We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +64 98874342 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
A business is typically driven by information. It is best if the information is received quickly and accurately. Blockchain is the best technology. Do you know What is Blockchain? It offers real-time, shareable, and fully transparent data kept on an immutable ledger that is accessible only by authorised network members.
It is the reason in 2021, the market for Blockchain Technology was estimated to be worth £4.92 billion. By 2030, it is predicted to rise to £1041.12 billion, or perhaps to a compound annual growth rate of 82.8%.
Blockchain is a decentralised, immutable ledger that makes it easier to track assets and process data in a corporate network. Blockchain Technology has the ability to track orders, payments, finances, production, and much more. Additionally, because everyone has access to the same version of the truth, you can see every aspect of a transaction from beginning to end, increasing your confidence and introducing you to new prospects.
Table of Contents
1) What is Blockchain?
2) Why is Blockchain Important ?
3) What are the key Elements of Blockchain?
4) How Blockchain Technology Operates ?
5) How do Different Industires use Blockchain?
6) Benefits of Blockchain
7) Drawbacks of Blockchain
8) Different Types of Blockchain Networks
9) Is Blockchain Secure?
10) Bitcoin vs Blockchain
11) Conclusion
What is Blockchain?
A shared database or ledger that is accessible by all of the nodes in a computer network is known as Blockchain Technology. A Blockchain is a digital database that electronically stores data. The most well-known use of Blockchain Technology is for preserving a secure and decentralised record of transactions in cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin.
Multiple transactions are included in each block of the chain, and every time a new transaction takes place on the Blockchain, a record of that transaction is posted to the ledger of every user. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) refers to a decentralised database that is governed by numerous users. The uniqueness of a Blockchain is that it fosters confidence without the requirement for a reliable third party by ensuring fidelity and blockchain data privacy.
Unlock Interview Questions with our Top 75+ Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers!
Why is Blockchain Important?
For ages, organisations and individuals have used traditional database technologies that posed several data storage, processing and transfer issues. However, this task has become easier and faster with the introduction of Blockchain Technology. It has become integral to various industries- finance, media and communication, and retail. It is important because:
1) A Blockchain is a particular kind of shared database that varies from other traditional databases; Blockchains save data in blocks that are subsequently connected via cryptography.
2) Blockchain is utilised in the context of Bitcoin in a decentralised manner, ensuring that no one user or organisation has power but rather that all users collectively maintain control.
3) Since decentralised Blockchains are immutable, the data entered into them cannot be changed. This implies that transactions made using Bitcoin are publicly visible and permanently recorded.
4) On a Blockchain network, practically anything of value may be recorded and traded, lowering risk and increasing efficiency for all involved due to its tamper-proof system to record transactions.
The above stated features of Blockchain Technology makes its demand grow higher and higher in each and every industry across domains.
Learn the fundamentals of Ethereum with our Ethereum Developer Training – Join now!
What are the Key Elements of Blockchain?
The fundamental elements of Blockchain are:
1) Shared Ledger- The shared ledger's immutable record of transactions is available to all network users. This shared ledger eliminates the duplication of effort that is inherent in conventional corporate networks by simply recording transactions once.
2) Permissions- Permissions guarantee the security, authenticity, and verifiability of transactions. Organisations can more easily adhere to data protection laws like those outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) with the option to restrict network participation.
3) Smart Contracts- A set of rules, referred to as a smart contract, is recorded on the Blockchain and is automatically carried out to speed up transactions. A smart contract can specify parameters for corporate bond transactions, stipulate how much must be paid for travel insurance, and much more.
4) Consensus- With consensus, the network-verified transaction is approved by all parties. Blockchains have a variety of consensus processes, such as multi-signature, proof of stake, and PBFT ( Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance).
5) Immutable Records- Once a transaction has been added to the shared ledger, no participant may alter or interfere with it. A subsequent transaction must be added to undo an error in a transaction record before both transactions are displayed.
How Blockchain Technology works?
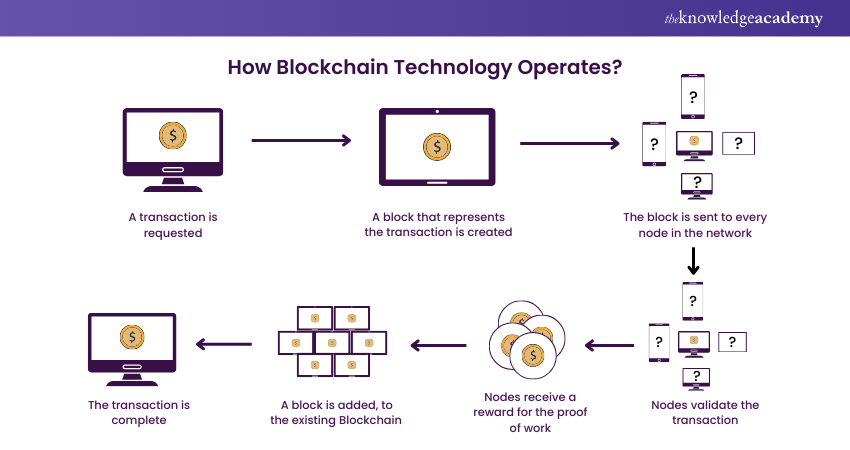
You may have observed that several companies have been incorporating Blockchain Technology in recent years. But how does Blockchain Technology actually operate? Is this a meaningful modification or merely an addition? Let's start by understanding how Blockchain Technology functions since it is still in its growing phase and has the potential to be revolutionary in the future.
1) As each transaction occurs, it is recorded as a “block” of data: These exchanges demonstrate the movement of an asset, which may be a tangible good(product) or an intangible good (intellectual). Who, what, when, where, how much, and even the condition—such as the temperature of a food shipment—can all be recorded in the data block.
2) Each block is connected to the ones before and after it: As an object moves from one location to another or ownership changes, these blocks create a chain of data. Blocks link securely to prevent modification or insertion, ensuring precise timing and order of transactions.
3) Transactions are blocked together in an irreversible chain – a Blockchain: Each new block reinforces the prior block's verification and then, consequently, the entire Blockchain. This gives the Blockchain its crucial strength of immutability and makes it tamper-evident. By doing this, you and other network users may create a trusted ledger of transactions and eliminate the chance of tampering by unauthorised individuals.
Learn how bitcoins work and how to secure bitcoins. Register for our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course – Sign up today!
How do Different Industries use blockchain?
Blockchain is being used by several businesses to reduce friction, create trust, and unleash new values. The following is a list of such industries:
1) Healthcare – Blockchain Technology in healthcare can help record patients' health and personal data and manages clinical trials and medicine supply chains. It also helps healthcare researchers to unlock genetic codes. It also helps maintain smart contracts for medical insurance, remote monitoring, and much more.
2) Government – It simplifies the process of filing taxes, issuing birth certificates, and other government processes that need paperwork and are potential fraud entities.
3) Supply Chain – These industries can efficiently complete transactions without third-party involvement. Blockchain in supply chain also facilitates the integration of financial and logistics services.
4) Media and Advertising – Companies can verify and maintain copyright data to improve productivity and reduce costs in copyright processing.
5) Financial Services – Banks and stock exchanges use Blockchains Technology to maintain online payments, accounts and market trading.
6) Travel and Transportation – Blockchain helps businesses track truck fleets, routes, traffic incidents, and other related operations.
Benefits of Blockchain
Business incorporate this technology as Blockchain technology provides multiple benefits for managing asset transactions, such as:
1) Improved Safety
Blockchain systems provide the necessary level of security and trust for contemporary digital transactions. Worries about software tampering for counterfeit money are alleviated by Blockchain's cryptography, decentralisation, and consensus principles. This leads to a strong system that is almost impossible to tamper with, without any one weak point and no chance for a single user to change transaction records.
2) Improved Effectiveness
Business transactions between companies frequently encounter delays and operational obstacles, particularly in cases where compliance and external regulatory bodies play a role. Blockchain technology enhances the efficiency of transactions by using Smart Contracts and ensuring transparency.
3) Fast-tracked Audit
Businesses must securely create, transfer, store, and recover electronic transactions in a way that can be verified. Blockchain's unchangeable records in chronological order guarantee that data is organised by time, increasing transparency and improving the efficiency of audits.
Drawbacks of Blockchain
Although Blockchain has proved to be one of the most reliable technologies in today's world, it also has a flip side. Like every other technological advancement, this also comes in handy with certain blockchain disadvantages.
So, let’s learn what these are:
1) Expensive Technology- Users continue to make payments to validate transactions on this platform. It is primarily the Blockchain that does not use cryptocurrency. Thus, the miners are required to pay to validate transactions.
2) Unauthorised Trading- Since miners are allowed to change and update Blockchain networks, it is prone to illegal trading and attacks by malicious entities. As a result, it becomes easily migrate cryptocurrencies.
3) Speed and Data Inefficient- Blockchain size is one of the significant issues that are yet to be dealt with by the experts. This reduces the scalability of Blockchains moving forward. Apart from that, the bitcoin network can only manage about seven transactions per second which are lower than other cryptocurrencies.
4) Difficult to Regulate- The hold of cryptocurrency networks with the government makes it challenging to end. As the decentralised network grows, governments could theoretically prohibit owning cryptocurrencies and even participating in their networks.
Different Types of Blockchain Networks
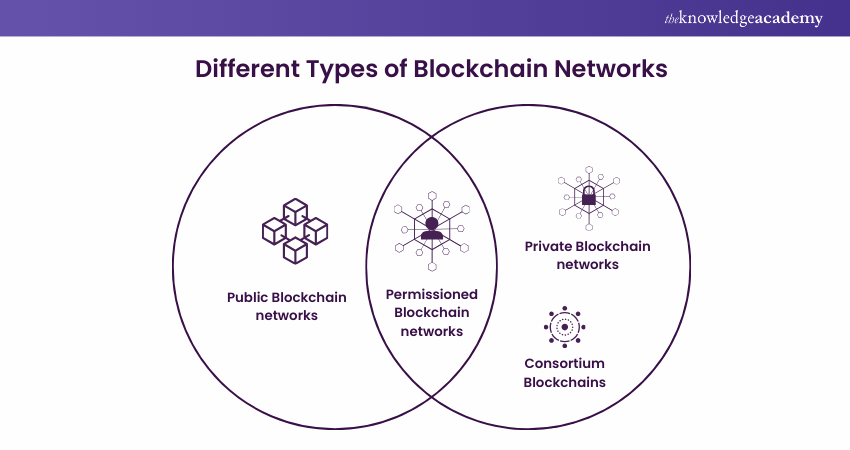
Building a Blockchain network can be done in several ways. They may be permitted, public, private, or constructed by a consortium.
1) Public Blockchain Networks- Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have their roots in public Blockchains, which also helped spread Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) to a broader audience. Public Blockchains also assist in removing some difficulties and problems, such as centralisation and security issues. Rather than being kept in one place, data is spread throughout a peer-to-peer network using DLT. For authenticating information, a consensus technique is used; proof of stake (PoS) and proof of work (PoW) are two popular consensus methods.
2) Private Blockchain Networks- A private Blockchain network is a decentralised peer-to-peer network, just like a public Blockchain network. However, one entity controls the network's governance, carrying out a consensus protocol and keeping track of the shared ledger. Depending on the blockchain use case, this can significantly increase participant confidence and trust. It is possible to host a private Blockchain on-site and to operate it behind a company's security system.
3) Permissioned Blockchain Networks- Permissioned Blockchain networks, also referred to as hybrid Blockchains, are private Blockchains that grant approved users privileged access. These kinds of Blockchains are frequently put up by businesses in order to combine the finest aspects of both worlds. They also allow for greater structure when deciding who can join in the network and in which transactions.
4) Consortium Blockchains- The duties of maintaining a Blockchain might be split among several groups. Who is permitted to submit transactions or access the data is decided by these pre-selected organisations. When everyone involved in a business transaction needs to have authorisation and share ownership of the Blockchain, a consortium Blockchain is the best option.
Is Blockchain Secure?
The introduction of Blockchain Technology to businesses has done miracles. Due to its decentralised network, it has gained trust across the world. But is it secure to work with? Let's find out:
1) New blocks are stored chronologically, i.e., every new block is added at the end of the chain. Thus, it becomes difficult to reach and tamper with the block contents.
2) Even if there is some malicious attack on any crypto, each block has hash encryption and the previous block's hash. If the hash codes are altered, they will no longer align with everyone else's copy over the network, thus, providing network security.
3) The growing cryptocurrency networks make it difficult for attackers to reach every copy. Thus, they will have to invest high amounts of money and resources.
4) In case of any attack, the members can develop a new version of the chain that has not been affected, making the attacker’s efforts go to waste.
Thus, it is developed so that participating in the network is far more economically useful than attacking it.
Bitcoin vs Blockchain
Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta introduced blockchain in 1991 to create a system where document timestamps couldn’t be tampered with. This plan became fully functional in 2009 with the introduction of Bitcoin. Bitcoin is based on blockchain.
Blockchain is used to record a ledger payment done in Bitcoins. However, it can also be used to permanently record any amount of data points in various forms, such as vote counts, product inventories, transactions, etc. Most importantly, Bitcoins remain anonymous, while Blockchain includes transparency.
What are Blockchain Protocols?
The phrase "Blockchain protocol" describes different Blockchain platforms used for developing applications. Every protocol applies core Blockchain principles to meet the needs of particular sectors or uses. The examples provided below:
1) Fabric in Hyperledger
Hyperledger Fabric provides a set of tools and libraries as an open-source initiative. It allows businesses to efficiently create private blockchain applications quickly. Its distinctive identity management and access control make it ideal for supply chain tracking, trade finance, loyalty programs, and financial asset settlement, among other applications.
2) Etherum
Ethereum is a platform that is decentralised and open-source, designed for creating public Blockchain applications. Ethereum Enterprise is designed specifically for business applications.
3) Corda
Corda is a Blockchain project that is open-source and created specifically for business uses. It enables the building of compatible Blockchain networks that guarantee strong privacy in transactions. Corda's advanced contract technology allows businesses, especially financial institutions, to conduct direct transactions involving value.
4) Quorum
Quorum is a Blockchain protocol that is open-source and based on Ethereum. Its purpose is tailored for private Blockchain networks, in which one member controls all nodes, or consortium Blockchain networks, where multiple members have ownership over parts of the network.
How is Blockchain Different From the Cloud?
The term “cloud” refers to online-accessible computing services. These services have Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Cloud providers handle the hardware and infrastructure, offering access to these resources over the internet. Beyond Database Management, they provide a wide range of services.
For those looking to join a public Blockchain network, providing hardware resources to hoard a ledger copy is necessary. This can be achieved using a server from the cloud. Additionally, some cloud providers offer vast Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) solutions.
What is Blockchain as a Service?
Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based managed Blockchain service offered by a third party. It enables the development of Blockchain apps and digital services with infrastructure and tools managed by the cloud provider. By adapting current Blockchain technology, BaaS speeds up and simplifies the adoption of Blockchain.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology enhances security and transparency with immutable transaction records. It’s transforming finance, healthcare, and supply chains. Challenges like scalability and regulations exist. However, ongoing advancements suggest blockchain will be crucial for digital infrastructure, driving innovation and trust.
Solve complicated business problems with our Blockchain Training – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The fundamental concept of blockchain involves establishing a decentralised digital ledger that records transactions on multiple computers to prevent any retroactive alteration of the recorded transactions. Each block in the blockchain records transactions and is added to the chain in sequence once completed.

Blockchain's primary goal is to offer a secure and transparent method to document and authenticate transactions without relying on a central authority. This technology seeks to decrease the number of middlemen, boost the precision and effectiveness of transactions, and enhance security.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Blockchain Training, including the Blockchain Course, Ethereum Developer Training, and Bitcoin And Cryptocurrency Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into 10+ Interesting Blockchain Facts.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Blockchain, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Advanced Technology skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Blockchain Training Course
Blockchain Training Course
Thu 16th Jan 2025
Thu 6th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


