IoT sensors in agriculture to optimise crop management, irrigation, and resource allocation.
h) Traffic management: AI uses data from IoT-connected traffic sensors to optimise traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve transportation systems.
i) Wearable technology: AI processes data from wearable IoT devices, offering personalised insights into health and fitness for users.
j) Home automation: AI-driven smart home systems use IoT to control lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Master the features and capabilities of AI, by signing up for our Google BARD Training now!
8) AI in Warehouse Management
AI-driven warehouse management systems improve efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall productivity in the increasingly complex world of logistics. By automating tasks, optimising processes, and providing real-time insights, AI empowers businesses to meet customer demands more effectively and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving supply chain landscape:
a) Inventory optimisation: AI analyses historical data and real-time demand to optimise stock levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring products are readily available.
b) Order picking and packing: AI-powered robots and automated systems streamline order fulfilment by optimising the picking and packing processes for maximum efficiency.
c) Route optimisation: AI determines the most efficient routes for order delivery, considering factors like traffic, delivery windows, and order priorities.
d) Predictive maintenance: AI monitors warehouse machinery and equipment, predicting maintenance needs to minimise downtime and maximise productivity.
e) Quality control: AI-based vision systems inspect incoming and outgoing goods for defects, ensuring high-quality products reach customers.
f) Labor management: AI helps optimise workforce scheduling, allocating tasks based on real-time demand and worker availability.
g) Space utilisation: AI assesses warehouse layout and recommends optimal storage configurations to make the best use of available space.
h) Real-time tracking: AI-enabled tracking systems provide real-time visibility into the location and status of inventory and shipments.
i) Returns processing: AI streamlines the returns process by automating inspections and restocking decisions.
j) Data Analytics: AI analyses warehouse data to identify trends, performance bottlenecks, and areas for improvement, helping companies make data-driven decisions.
i) AI for purchasing price variance
AI in purchasing price variance analysis enhances the accuracy and efficiency of procurement processes by identifying and addressing cost discrepancies. It empowers organisations to make data-driven decisions, negotiate better prices, and improve supplier relationships while optimising their bottom line:
a) Data analysis: AI processes vast amounts of purchasing data to identify discrepancies between expected and actual purchase prices.
b) Real-time monitoring: AI continuously monitors purchase orders, receipts, and supplier invoices for price variations.
c) Price negotiation: AI suggests optimal negotiation strategies based on historical data and market trends to reduce purchasing costs.
d) Invoice matching: AI automates the reconciliation of invoices with purchase orders and receipts, minimising errors and discrepancies.
e) Supplier performance evaluation: AI assesses supplier performance by analysing their ability to deliver products at agreed-upon prices.
f) Forecasting: AI predicts potential price variances by considering factors like market volatility and historical price trends.
g) Risk mitigation: AI identifies supplier-related risks that may lead to price variances, allowing for proactive risk management.
h) Inventory optimisation: AI's insights into price variances help optimize inventory levels and reduce carrying costs.
i) Efficiency enhancement: AI streamlines procurement processes by automating routine tasks, enabling procurement professionals to focus on strategic activities.
j) Cost savings: AI for purchasing price variance contributes to cost reduction, leading to improved profitability and resource allocation.
Optimise your career with the power of AI, by signing up for our Artificial Intelligence Tools Training now!
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI in Manufacturing is a transformative force driving innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness in the industry. Its applications span from predictive maintenance to process optimization, offering a promising future for AI-driven manufacturing systems. Embracing this technology is key to staying ahead in the rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


