We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Leadership is key to any successful organisation, steering it through challenges and opportunities. But not every leadership style fits every goal. One unique style is Bureaucratic Leadership. Before you decide to use it, it's important to understand what it involves. Check out this blog to learn about Bureaucratic Leadership, its main features, pros and cons, and how it can bring discipline to your workplace.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Bureaucratic Leadership?
2) Exploring the Characteristics of Bureaucratic Leadership
3) Qualities of Bureaucratic Leadership
4) Advantages and Disadvantages of Bureaucratic Leadership
5) Key Examples of Bureaucratic Leadership
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is Bureaucratic Leadership?
Bureaucratic Leadership is a style where leaders follow a strict chain of command, adhere to established regulations, and ensure their followers do the same.
While the term might seem unappealing at first, many organisations have thrived under this leadership framework. Bureaucratic Leadership can be particularly beneficial for businesses that rely on efficient management structures.
Bureaucracy itself involves appointing individuals through a rigorous selection process. These individuals handle official matters and execute business orders, including laws, rules, and policies.
This leadership style showcases attributes like professionalism, a clear hierarchy, selective authority, assigned responsibilities, and rule-based decision-making. These qualities make Bureaucratic Leadership disciplined and structured.
Exploring the Characteristics of Bureaucratic Leadership
Now that you have learnt What is Bureaucratic Leadership, it’s time to learn about its key characteristics. Maximillian Karl Emil Weber, the founding father of Bureaucratic Leadership, German Sociologist, Historian, Jurist and Political Economist, has a strong hold over the defining factors of Bureaucratic Leadership. Max was confident about the positive impact of this Leadership style in any organisation.
Additionally, he also envisioned the transformation of businesses into large factories and massive establishments. He then devised the following characteristics of Bureaucratic Leadership:
Decision-making Hierarchies
The hierarchical structure is the defining characteristic of Bureaucratic Leadership. The stringent protocol between officers and their subordinates of various departments forms the firm and robust backbone of the hierarchy.
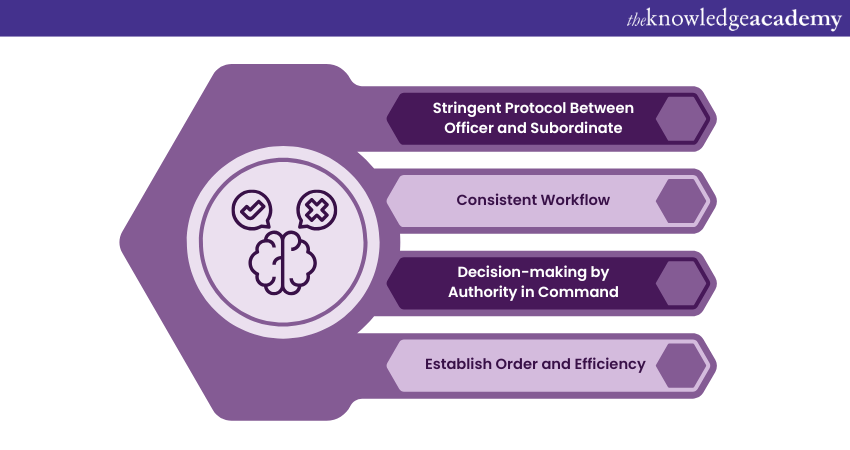
This structure maintains consistency in the workflow throughout the system. More importantly, the authority in command of the bureaucracy hands down the decision-making schedule, which helps establish order and efficiency in a business establishment.
Transactional Relationships
Bureaucratic relationships in an organisation always remain transactional because they help employees from various departments to maintain a healthy balance between professional relationships and their personal lives. Transactional relationships are essentially based on mutual benefit and needs between two individuals.
Both individuals have certain expectations that they want the other to fulfil, during which they typically exchange some service or support. Any human emotions such as love, compatibility or chemistry are generally out of the equation of a transactional relationship.
In a Bureaucratic management system, professionals typically depend on their colleagues or other professionals to accomplish tasks before they can proceed to new ones. For example, if professional ‘X’ has an expectation that professional ‘Y’ can fulfil, ‘Y’ may agree to help ‘X’ on the condition of a barter-based system where each helps the other with a favour.
These relationships entail that professional ‘X’ has to finish the task for ‘Y’ before ‘Y’ can finish the task for ‘X’. This translates to a more transactional than personal nature of the relationship between X and Y, which helps improve the understanding of their responsibilities in an organisation.
Role-based Specialisations
Seasoned and experienced individuals can accomplish only certain responsibilities in a Bureaucratic management system. This means that the Bureaucratic Leadership style official appoints only those individuals who are best suited for the position in the organisation. The employees of any department must be equipped with a comprehensive understanding and expertise in the subject.
Well Defined Responsibilities
Every employee in a Bureaucratic-styled organisational structure is obligated to abide by certain rules and protocols. Bureaucratic leaders generally assign responsibilities to their subordinates along with a framework for performing their daily activities. This ensures that they hold a good understanding of their stature and keeps them in the know-how about their job functions.
Professionalism
A Bureaucratic Leadership style maintains a high level of professionalism with a practice of impartial decision-making. It is because it believes in not favouring any one individual over the other, which is one of the pillars of its organisational status.
Enhance your Leadership abilities, by signing up for our Leadership Skills Course now!
Qualities of Bureaucratic Leadership
A system that functions on a Bureaucratic system of management generally appoints its leader panel only after an extensive examination and evaluation of their attributes, their experience with positions of authority and professionalism. This type of Leadership requires a properly defined skill set to fulfil the job role’s responsibilities.
Here is a list highlighting the qualities required for an individual to be deemed the right fit for a Bureaucratic leader’s post:
Specialisation
Employees are assigned specific roles and duties based on their skills and expertise. This ensures that the right individuals are in the right positions, leading to improved performance through structured repetition.
Hierarchical Structure
Bureaucratic management follows a strict hierarchy with clear arrangements between departments and individuals. Decisions are made centrally and communicated downwards, allowing managers to allocate duties and monitor progress effectively.
Impersonality
The focus is on collective achievement rather than individual accomplishments. This approach prioritises equality, performance, and consistency, ensuring that operations are rational and free from personal biases or emotions.
Division of Labour
Responsibilities and tasks are clearly demarcated among employees, eliminating ambiguity and enhancing efficiency. Each team or individual knows their specific duties, contributing to the organisation's overall objectives.
Procedures, Rules, and Guidelines
A comprehensive set of rules and guidelines directs employee conduct and daily tasks. These regulations provide a framework for handling various issues, ensuring that both minor and major tasks are performed consistently and effectively.
Standardisation and Impartiality
Bureaucratic Leadership ensures fair and impartial treatment of all employees. By managing conduct and behaviour without favouritism, it minimises discrimination and promotes fairness. Employees are subject to the same rules and disciplinary measures, fostering a sense of equality and contentment within the organisation.
Learn to make important decisions by signing up for our Decision-making Skills Training now!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bureaucratic Leadership
Here is a list highlighting the various advantages of Bureaucratic Leadership:
a) Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Clear rules and protocols establish expectations for all positions, ensuring organisational order.
b) Job Security: Employees adhering to guidelines and performing well have strong career growth prospects.
c) Division of Labour: Roles are assigned based on expertise, maximising efficiency and task accuracy.
d) Creativity at Higher Levels: Innovation is encouraged but typically limited to higher authorities, enabling strategic management.
e) Predictability: A structured, result-focused approach minimises errors and ensures consistent outcomes.
f) Learning from Success: Previous achievements guide current strategies, ensuring continued success cost-effectively.
g) Scalability: Bureaucratic systems facilitate growth and expansion, driving upward progress within the industry.
The following are the disadvantages of Bureaucratic Leadership:
a) Rigid Efficiency: Strict responsibilities may hinder employees' productivity and flexibility.
b) Limited Creative Freedom: Subordinates are confined to routine tasks, stifling innovation at lower levels.
c) Resistance to Change: Adaptation to organisational changes is slow due to a rigid, routine-based structure.
d) Stalled Personal Growth: Employees focus on collective goals, often at the expense of individual development.
e) Command Chain Inefficiency: Hierarchical decision-making slows problem-solving and strategy implementation.
f) Lack of Incentives: Absence of rewards for good performance reduces motivation to excel.
g) Growth Hindrance: Bureaucratic systems can stifle efficiency and progress, especially for smaller organisations.

Learn the techniques to effectively handle a team by signing up for our Introduction to Supervising a Team Course now!
Key Examples of Bureaucratic Leadership
Here is a list of important examples that are a great representation of Bureaucratic Leadership:
Winston Churchill
Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a statesman, soldier and writer who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice in the Second World War. After his service in the army, he acquired experience in managing a country in times of war.
Additionally, Winston Churchill followed a goal-oriented approach where his subordinate officials understood the structure and their responsibilities. Moreover, his style of delegating authority faced significant critique, putting him in the middle of controversies. However, his critics soon discovered it was futile to persuade a leader as firm as him, making him one of the greatest leaders of all time.
Sinjo Sogo of the Japanese National Railways
Another great example of a Bureaucratic leader is Sinjo Sogo, the fourth President of the Japanese National Railways. His Leadership style helped the country go through a revolution in its railway networks.
Sogo emphasised modernising specialisations at the workplace. He especially instituted a robust set of regulations and protocols that helped the country accomplish the most revolutionary Engineering masterpiece in the history of innovation.
Steve Easterbrook of McDonald’s
A food establishment as massive and globally spread out as McDonald’s has a foundation in Bureaucratic Leadership style. He instituted a rule that all employees of the business abided by the authority’s orders.
He also made a rule that employees will be involved in negligible decision-making and maximum productivity. These measures have translated and demonstrated the establishment’s consistent performance across its international outlets
Conclusion
We hope that you have now understood the concept of What is Bureaucratic Leadership. An organisation has a higher chance of achieving business success from a Bureaucratic form of management. This Leadership style is pivotal to authority and a hierarchical chain of command, along with a robust set of regulations and protocols to be followed by all employees. Moreover, such a management system ensures maximum levels of efficiency and productivity at the workplace.
Attain the necessary skills to lead any team by signing up for our Leadership Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Following are the 5 big Bureaucratic Leadership Styles:
a) Autocratic: Centralised control, quick decisions
b) Democratic: Collaborative decision-making
c) Laissez-faire: Minimal supervision, self-driven teams
d) Transformational: Inspires innovation and change
e) Transactional: Rewards-based leadership

Structured societies, well defined roles and responsibilities, employment securities make Bureaucratic Leadership strong on discipline. The division of labour based on the level of expertise is effective; a programmatic approach guarantees operability. Regarding Other Benefits, it also has implications for flexibility and the growth.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including the Leadership Skills Training, Design Thinking Course and the Technical Team Leading Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Creative Leadership.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Bureaucratic Leadership, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Leadership Skills Training
Leadership Skills Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


