We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Picture your digital world as a fortress. Just as you wouldn't leave the gates unguarded, you need a robust defense to protect your online realm. This is where the concept of a Firewall becomes essential. But What is a Firewall, and why is it indispensable for your Cyber Security?
In this blog, we will explore What is a Firewall, how it functions and the different categories that exist within the market. From learning about its evolution to using different sections of it today, this blog will arm you with the information to protect your online world.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Firewall?
2) The History of Firewalls
3) How do Firewalls Work?
4) Different Types of Firewalls
5) Why do we Need Firewalls?
6) Difference Between Firewall and Antivirus
7) Examples of Firewalls
8) Conclusion
What is a Firewall?
A Firewall can be described as a network security tool that performs the function of selecting the traffic to permit or block in the network based on given rules or directions.
It is located at the interface of trusted and untrusted networks; a Firewall examines the packets passing to and from each network and implements a set of security rules and benchmarks. They act at the preliminary stage to protect the network from the effects of malicious data packets that are channeled in the network.
A Firewall may be implemented as either a hardware appliance or software or both. Organisation’s key objective is to create a protected environment for computer networks, thus excluding threats coming from outside, viruses as well as unauthorised access to information.
The History of Firewalls
Firewalls had their roots back in the late 1980s when the internet started to take root. Originally, they were merely packeting filter technology designed for observing and managing network traffic. However, by the mid of the 1990s more advanced Firewalls known as Stateful Firewalls enabled it to inspect the state and context of the connections.
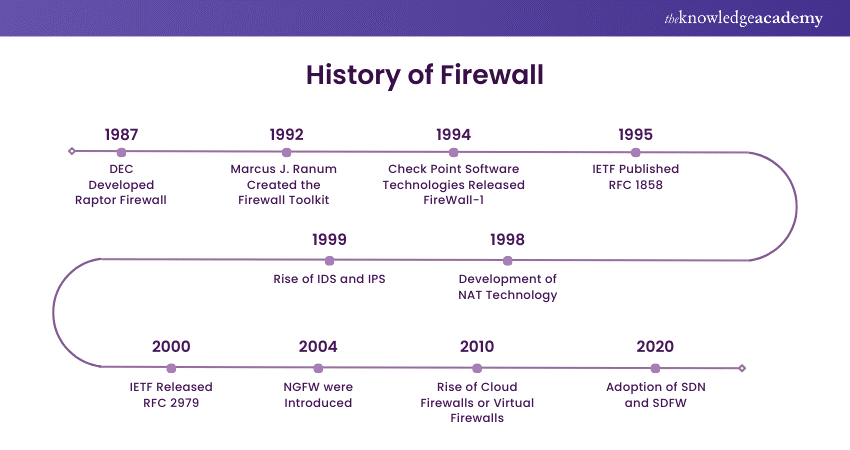
In the 21st century, firewalls evolved beyond simple packet filters, incorporating advanced techniques like intrusion detection and prevention, deep packet inspection, and application layer filtering. These innovations significantly enhanced Cyber Security measures.
Today, Next-generation Firewalls (NGFWs) are an indispensable addition to the modern approach to Cyber Security due to many integrated features and functions that combine traditional and innovative core and uses Artificial Intelligence.
How do Firewalls Work?
Firewalls operate by examining data packets that move between a device or network and external sources. Each packet is evaluated against a set of security rules to decide whether it should be allowed or blocked. Firewalls can:
a) Permit or Deny Access: Firewalls evaluate incoming and outgoing packets by analysing their source IP address, destination IP address, and port numbers.
b) Monitor Traffic: Firewalls continuously observe network traffic to detect unusual patterns. For example, if an IP address suddenly sends an unusually high number of requests, it could indicate a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
c) Filter Content: Firewalls can block access to malicious or inappropriate content, such as harmful websites, phishing emails, or infected files. This is particularly useful for protecting against malware, or other cyber threats that rely on deceptive content.
Different Types of Firewalls
There are various types of Firewalls, each catering to different security needs:
1) Static Packet-Filtering Firewall
This is the most basic type of Firewall. It examines data packets against predefined security rules, such as source/destination Intellectual Property (IP) addresses and port numbers. While efficient, it lacks the ability to analyse the context or state of the traffic.
2) Circuit-level Gateway Firewall
These Firewalls operate at the session layer, verifying the legitimacy of connection requests. They ensure that packets belong to a valid session before allowing them through, providing basic security with minimal impact on network performance.
3) Proxy Firewall
Also known as application-level Firewalls, proxy Firewalls act as intermediaries between users and the resources they access. They filter traffic at the application layer, making them highly secure but potentially slower due to the detailed inspection.
4) Hybrid Firewall
A hybrid Firewall combines multiple Firewall types to offer comprehensive protection. For example, it might integrate packet filtering with application-layer inspection, addressing both basic and advanced security requirements.
5) Stateful Inspection Firewall
Stateful Firewalls track the state of active connections, analysing packets within the context of these sessions. They offer a balance of performance and security, making them a popular choice for modern networks.
6) Next-generation Firewall (NGFW)
Features of the NGFWs are enhanced features from traditional Firewalls and include deep packet inspecting, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) as well as real-time threat intelligence. They are meant to work for protection against more sophisticated threats such as zero-day and ransomware.
Step into the world of network with our Cyber Security Awareness Course - Join today!
Different Methods of Firewall Delivery
Firewalls can be deployed in various ways to suit different network environments:
1) Hardware-based Firewalls
These are tangible appliances that sit at the edge of the network against the Internet. They are most suitable for organisations that need highly dedicated security solutions that can handle large traffic with little or no delay.
What They are?
Hardware Firewalls are physical objects that are connected to your network and often positioned on the network periphery. These Firewalls can be employed to filter incoming or outgoing information as the main security point for the network.
How They Work?
These are device-level controllers that have their own microcontrollers and other resources which make them independent of a host controller. They patrol the traffic entering into a network and depending on set protocols they either drop or permit to enter into the network.
2) Software-based Firewalls
Stored in computers or servers and only runs when initiated, software Firewalls are ideal for individual computer users and businesses with a few employees. They are simple and easy to modify and at the same time are dependent on the host system.
What They are?
Application Firewalls can be defined as software applications which are fixed in computers or separate machines, such as, desktops, laptops or servers. The roles and responsibilities include acting as shields to the specific system to which they are attached.
How They Work?
They regulate and arrest traffic on or through the host machine. Since they are software-controlled, they depend on the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and memory of the host system upon which they operate.
3) Cloud Firewalls
Cloud Firewalls are Internet based Firewalls which offer elastic, flexible security for cloud infrastructures also referred to as Firewall as a Service (FWaaS).
What They are?
A cloud Firewall is a type of Firewall that is implemented in the cloud computing environment and avails itself as a service. They secure cloud structures, applications, and distributed network systems.
How They Work?
Cloud Firewalls control traffic on your network or devices by running it through a cloud management interface. Some of them work in synergy with the contemporary Information Technology (IT) platforms, such as remote workers and hybrid cloud systems.
Protect data and strengthen your systems with our Cyber Security Risk Management Course - Sign up today!
Why do we Need Firewalls?
Firewalls are one of the most basic components of protection since they are walls that shield against attempts at access and conceal the data. Let’s break down their key roles and why they are essential:
a) Prevent Unauthorised Access:
Firewalls control all the traffic in and out of your system, therefore only the permitted parties gain access to your network. Firewalls just eliminate unauthorised attempts of getting through accessing the loopholes that hackers or malicious bots are likely to exploit, hence leading to unauthorised access or a breach.
Example: If a hacker attempts to gain access to your company server using a potentially suspicious because the IP address is not authorised, the Firewall notes the intrusion and denies the connection thereby protecting your company’s network.
b) Protect Sensitive Data:
Any confidential data that a company possesses is a potential target today, including financial statements, individual information, and patented information. Firewalls serve as access control points, which help to prevent traffic reaching your network, which can contain things like phishing attacks or data exfiltration attempts.
Example: One important instance of where a Firewall comes in handy is when it is able to prevent an infected Personal Computer (PC) from sending data to an attacker.
c) Mitigate Malware Risks:
Malware can get into a system through links of malicious websites or downloads as well as through email attachments. This risk is managed through the help of Firewalls that do not allow access to such unhealthy content. Their main function is to prevent malware from appearing with the network and becoming a part of it.
Example: If an employee falls for a phishing website where he had clicked a malicious link, then the Firewall alerts the browser to the fact that the site is a virus site, and the browser cannot establish a connection with it.
d) Maintain Network Performance:
Firewalls control traffic because the network should not be flooded with excessive and undesirable data inquiries. This enhances efficiency and user legitimacy to gain access to the network without interferences.
Example: There are times when a network is attacked by many fake traffic, a common thing known as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, the Firewall will ensure that the bad requests are eliminated thus nether slowing down or failing the network.
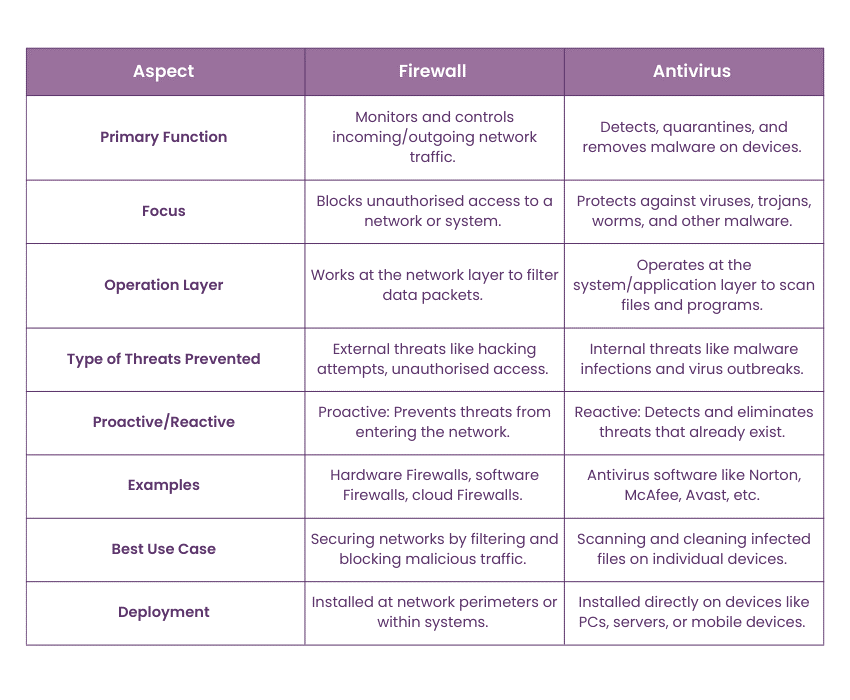
Difference Between Firewall and Antivirus
Here is the difference between the Firewall and Antivirus:
Examples of Firewalls
Some well-known Firewall solutions include:
a) Cisco ASA: A capable ‘Firewalls’ of physical build with a mix of enterprise features
b) Palo Alto Networks NGFW: The next-generation Firewall – a product that addresses today’s evolving threats.
c) Sophos XG Firewall: It merges Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) with an intelligent analytics solution.
d) Windows Defender Firewall: Additional software Firewall, which is built into Windows Operating Systems (OS).
e) Cloudflare WAF: A Firewall hosted in the cloud and developed for site and applications protection. Cloudflare offers a robust and comprehensive Web Application Firewall (WAF) service that provides advanced protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what a Firewall is and its various types is crucial for safeguarding your digital world. As cyber threats evolve, so must your defences. Stay informed, stay protected, and let Firewalls, along with Cloudflare alternatives, be your first line of defence in the ever-changing Cyber Security landscape.
Learn to detect, defend and deter cyber threats with our Introduction To System And Network Security - Register today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are NGFWs, and How do They Differ from Traditional Firewalls?

It is characterised by the incorporation of typical functions of a basic Firewall into more sophisticated features of Firewalls in the Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs), which encompass deep packet inspection, Intrusion Prevention System and application-layer filtering.
How do Firewalls Help with Regulatory Compliance?

With the aid of Firewalls, organisations working under regulatory body compliance can protect the essential data. They help organisations to fulfill the requirements of regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), etc.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Trainings, including the Cyber Security Awareness, Cyber Security Risk Management and the Incident Response Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Malware Analysis.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Network Security and Firewall, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Security Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to System and Network Security
Introduction to System and Network Security
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


