We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +61 1-800-150644 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the digital age, Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) has become an important tool for online platforms and content creators. Ranking higher in search engine results can significantly impact a website's visibility and success. But do you know about the History of Search Engine Optimisation and its evolution from its inception to its present-day importance?
If you wish to learn about the intriguing journey of SEO, exploring its early beginnings and the key milestones that have shaped it over time, this blog is just for you. This blog on the History of Search Engine Optimisation showcases its evolution from keyword-centric practices to a more user-focused and content-driven approach. Read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is SEO?
2) The early History of Search Engine Optimisation
3) The age of Google in SEO
4) Modern-day SEO
5) The Future of SEO
6) Conclusion
What is SEO?
SEO is basically the practice of enhancing a website's ranking and visibility on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs). Through a carefully crafted set of strategies and practices, SEO focuses on making a website more search engine-friendly, increasing its likelihood of being discovered by potential visitors.
SEO helps search engines understand the website's relevance to specific queries. It optimises the website's content, structure, and user experience, ultimately leading to higher rankings.
The significance of SEO lies in its ability to drive organic traffic to a website. When a website starts ranking higher in search results, it gains more exposure to users actively seeking relevant information or products. As a result, increased organic traffic can lead to higher brand awareness, a greater number of conversions, and overall business growth.
In essence, SEO is the backbone of Digital Marketing, empowering websites to compete effectively in the vast online landscape and connect with their target audiences. By implementing SEO best practices, businesses can create a strong online presence and maximise their potential for success in the competitive digital realm.
Learn how to use technology for marketing with our Digital Marketing Courses!
The early History of Search Engine Optimisation
In the early days of the internet, the need for SEO arose as websites struggled to be discovered in the rapidly expanding online space. With limited search engines and an abundance of information, website owners sought ways to increase visibility and reach their target audience effectively.
As search engines like Archie and WebCrawler emerged, website indexing and search capabilities became critical. This led to the foundation of SEO practices to improve rankings and attract organic traffic.
Further, SEO became a necessity as the internet's growth outpaced users' ability to find relevant content efficiently. Website owners recognised the value of being indexed and discovered by search engines like Google. As competition grew, the focus shifted from keyword stuffing to providing valuable content that aligned with user intent.
Thus, the early history of SEO was shaped by the quest to stand out in a rapidly expanding digital landscape and connect with users seeking relevant information online. Here is a brief detailed look at the early History of Search Engine Optimisation:
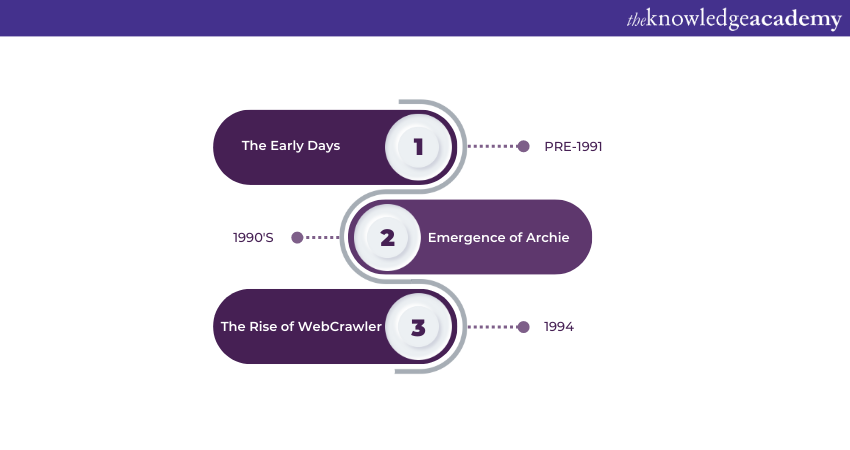
The Early Days: Pre-1991
The roots of SEO can be traced back to the early days of the internet when search engines were still in their infancy. In 1991, Tim Berners-Lee introduced the World Wide Web to the public, marking the beginning of a new era in human communication and information exchange. The concept of the internet was taking shape, but the idea of search engines, as we know them today, had not yet been realised.
During this period, the internet was primarily used for academic and research purposes, and websites were few and far between. There was no efficient way to index or categorise the growing amount of information available on the web. As a result, finding specific information required sifting through directories or manually browsing through websites, a time-consuming and labour-intensive process.
Emergence of Archie: 1990s
In 1990, a significant breakthrough occurred with the development of Archie, considered one of the earliest search engines. Archie, short for Archive, was created by Alan Emtage, Bill Heelan, and J. Peter Deutsch at McGill University in Montreal, Canada. Unlike modern search engines that crawl and index web pages, Archie operated as a tool for indexing files on FTP servers.
While Archie was not a traditional search engine in the sense we understand it today, it laid the foundation for future developments in the field of SEO. By allowing users to search for specific files and retrieve information more efficiently, Archie demonstrated the value of organising and cataloguing digital content.
The rise of WebCrawler: 1994
In 1994, Brian Pinkerton, a Computer Science graduate student at the University of Washington, created WebCrawler, another critical milestone in the history of SEO. WebCrawler was historically the first search engine to enable a full-text search capability. Unlike Archie, which focused on indexing files, WebCrawler could search for specific words within web pages.
This innovation marked a significant advancement in the field of SEO. WebCrawler's search capabilities made it easier for users to find relevant information online. It operated by crawling the web and building an index of web pages. This helped users to enter keywords and receive a list of relevant pages. WebCrawler quickly gained popularity and became one of the most widely used search engines of its time.
WebCrawler's success inspired the development of other search engines, such as Lycos and AltaVista, which further improved search capabilities. These early search engines formed the basis for modern search engine technologies and set the stage for the rapid growth of SEO as an essential aspect of online visibility and success.
Learn to improve the ranking of your website on the internet with our SEO Masterclass!
The age of Google in SEO
Another milestone in the History of Search Engine Optimisation was in the 1990s. This period witnessed the rise of Google, which ultimately became a dominant search engine worldwide.
Google introduced a revolutionary algorithm in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, referred to as PageRank. This algorithm evaluated the relevance of web pages based on the quality and number of links pointing to them, providing more accurate search results. Here's how SEO evolved in the 1990s:
Google's emergence and PageRank algorithm: Late 1990s
In the late 1990s, search engines were becoming increasingly prevalent as the internet's popularity surged. However, the quality of search results was often questionable, with many irrelevant or spammy websites ranking high due to simple keyword matching. Google's founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, recognised the need for a more effective way to rank web pages.
In 1998, they unveiled Google, which quickly set itself apart from other search engines. At the core of Google's success was its PageRank algorithm. Instead of solely relying on keywords, PageRank analysed the links between web pages. It treated each link as a vote of confidence, with pages receiving more votes considered more valuable and, therefore, receiving higher rankings.
The idea behind PageRank was that pages with numerous high-quality links pointing to them were likely to be more relevant and trustworthy sources of information. As a result, Google provided users with more accurate and valuable search results.
The advent of keywords: Early 2000s
As the internet continued to grow exponentially, website owners sought ways to improve their search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic. This led to the emergence of keyword research and optimisation.
Website owners began to realise that incorporating relevant keywords strategically within their content could align their web pages with user search queries. By targeting specific keywords, web admins could increase the likelihood of their pages ranking higher in search results when users perform relevant searches.
Keyword optimisation became a vital aspect of SEO, and marketers started to focus on finding the most relevant and high-traffic keywords for their content. However, the emphasis was on creating valuable, informative content that genuinely satisfied users' search intent rather than keyword stuffing.
Backlinks and link building: Mid-2000s
In the mid-2000s, search engines, especially Google, placed increasing importance on backlinks as a ranking factor. Backlinks are simply links from different websites that point to a particular page. The idea was that if other reputable websites link to a page, it must be valuable and relevant.
This shift in focus gave rise to the practice of link-building. Website owners and SEO professionals actively sought to acquire backlinks from authoritative and reputable sources. However, the emphasis was on natural, organic link-building rather than manipulative practices aimed at artificially inflating the number of backlinks.
The importance of backlinks in SEO led to a greater emphasis on creating valuable and shareable content, as quality content was more likely to attract links from other websites organically.
Learn digital marketing strategies with our Digital Marketing Masterclass!
Modern-day SEO: Present
Nowadays, SEO is a necessity due to the vast online competition and the changing behaviour of internet users. With billions of websites vying for attention, businesses and website owners need SEO to improve visibility and rank higher in search results. Users have become increasingly reliant on search engines to find products, services, and information, making SEO crucial for attracting organic traffic and reaching the target audience effectively.
The evolution of SEO is a response to search engine advancements and user preferences. As search engines prioritise user experience and relevant content, SEO strategies have shifted towards producing high-quality, user-centric content. Mobile optimisation is essential as more users access the internet through mobile devices.
Moreover, the role of social media in SEO has grown over time as technical aspects like website speed and site architecture started to have a greater impact on rankings. Today's SEO landscape revolves around delivering valuable, engaging content and optimising websites for users and search engines. Some real-life use cases of SEO in modern times are as follows:
The mobile revolution
The rise of smartphones and mobile devices has significantly shaped the modern era of SEO. With more people accessing the internet through their mobile devices than ever before, search engines have prioritised mobile-friendly websites. With time SEO has started to prioritise mobile optimisation, as it directly impacts a website's rankings in both mobile and desktop search results.
Websites that offer seamless and user-friendly experiences on mobile devices have become more likely to rank higher in mobile search results. This emphasis on mobile optimisation is driven by the search engines' desire to provide users with the best possible experience, regardless of the device they use to access the internet. Mobile-friendly websites load quickly, have responsive designs, and provide easy navigation. As a result, it ensures that users can find the information they need effortlessly.
Content is king
In modern SEO, content quality and relevance have become paramount. Search engines have evolved to recognise and reward websites with valuable and informative content for users. High-quality content that satisfies users' search intent is likely to rank higher in search results.
The saying "Content is King" holds true, as content plays a crucial role in attracting organic traffic and engaging visitors. Content marketing has become an integral part of SEO strategies, with businesses and website owners investing in creating valuable and shareable content such as blogs, articles, infographics, and videos.
More importantly, the focus is no longer solely on stuffing content with keywords to rank higher; instead, it's about crafting content that addresses the needs and queries of the target audience. Engaging, informative, and relevant content not only helps websites rank higher but also establishes them as authoritative sources within their respective industries.
The role of social media
Social media platforms have also emerged as significant players in modern SEO. Different social signals, such as likes, shares, and comments on social media posts, are now considered in search engine algorithms. These signals indicate the popularity and relevance of content, contributing to a website's overall SEO performance.
A strong social media presence can positively impact a website's rankings. When content is widely shared across social media platforms, it signals to search engines that it is valuable and resonates with users. Consequently, the content is more likely to receive higher search rankings, increasing visibility and organic traffic.
Social media also plays a role in building brand awareness and creating engagement with the target audience. Businesses that actively engage with their followers on social media platforms can foster a loyal community and attract more website users.
Technical SEO
While content quality and user experience are essential, technical SEO remains a critical aspect of SEO strategies. Technical SEO involves optimising the backend of a website. This improves its overall search engine visibility and overall performance. Here's the list of some key components of technical SEO:
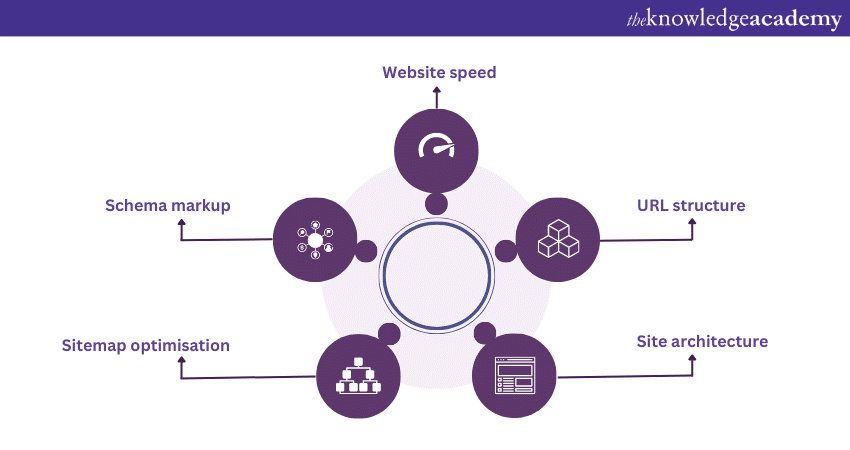
a) Website speed: Search engines prioritise websites that load quickly, as faster-loading websites offer better user experiences. Optimising images, leveraging browser caching, and reducing unnecessary scripts are some techniques used to improve website speed.
b) URL structure: Creating user-friendly and descriptive URLs helps search engines and users alike. Clear URLs that contain relevant keywords provide valuable context for search engine crawlers.
c) Site architecture: A well-organised site structure improves website navigation and user experience. A logical hierarchy of pages with clear categories and internal linking enhances search engine crawlers' ability to index and understand the website's content.
d) Sitemap optimisation: A sitemap is a file that provides search engines with an organised list of pages on a website. Optimising and regularly updating the sitemap makes sure that search engines can crawl and index all pages with greater efficiency.
e) Schema markup: Implementing a schema markup on a website provides structured data about the content for the search engine. It helps them display rich snippets in search results. Rich snippets, such as product information or star ratings, can improve click-through rates.
Learn audience engaging techniques with our Social Media Masterclass!
The Future of SEO
As technology advances and user behaviour evolves, the landscape of Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) continues to undergo significant transformations. The future of SEO promises to be dynamic, challenging, and filled with opportunities for businesses and website owners. Here's a glimpse into what the future holds for SEO:
Voice search and AI revolution
Voice search's popularity has become more prominent over time, thanks to the rise of smart speakers and virtual assistants like Amason Echo and Google Assistant. As AI-powered voice recognition technology improves, more users will rely on voice commands to search for information. Consequently, SEO strategies will need to adapt to accommodate natural language queries and long-tail keywords.
Optimising for voice search will involve creating content that answers specific questions and optimising for featured snippets, as search engines often use these snippets to provide voice search results. As voice search becomes more prevalent, businesses must ensure their websites are mobile-friendly and structured for optimal voice search performance.
Enhanced User Experience (UX)
UX has always been a critical aspect of SEO, and its importance will only grow in the future. Search engines continuously refine their algorithms to prioritise websites that offer seamless and engaging user experiences. Websites that load quickly have intuitive navigation, and provide valuable content will rank higher in search results.
Mobile optimisation will remain a priority as mobile devices continue to dominate internet usage. Websites must be responsive and adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes to cater to mobile users effectively.
Personalisation and intent-based SEO
Search engines are increasingly tailoring search results based on individual user preferences and behaviour. Personalisation will play a significant role in shaping SEO strategies as websites seek to provide customised experiences to users.
Intent-based SEO will focus on understanding user search intent and providing content that aligns with what users are seeking. Websites that can accurately predict and meet user intent will enjoy higher search rankings and better user engagement.
Video and visual search
The popularity of video-based content continues to rise, and search engines are enhancing their ability to index and display video content in search results. Video SEO will become an integral part of SEO strategies, with businesses optimising video titles, descriptions, and tags to improve visibility.
Visual search, powered by AI and image recognition technology, is also on the rise. Users can now search for products or information by uploading images instead of using text-based queries. Visual search optimisation will become crucial for e-commerce websites and businesses relying on visual content.
Blockchain and data security
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionise SEO by improving data security and eliminating fraudulent practices like click fraud. Blockchain can provide more transparent and secure tracking of website traffic and interactions, ensuring that data is accurate and trustworthy.
Local SEO and hyperlocal targeting
Local SEO will keep being essential for businesses with physical locations. As users increasingly rely on mobile devices to find nearby businesses and services, hyperlocal targeting will become more critical. Websites must optimise for local searches and ensure their Google My Business profiles are up to date to attract local customers.
EAT and expertise in SEO
Google's EAT (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) principle will gain more prominence in SEO. Websites that demonstrate expertise, authority, and trustworthiness in their respective fields will receive better search rankings. Brands will need to build their online reputation and establish themselves as credible sources of information.
Conclusion
We hope that after reading this blog, you have learned everything about the intriguing History of Search Engine Optimisation. From tracing its evolution from the early days to modern practices, its story is fun and surprising. By adapting to emerging trends and prioritising user-centric strategies, businesses can thrive in the ever-changing digital landscape. Stay agile, and success in SEO is within reach.
Advertise your products through Google with our Google Ads Masterclass!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Digital Marketing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Digital Marketing Course
Digital Marketing Course
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


