We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

If you are an International Trade enthusiast, you might have heard about the terms Import and Export. But there’s a huge Difference Between Import and Export. These two terms refer to exchanging goods and services across national borders.
Importing means bringing goods or services into your country from another country, while Exporting means sending goods or services to another country. However, this is just scratching the surface: Import and Export differ based on various parameters. In this blog, we will explain the Difference Between Import and Export in more detail and how they affect the economy, the environment, and society.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Import
2) What is Export?
3) What is the Difference Between Import and Export?
4) Challenges in Import and Export
5) Trade policies in Import and Export
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is Import
In the context of trade, Import refers to bringing goods or services into a country from abroad for consumption, distribution, or resale. It is a fundamental aspect of international commerce, contributing to the global exchange of products and fostering economic interdependence among nations. Imports encompass various goods, including raw materials, finished products, and services, fulfilling domestic demand and supplementing local industries. However, Imports can have the following pros and cons:
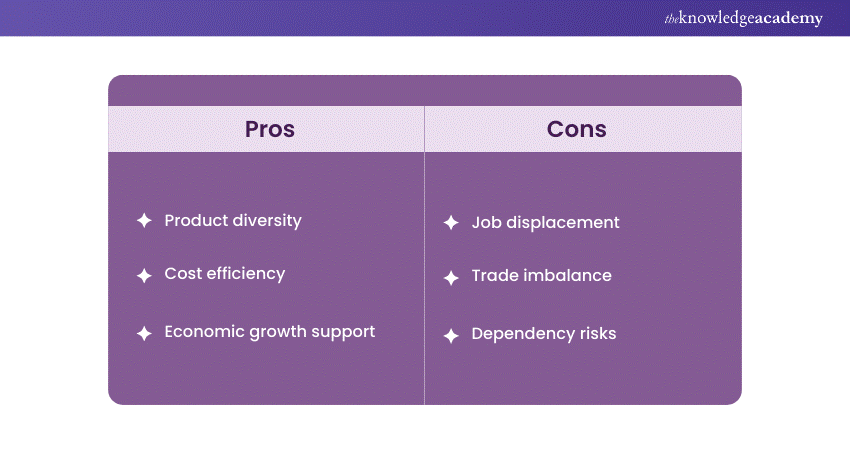
The Importation process involves customs clearance, compliance with trade regulations, and payment of applicable duties and taxes. Nations engage in Imports to access resources not readily available domestically, capitalise on comparative advantages, and diversify their markets. This contributes to the richness and complexity of the global economic landscape.

What is Export?
Export refers to selling goods or services produced within one country to buyers located in another nation. It is a fundamental component of International Trade, contributing to economic growth and fostering global business relationships. In Export, businesses aim to capitalise on comparative advantages, leveraging their expertise, resources, or technology to offer products or services in foreign markets. However, Exports can have the following pros and cons:
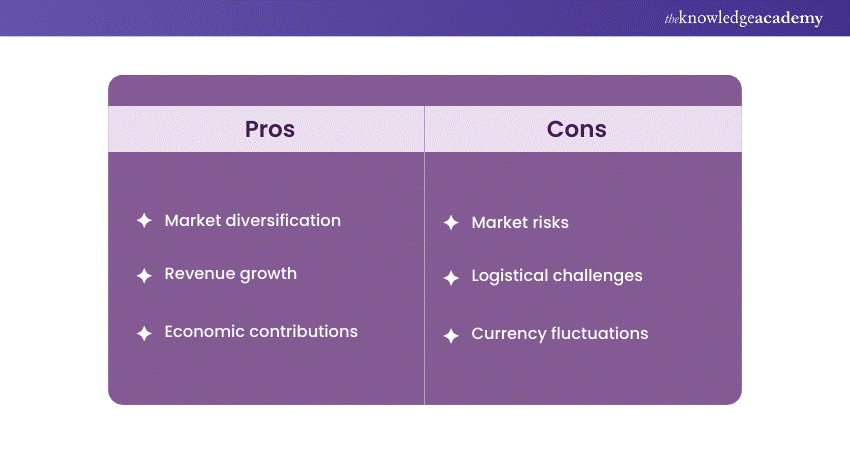
Governments often play a role in regulating Exports through trade policies and agreements. Exporting not only enhances a country's economic vitality but also encourages cultural exchange and cooperation on a global scale. Successful Export practices require businesses to navigate diverse regulations, logistics, and market dynamics, emphasising adaptability and strategic planning.
Enhance your knowledge of the current trends and policies with our Industry Training!
What is the Difference Between Import and Export?
International Trade, characterised by the exchange of goods and services across borders, is a complex network involving Imports and Exports. Both play vital roles in shaping the economic landscapes of nations, influencing trade balances, fostering economic growth, and facilitating global cooperation. However, both processes play different roles in International Trade. These differences are as follows:
1) Trade direction
Imports and Exports form the lifeline of global trade, delineating the movement of goods and services across international boundaries. Imports constitute the procurement of goods or services produced abroad, enriching a country's domestic supply with diverse foreign products. This infusion contributes to economic diversity and meets the demands of consumers who seek access to international offerings.
On the flip side, Exports entail the sale of domestically manufactured goods or services to overseas markets. This outbound flow fulfils international demand and positions a country within the intricate web of global commerce. Thus, it helps enhance economic growth and fosters bilateral and multilateral trade relationships.
2) Effect on trade balance
A nation's trade balance, a pivotal economic indicator, is intricately tied to the dynamics of Imports and Exports. A trade deficit materialises when a country's Import expenditures exceed the earnings from its Exports. This scenario indicates that the nation is spending more on foreign goods and services than it earns through Export activities. A trade deficit can impact a nation's economy by influencing currency exchange rates, affecting domestic industries, and contributing to overall economic instability.
Conversely, a trade surplus signifies a more favourable economic situation. This occurs when a nation's Exports surpass Imports, resulting in excess funds. A trade surplus can enhance a country's economic standing by contributing to foreign exchange reserves, stimulating domestic industries, and supporting overall economic growth.
3) Objective
Imports are a strategic means for a country to bolster its domestic supply by acquiring goods or services that may be unavailable or in insufficient quantities domestically. The primary aim is to efficiently meet the demands of consumers and industries, ensuring a well-rounded and diverse array of products.
Conversely, Exports are crafted to capitalise on a nation's production capabilities. Through selling products or services in foreign markets, Export can stimulate economic growth, generate substantial revenue, and fortify their global market presence. These reciprocal activities contribute to the intricate tapestry of international commerce, fostering economic interdependence and cooperation among nations.
Learn more about communicating effectively with our Facilitation Skills Training – register now!
4) Motivations
Importing nations often pursue raw materials, goods, or services that may be scarce or more economically viable abroad, enabling them to fulfil the diverse needs of their population. This strategic sourcing contributes to economic efficiency and consumer welfare.
On the flip side, Exporting countries are propelled by motivations such as comparative advantage, technological expertise, specialised skills, or cost-effectiveness. By leveraging these strengths, they aspire to carve a competitive niche in the global market, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
5) Products and services
Imports cover a wide array, ranging from essential raw materials and consumer goods to cutting-edge machinery, technology, and specialised services like consultancy or software. This influx of goods and services contributes to a nation's economic vitality and technological advancements.
Conversely, Exports encapsulate products and services in which a country exhibits prowess or holds high international demand. This can include manufactured goods, agricultural products, technological innovations, or professional services. The dynamic interchange of such commodities fuels economic growth, fosters invention, and establishes interconnected relationships in the intricate web of global trade.
Challenges in Import and Export
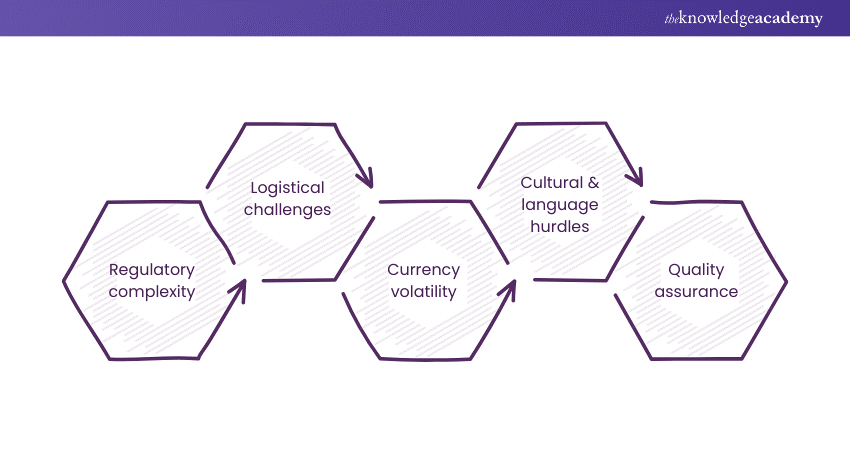
Imports and Exports are integral to the global economy, facilitating the exchange of goods and services across borders. While this process contributes significantly to economic growth and international cooperation, it has challenges.
One prominent challenge in International Trade is regulatory compliance. Each country has its own set of regulations, tariffs, and trade barriers, creating a complex web of compliance requirements. Businesses engaged in Import and Export activities must navigate these regulations to ensure adherence to legal frameworks, which often requires a deep understanding of International Trade laws and local regulations.
Another significant challenge is currency fluctuations. The value of currencies in the foreign exchange market can be volatile, influencing the costs and profitability of Imported or Exported goods. Exchange rate risks pose challenges for businesses engaged in cross-border trade, necessitating strategies to manage and mitigate currency-related uncertainties.
Logistical hurdles also play a crucial role in the challenges faced in Import and Export. Efficient transportation, warehousing, and Supply Chain Management are vital for the smooth movement of goods across borders. Delays, disruptions, or inefficiencies in logistics can lead to increased costs, delayed deliveries, and potential damage to goods, impacting the overall trade process.
Trade barriers and protectionist measures adopted by certain countries can pose challenges for businesses seeking to expand their international footprint. Tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions can hinder the free flow of goods and services, limiting market access and affecting the competitiveness of products in foreign markets.
Emerging technologies and digital transformation bring opportunities and challenges to the Import and Export landscape. While Blockchain and digital documentation can streamline processes, they require adaptation and investment. Ensuring cybersecurity and data protection is crucial in an increasingly interconnected and digitised trade environment.
Trade policies in Import and Export
International Trade is governed by national policies that regulate Imports and Exports. These policies are pivotal in shaping a country's economic landscape. So, let’s have a quick look at each of these policies:
Import policies
Import policies are a set of regulations and measures a country implements to control foreign goods and services inflow. These policies safeguard domestic industries, protect national interests, and maintain economic stability. Key components of Import policies include the following:
1) Tariffs: Tariffs are taxes imposed on Imported goods, influencing their cost and competitiveness in the domestic market. Governments may use tariffs strategically to protect local industries, generate revenue, or address trade imbalances.
2) Quotas: Quotas limit the quantity of specific goods Imported within a specified period. By imposing quotas, governments aim to control the saturation of foreign products in the domestic market, ensuring a fair balance between Imported and domestically produced goods.
3) Licensing Requirements: Licensing requirements mandate that certain Imported goods can only enter the country if specific criteria are met. This could include safety standards, environmental regulations, or adherence to particular quality benchmarks.
Export policies
Export policies are formulated to facilitate and regulate the outflow of domestically produced goods and services to foreign markets. These policies aim to promote economic growth, enhance global competitiveness, and strengthen a country's presence in International Trade. These include the following:
1) Export Incentives: Governments often provide incentives to encourage Exports, such as tax benefits, financial support, or reduced regulatory burdens. These incentives are designed to boost the competitiveness of domestic products in the global market.
2) Trade Agreements: Countries engage in trade agreements to facilitate smoother Exports by reducing trade barriers, tariffs, and bureaucratic hurdles. Bilateral and multilateral agreements create a conducive environment for increased Export activities.
3) Export Licensing: Similar to Import licensing, Export licensing may be required for certain goods to ensure compliance with international regulations, sanctions, or security concerns.
Do you want to learn more about Import and Export? Sign up now for our Importing and Exporting Masterclass!
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the Difference Between Import and Export is pivotal for navigating the complex landscape of International Trade. From trade direction to economic impacts, we hope that this breakdown equipped you with insights crucial for global commerce. So, embrace this knowledge to make informed decisions, fostering a thriving presence in the interconnected world of Imports and Exports.
Enhance your knowledge about managing Supply Chain – sign up now for our Supply Chain Management Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

The primary distinction lies in the direction of trade. Imports involve bringing goods and services into a country from abroad, addressing domestic needs or supplementing local production. On the other hand, Exports entail sending goods and services produced within a country to foreign markets. The key difference lies in whether the nation is receiving external products or contributing its own to the global market, shaping its trade dynamics and economic interactions on a global scale.

Imports and Exports significantly influence a country's trade balance. If a nation Imports more than it Exports, it incurs a trade deficit, impacting its economic health. Conversely, Exporting more than Importing results in a trade surplus, contributing positively to the country's economic well-being. The trade balance reflects the overall health of a nation's economy.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Industry courses, including Importing and Exporting Masterclass, Logistics Management Training, and Export and Trade Compliance Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Logistics and its Importance.
Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Logistics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Import and Export skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Import Export Course
Import Export Course
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


