We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

According to Statista, the total spending on Cybersecurity technologies increased to 55.86 billion GBP. If you wish to get into an introductory overview of Ethical Hacking, covering the definition of Cybersecurity, types of hackers, legal and moral aspects and benefits/challenges, this blog is for you. Read this blog to learn what Ethical Hacking is and understand its purpose and its principles, techniques, and ethical considerations.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Ethical Hacking
2) The process of Ethical Hacking
3) Common Ethical Hacking techniques
4) Benefits and challenges of Ethical Hacking
5) Conclusion
Understanding Ethical Hacking
Ethical Hacking involves authorised attempts to bypass security systems and identify vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or applications. Its scope extends to testing and enhancing security measures, protecting against potential cyber threats, and ensuring the integrity of digital assets.
Understanding the definition, scope, and various types of hackers, along with the legal and moral aspects, provides a foundation for comprehending the role of legalised hacking in Cybersecurity.
Try our Ethical Hacking Training and learn to bypass the security of systems legally!
Types of hackers
Although the concept of Hacking is quite simple on its own, it isn’t limited to one role or category. There are various roles in Ethical and non-Ethical Hacking alike. The three most prominent categories Hackers are separated into are as follows:

a) White Hat Hackers: These Ethical Hackers work within legal boundaries, using their skills to identify vulnerabilities and help organisations improve their security posture. They are commonly responsible for bug testing the applications and website before publicly releasing them. The term “Ethical Hacking” generally refers to their work, thus also being referred to as White Hat Hacking.
b) Black Hat Hackers: Also known as Malicious Hackers, they engage in illegal activities to exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain or malicious intent. They are often responsible for Cybersecurity breaches and stolen data leading to huge losses to an organisation.
c) Grey Hat Hackers: This group operates in a morally ambiguous space, exploiting vulnerabilities without explicit permission but intending to notify organisations about the weaknesses discovered. As a result, Grey Hat Hackers are often unpredictable, as the intent behind their actions tends to be unknown.
Legal aspects of Ethical Hacking
White Hat Hacking operates under strict legal and moral considerations; thus, they must obtain proper authorisation before conducting any security assessments. They should adhere to ethical guidelines, respect privacy, and ensure their actions do not disrupt systems, networks or cause harm to others.
Key skills and knowledge required for Ethical Hackers
White Hat Hackers need a diverse skill set to identify vulnerabilities and secure systems effectively. Key skills include programming languages, network protocols, and Operating Systems proficiency. They must know hacking techniques, security tools, risk assessment, and strong problem-solving abilities.
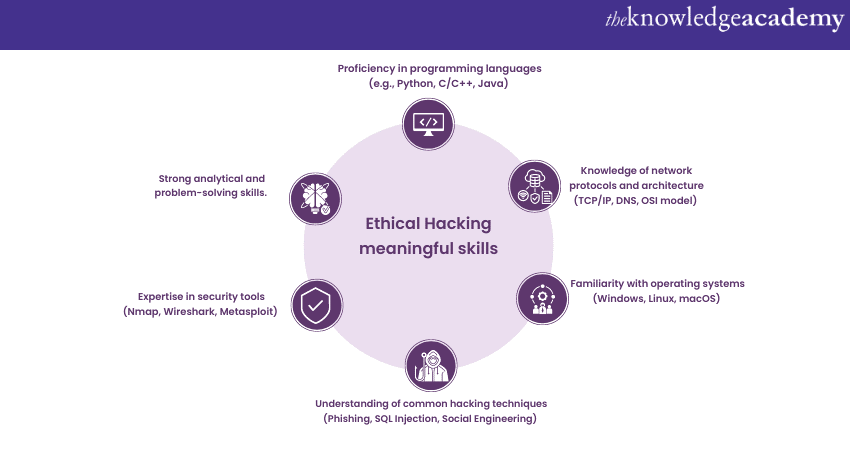
White Hat Hackers should also possess excellent communication skills to report findings and collaborate with stakeholders effectively. Furthermore, recognising the essential skills and knowledge required for Ethical Hacking emphasises the expertise and dedication needed to contribute effectively to maintaining digital security.
Learn the basics of Ethical Hacking with the Ethical Hacking Professional Course!
The process of Ethical Hacking
The process of White Hat Hacking follows a systematic approach divided into multiple phases. Each phase plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing security weaknesses. These phases enhance the overall security posture of the target system or network.
Pre-engagement phase
In the pre-engagement phase, the White Hat Hacker establishes clear communication with clients to understand their objectives, scope, and specific requirements. This includes defining the rules of engagement, obtaining proper authorisation, and signing necessary agreements. Gathering relevant information about the target system or network is crucial before proceeding.
Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance involves gathering information about the target, such as IP addresses, domain names, employee details, network infrastructure, and publicly available data. This phase aims to identify potential entry points and weak spots that can be exploited. Techniques like Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) gathering and network scanning help gather valuable insights.
Vulnerability assessment
During the vulnerability assessment phase, the White Hat Hacker employs various tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities in the target system or network. This includes conducting vulnerability scans, analysing configuration weaknesses, and assessing the effectiveness of security controls. The goal is to uncover potential weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
Exploitation
In the exploitation phase, the White Hat Hacker exploits identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorised access or escalate privileges within the target system or network. This involves using various hacking techniques and tools to penetrate the defences and assess the impact of the vulnerabilities. The objective is to understand the potential damage an attacker could inflict.
Post-exploitation
After successfully gaining access to the target system or network, the White Hat Hacker focuses on maintaining persistence and exploring the compromised environment further. This phase involves lateral movement, privilege escalation, data extraction, and potentially gaining control over critical systems or sensitive information. It aims to simulate real-world scenarios and assess the extent of damage that an attacker could cause.
Reporting
The reporting phase is essential for effective communication between the White Hat Hackers and the client. A comprehensive report detailing the findings, vulnerabilities, potential risks, and recommended countermeasures is generated. The report should be clear, concise, and actionable, providing the client with a roadmap to address and mitigate the identified vulnerabilities.
Common Ethical Hacking techniques
White Hat Hackers use various approaches to assess the security of systems, networks, and applications. Here are some techniques they employ to help organisations identify vulnerabilities, strengthen defences, and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of digital assets.
Network scanning and enumeration
Network scanning involves systematically exploring a target network to gather information about active hosts, open ports, and services running on them. Enumeration further extracts details like user accounts, shares, and network resources. These techniques help White Hat Hackers identify potential entry points and vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
Social engineering
Social engineering is a technique that exploits human psychology to manipulate individuals into performing certain actions or revealing sensitive information. It involves tactics like phishing emails, pretexting, baiting, or impersonation. Ethical Hackers use social engineering to test an organisation’s awareness and educate employees about the risks associated with such attacks.
Password cracking
Password cracking involves discovering passwords by systematically trying combinations or using specialised tools. Ethical Hackers use this technique to test the strength of user passwords and identify weak or easily guessable passwords. This helps organisations enforce stronger password policies and enhance authentication security.
Denial of Service (DoS)
Denial of Service attacks aims to disrupt the availability of a system or network by overwhelming it with a flood of traffic or exploiting vulnerabilities to exhaust system resources. Ethical Hackers perform DoS attacks to test the resilience and responsiveness of the target infrastructure, allowing organisations to implement appropriate mitigation measures.
Wireless hacking
Wireless hacking involves exploiting vulnerabilities in wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi, to gain unauthorised access or intercept network traffic. Ethical Hackers use tools and techniques like brute-forcing Wi-Fi passwords, exploiting weak encryption, or conducting Man-in-the-Middle attacks to identify security weaknesses and enhance wireless network security.
Web application hacking
Web application hacking focuses on identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in web applications, including websites and web services. Ethical Hackers use techniques like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and Session Hijacking to assess the security of web applications. This helps organisations address potential risks and protect sensitive data.
Try our Mastering Metasploit Framework Course and use Metasploit in Penetration Testing!
Benefits and challenges of Ethical Hacking
Understanding the benefits and challenges most White Hat Hackers face allows organisations to make informed decisions about implementing proactive security measures. Ethical Hacking is a valuable tool in safeguarding organisations against cyber threats and strengthening their overall security posture. Some of its challenges and benefits are as follows:
Benefits of Ethical Hacking for organisations:
White Hat Hackers are vital in most organisations to keep them safe from external attacks and cyber threats. Some of its benefits are as follows:
1) Proactive vulnerability assessment: Ethical Hackers identify vulnerabilities, enhancing security.
2) Improved incident response: Simulated attacks refine incident response capabilities.
3) Enhanced security awareness: Educates employees, reducing successful attacks.
4) Compliance and regulatory requirements: Meets data protection and Cybersecurity standards.
5) Safeguarding reputational and financial risks: Prevents damage, maintains trust, and protects the brand.
Challenges and limitations of Ethical Hacking
White Hat Hacking has many benefits, and it also has an equal number of challenges, some of them being as follows:
1) Scope limitations: Define assessment scope accurately to maximise coverage
2) Evolving threat landscape: Continuous learning to keep up with emerging threats
3) False positives negatives: Skilled hackers needed to interpret findings accurately
4) Legal considerations: Compliance with laws and ethical guidelines is essential
Balancing security and privacy concerns
Ethical Hacking requires a delicate balance between security and privacy concerns. Organisations must ensure that White Hat Hackers do not violate privacy laws or compromise sensitive data. Strong ethical frameworks, strict data protection measures, and transparent communication with stakeholders are essential to maintain this balance.

Conclusion
Ethical Hacking plays a vital role in ensuring robust Cybersecurity. It encompasses proactive vulnerability assessment, incident response improvement, and regulation compliance. Skilled White Hat Hackers are indispensable in addressing evolving threats. We encourage you to explore hacking as a rewarding career and develop this valuable skill set in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Batches & Dates
Date








 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


