We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a customer asking for their data to be deleted from your records. Have you ever wondered how your company handles such requests and whether it meets the stringent requirements of GDPR Compliance? Navigating the complexities of GDPR can seem daunting, but understanding its essentials can guide businesses to operate smoothly in the digital age.
Our comprehensive blog offers clear insights into the principles of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and practical steps for compliance. Dive in to discover how GDPR Compliance can transform your data management practices and safeguard your organisation against hefty fines and reputational damage.
Table of Contents
1) What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
2) What does GDPR Compliance mean?
3) GDPR Terminology
4) Why is GDPR Essential for Your Website?
5) GDPR Compliance Checklist
6) Important Things to Know About GDPR Compliance
7) Benefits of GDPR Compliance
8) Conclusion
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU regulation that manages data privacy and security of citizens, the European Union and the European Economic Area. It grants individuals control over their personal data and creates consistency through only one authority in the EU for the simplification of international business.
In essence, it imposes the company’s respect and secure personal data, be it from collection, processing or where it is stored. The GDPR aims at providing transparency, privacy, and accountability of the companies, and it grants individual the right to get access, correction, deletion, and restriction in processing of their data.
What Does GDPR Compliance Mean?
GDPR Compliance requires your company to manage customer data in strict alignment with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), focusing on the secure collection, processing, and protection of personal data for individuals within the EU and EEA.
Businesses must transparently disclose the personal data they collect, obtain informed consent, implement robust security measures to prevent breaches, and respond promptly to requests for data access or removal. Compliance involves adhering to the standards, rules, and regulations outlined in the GDPR, ensuring the organisation is prepared to address any inquiries regarding personal information.
Why is GDPR Essential for Your Website?
The GDPR—General Data Protection Regulation—happens to be another important part of your site because it ensures that in compliance with the GDPR, individual rights to private life will be protected from being intruded upon, misused, or abused. This ensures you are processing user personal data in a responsible and transparent way, thereby building trust with your audience. On the other hand, if there is non-compliance, then you should be prepared to face heavy fines, which can defame your name and standing financially.

Furthermore, compliance with GDPR indicates your ethical business practices and adds to the increased level of credibility of your brand, making the brand more attractive to potential customers. Applying GDPR Principles—such as data minimisation or user consent, for instance—to your business in that way means you do comply with those legal duties and at, the same time, offer your users secure and private data, which allows for a positive and respected milieu on the internet.
Protect data & ensure compliance! Join our GDPR Certification today and safeguard your organization from data breaches.
Who Does the GDPR Apply to?
The GDPR affects any organisation offering goods and services to EU residents, including those outside the EU. Online businesses should comply with GDPR as a precaution.
a) Data Controllers: Entities that determine the purpose and means of processing personal data. For example, a music school uses a digital screen to notify parents as a controller.
b) Data Processors: Entities that process data on behalf of controllers, following their instructions. For example, a marketer hired by a software company to send emails is a processor.
GDPR Compliance Checklist
Organisations are required to follow certain steps to achieve GDPR Compliance. By following these steps and integrating GDPR Requirements into their business processes, organisations can establish a solid Data Protection and privacy foundation. The steps include:
1) Assess Your Data
The first vital step to achieving GDPR Compliance is scrutinising the details of the data you collect, process, and store in your organisation. First, conduct a thorough data audit. After conducting a data audit, you will be able to identify what kind of personal data are processed, what their origin is, and the grounds for their processing. This will identify the dimension of data processing in your organisation.
2) Map Data Flows
Once you have assessed your data, it's essential to map the flow of Personal Data throughout your organisation. Document how data moves within your systems, including its collection, storage, and sharing with third parties. This mapping exercise enables you to identify any potential risks or vulnerabilities in data handling and implement appropriate measures to address them.
3) Website Security
No business can work without having the security of its website. One of the most critical things that we need to do is have a secure storage of our server's and website's data from any external threats. Making sure that you have an impenetrable security system that hackers cannot penetrate is a vital one.
4) Review and Update Policies
Review your existing privacy policies, procedures, and documentation to ensure they align with GDPR. Update and enhance them as necessary to reflect the principles and rights established by the regulation. Your policies should communicate how Personal Data is handled and what purposes it is used for.
5) Obtain Consent
Under GDPR, obtaining explicit and informed consent from individuals is a prerequisite for legal Data Processing. Review your consent about the GDPR and make sure that they meet these standards. Introduce a clear consent form that clarifies the purposes of Data Processing and enable people to grant, deny or reset their consent at any time.
6) Add a Banner for Cookies
In order to get GDPR based cookie consent from your customers, you should take the help of a cookie banner. This should be especially done when the website uses cookies, which are not essential. Cookie banners let the visitors know what information and how they use it thata website collects.
7) Verify the Forms on Your Website
If your website contains any kind of forms such as subscriptions, contact us pages, inquiries, etc., you must make sure that the following points are fulfilled:
a) To include a privacy statement: A privacy statement explains to users why you collect their data and what you intend to do with it. The customers, too, should be informed that they can withdraw their consent any time.
b) Opt-in option: It may be an unmarked checkbox or an immobilised switch to collect user data through user consent.
c) Add a checkbox: The main goal of the message is to let users know that they can get back to the site if they choose to.
8) Analyse Data Processors or Outside Services
One critical thing to do is know if the company's services directly using the datasets comply with the GDPR. Being aware of the privacy policies of any company/employer that you are directly or indirectly using is necessary.
For instance, if they are handling the work for your company, then you have to ensure that they will harmonise with the policy for the privacy. This would imply that they would have to follow the regulations of GDPR too.
9) Analyse the Global Data Transfer
If your company website relies on sending Personal User Data from the EU to non-EU countries, you must ask yourself the following questions:
a) Have you gone through the required GDPR Risk Assessment before the user data transfer?
b) Does the receiving country comply with the Data Protection requirements to ensure the protection of the transferred data?
c) Have all your agreements with the final beneficiary company/services been fulfilled?
10) Conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
According to the GDPR, conducting DPIA for high-risk Data Processing activities is mandatory. DPIA implies evaluating the risks and impacts on personal privacy and implementing appropriate measures to avoid them.
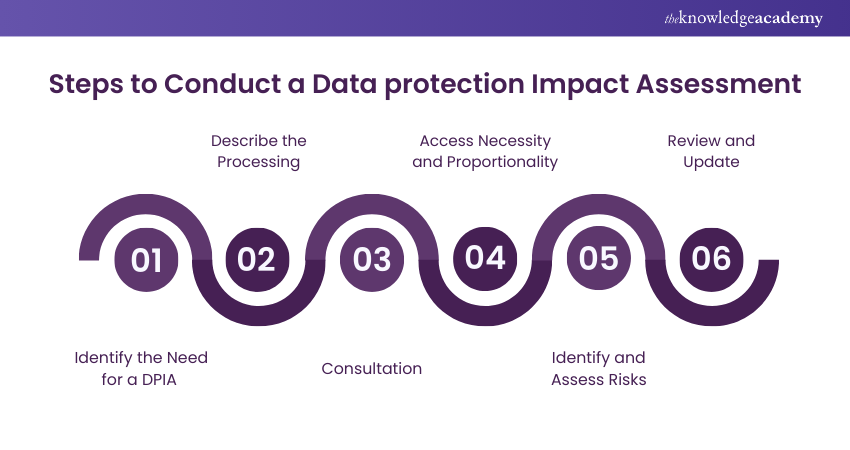
Categorise and assess the inherent risks emerging in your Data Processing and establish the particular safeguards to secure Personal Data.
Equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of Data Protection – join our Data Privacy Awareness Course now!
11) Implement Security Measures
Data safety is an important element of the implementation process of GDPR guidelines. It is necessary to ensure the rightful technical tools are used to protect personal data against unauthorised access, loss of it, or change. This trouble may consist of encryption, access controls, data backups on a regular basis, and employee data protection systems training. Audit and maintain your security policies regularly to ensure that they stay ahead of the curve in terms of security.
12) Data Subject Rights
The GDPR recognises several people's rights regarding their personal data. Train your employees and customers on these rights and set up measures and policies to respond to data subject requests in a timely and smooth manner. These rights include:
a) Right to Access: Make sure that the data is processed as requested and send the copies.
b) Right to Rectification: Correct incomplete or inaccurate records immediately.
c) Right to Erasure: Delete data when no longer needed and when the consent has been withdrawn.
d) Right to Restrict Processing: Some persons may prevent data processing in certain situations.
e) Right to Data Portability: Get data in a structured form and dispatch it to another controller.
f) Right to Object: Object to data processing, except in case of compelling reasons.
g) Rights for Automated Decision-making: Enlighten people with your speech, provide explanations and allow challenges.
h) Right to be Forgotten/ Right to Erasure: Data subjects have the right to request the deletion of their personal data. However, this right is not absolute and may be subject to exemptions under specific laws.
13) Data Breach Response
Develop a strong Data Breach response plan to deal with the unknown circumstances of information and security compromises. Determine the job profiles of your incident response team, define the policies for discovering, investigating, and reporting breaches, and ensure that the step of notifying the regulators and relevant third parties is being done in a timely manner, whenever needed. Instant and transparent communication is of utmost importance to relieve the impact on individuals and uphold the company’s accountability in the event of a data breach.
14) Data Protection Officer (DPO)
Hire a DPO or use an external DPO service provider if the GCDR mandates. The task of the DPO is to culminate your organisation`s Data Protection plan, guide it along with the GDPR, and be a partner for supervisory authorities. The individuals should at least be experts in Data Protection law and practice and they must be able to operate within your organisation independently.
15) Ongoing Adherence
GDPR Compliance is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Regularly review your data processing activities, policies, and procedures to ensure they meet GDPR requirements. Stay informed about changes in Data Protection laws and adjust your practices accordingly.
Since its inception in 2018, GDPR has been praised for its robust privacy protections. However, many enterprises initially struggled to understand its complexities. Being aware of key aspects of GDPR Compliance can help address privacy concerns, enhance data security, and manage potential violations effectively.
Join our Personal Data Protection Bill Training and gain a comprehensive understanding of the latest Data Protection regulations.
Important Things to Know About GDPR Compliance
Since its introduction in 2018, GDPR has been widely lauded for its groundbreaking approach to data privacy. It has set a new standard for protecting personal data. However, the complexities of GDPR have led to confusion for many companies trying to navigate its requirements. Here’s a summary of key aspects to understanding GDPR compliance, which will help improve your organisation’s data protection practices and avoid compliance issues.
GDPR Affects Every Country
GDPR regulations apply universally to any company that processes or provides goods and services to EU member countries. Regardless of where a company is based, if it handles data of individuals within the EU, it must comply with GDPR requirements to meet the necessary standards.
Designate a Representative Physically Located in the European Union
To ensure effective communication with regulatory authorities, your organisation must appoint a representative located in the EU. This representative acts as a liaison between your company and GDPR officials, manages records, maintains documentation, streamlines compliance efforts, and addresses any issues related to communication with the authorities.
Ignorance of GDPR Compliance Can Result in Hefty Penalties
Failure to comply with GDPR can result in significant fines. Initially, companies are given a grace period to familiarise themselves with GDPR requirements and implement necessary measures. Penalties are determined based on a tiered system and can reach up to 2% of the annual global turnover from the previous fiscal year.
Human Rights Are Prioritised Over User Experience
The primary goal of GDPR is to protect individuals' personal data and privacy. This legislation is designed to uphold the right to privacy and has challenged many companies, particularly those relying on unauthorised data processing. Prior to GDPR, personal data was often susceptible to misuse and exploitation.
Establish a strong foundation in Data Protection and GDPR by signing up for our Certified EU GDPR Foundation Course now!
Benefits of GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR Compliance goes beyond regulatory adherence; it brings numerous Benefits To Businesses. By implementing robust Data Protection measures and respecting individuals' privacy rights, organisations can experience the following advantages:
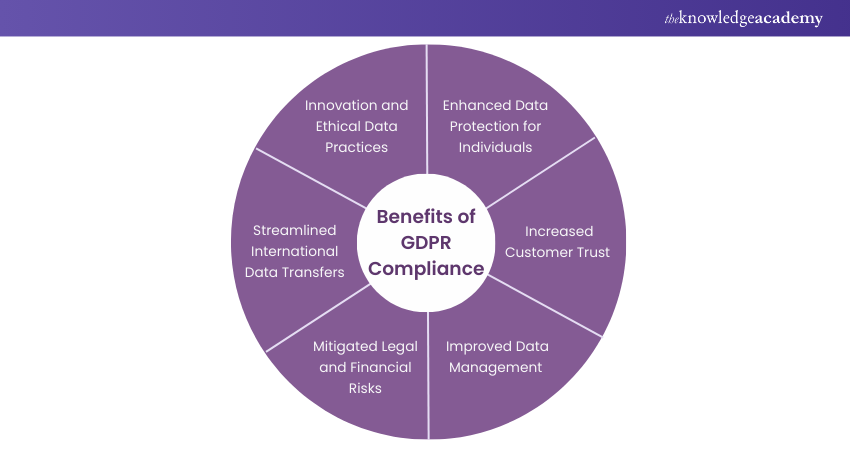
a) Enhanced Data Protection: GDPR strengthens the protection of personal data, granting individuals greater control over their information and ensuring a safer online environment for their data.
b) Increased Customer Trust: Adhering to GDPR fosters customer confidence by demonstrating responsible data handling. This trust encourages customers to engage more deeply with your services and remain loyal over time.
c) Improved Data Management: GDPR Compliance promotes meticulous data organisation within your organisation, leading to better management practices. This not only ensures compliance but also enhances operational efficiency.
d) Mitigated Legal and Financial Risks: Compliance with GDPR helps avoid costly fines and reputational damage by protecting customer data. This safeguards your business interests and financial health.
e) Streamlined International Data Transfers: GDPR facilitates smooth international data transfers by standardising privacy protections, ensuring that data flows seamlessly across borders while meeting privacy regulations.
f) Innovation and Ethical Data Practices: GDPR encourages innovative and ethical data practices, ensuring that businesses use data responsibly and protect individual privacy while driving responsible innovation.
Conclusion
Achieving GDPR Compliance is not only a legal requirement but also an opportunity for organisations to prioritise Data Protection and privacy. We hope the contents of this blog have helped in improving your knowledge about the steps required to be followed to achieve this compliance and the benefits of doing so.
Reduce data breaches with our GDPR Awareness Training – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Personal data under the EU GDPR includes any information that can directly or indirectly figure out an individual, including names, addresses, email addresses, IP addresses, and even online identifiers like cookies. It also covers sensitive data like health records, biometric data, and financial information.

GDPR Compliance is triggered when an organisation processes the personal data of individuals within the EU, regardless of the organisation's location. This includes collecting, storing, or using data for any purpose. Even non-EU companies must comply if they handle EU residents' data.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various GDPR Courses, including Information Systems Security Management Training, EU General Data Protection Regulation Awareness Course and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Benefits of GDPR.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your GDPR skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO)
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


