We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +48 221041849 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Digital Photography is not just about capturing a moment—it’s about transforming the way we see the world, thanks to its innovative blend of artistry and cutting-edge technology. With every click, Digital Photography brings you closer to turning ordinary moments into extraordinary visual narratives that previous generations of cameras failed to capture.
This blog is a detailed snapshot of What is Digital Photography, and the revolution that this field underwent, from film photography of the late 1800s to modern smartphone cameras. Read on and explore how passion and pixels can blend to create lasting memories!
Table of Contents
1) What is Digital Photography?
2) History of Digital Photography
3) Types of Digital Camera
4) Benefits of Digital Photography
5) Digital Photography Examples and Genres
6) Conclusion
What is Digital Photography
Unlike Normal Photography, Digital Photography captures images electronically. Instead of film, it uses an image sensor. This sensor detects and captures light, converting it into an electronic image. The resulting image is then stored as a Digital file.
These files are typically saved on memory cards. Other storage methods include hard drives and cloud services. Once stored, these files can be transferred, viewed, and edited on computers.
Digital Photography offers more than just convenience. Its precision and clarity often surpass traditional film. The ability to adjust settings, like ISO and shutter speed, ensures optimal results. Digital Cameras come equipped with these adjustable features.
There's also the advantage of immediate feedback. After taking a shot, the image can be instantly reviewed. This allows for immediate corrections if needed. Another facet is the resolution. Measured in megapixels, it determines image clarity. Higher megapixels generally mean better image quality. However, other factors also influence this.
From point-and-shoots to DSLRs, the variety of Digital Cameras is vast. They cater to every skill level and budget. Each has its unique features and benefits. In essence, Digital Photography combines technology with artistry, revolutionising how we perceive and document the world.
History of Digital Photography
To understand the revolutionary impact of Digital Photography, it’s worth tracing its history a little. Here's a brief look back on how it all transpired:
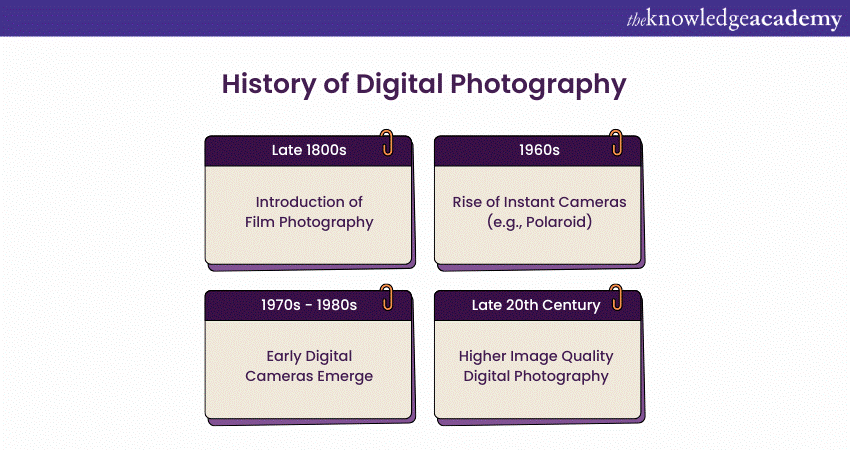
1) Before digital cameras, photography was primarily captured in film back in the late 1800s. Film cameras require a negative image to be developed and printed in a darkroom, which demands time and patience. It takes several minutes or hours, depending on the type of film, the method utilised, and the developer's expertise.
2) Many photographers still find that film shooting creates something unique in an image. Its only downfall is that you must wait until your photos are developed to see how they turn out. So, for novices, anyone testing out a new camera’s settings, and even professional photographers, it can be hard to learn what’s working for you until the moment has passed.
3) Instant cameras such as Polaroid [MP1] resolved this issue when they became popular in the ’60s, allowing users to develop and view their photographs instantly.
4) Early digital cameras started to hit the scene in the '70s and '80s. Because of their exclusivity, they were expensive. As technology advanced, they produced low-resolution photographs.
5) However, with the digital revolution in the late 20th century, the quality of Digital Photography cameras began to surpass that of film and instant cameras. Different types of digital cameras were being made, the technology was better, and so was the final image. Ultimately, digital cameras became affordable and available to the masses.
Master the art of Photography by registering for our Photography Course now!
Types of Digital Camera
Whether it’s eccentric fashion portraits or a sky-diving adventure you want to capture, plenty of digital camera categories are out there to suit your needs. We explore some of them below:
a) Compact Cameras:
These are also referred to as ‘point-and-shoot’ cameras. They are small, portable cameras with built-in lenses and automatic settings. Many casual photographers and travellers opt for a compact camera, as they require little technical knowledge to use and don’t need any additional equipment (like lenses) to lug around.
b) DSLR Cameras:
Digital Single Lens Reflex (DSLR) is the most well-known type of digital camera (and a go-to choice for professional photographers and serious hobbyists). They use a mirror to reflect the image from the lens into an optical viewfinder.
The biggest draw to DSLRs is that they allow for interchangeable lenses, manual controls, and high-quality sensors, which together provide the user with lots of creative control. Their versatility makes them a great camera for lots of purposes—so whether you’re capturing portraits, scenic landscapes, or motion shots, with the right settings and equipment, a DSLR will do the trick. However, for those looking for convenience and portability, Mobile Photography offers an excellent alternative without compromising on quality.
c) Bridge Cameras:
Bridge cameras are a good option if you’re looking for something in between the two. They have a more powerful zoom lens than compact cameras, with some of the manual controls and image quality of DSLRs. They tend to strike a good balance between features and affordability, too.
d) Medium Format Cameras:
These use larger image sensors than those in traditional DSLRs and, as a result, can deliver digital photos of incredible quality – both in terms of detail and colour reproduction. These are the cameras behind many iconic fashion portraits, but you’ll find them in advertising, too.
e) Action Cameras:
Action cameras might be more up your street for sports fanatics or adventurers. Whether you’re excited about hiking, surfing, or capturing sports, there are a whole host of cameras out there to suit your needs.
Action cameras are made with features to help capture fast-paced action and movement. Since they can be taken to ocean floors and icy mountain tops, they’re usually small, compact and more robustly made than other cameras (waterproof and shockproof).
Benefits of Digital Photography
The transition from film to Digital has not only made capturing moments easier but also brought along numerous benefits. Here are the key advantages:
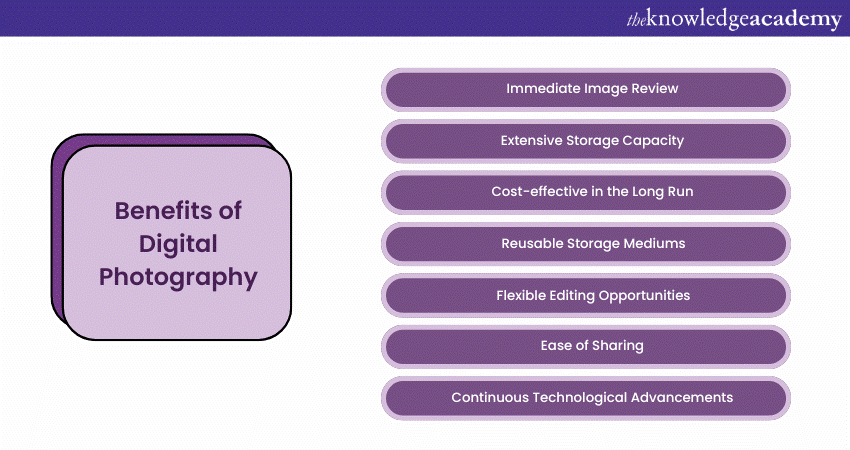
a) Immediate Image Review: One of the joys of Digital Photography is the capacity to instantly view and evaluate your shot. If something isn't right, you can take another.
b) Extensive Storage Capacity: Modern memory cards can store vast numbers of images, allowing Photographers to shoot freely without constantly changing storage mediums.
c) Cost-effective in the Long Run: After the initial investment in equipment, there's no need to keep buying film or paying for its development.
d) Reusable Storage Mediums: Once you've secured your Photographs elsewhere, memory cards can be cleared and reused multiple times, maximising value.
e) Flexible Editing Opportunities: Digital images can be edited using software. Adjustments like cropping, colour enhancement, or applying filters are all possible.
f) Ease of Sharing: One can send to friends, upload them to social media, or create Digital albums effortlessly.
g) Continuous Technological Advancements: As technology improves, Cameras receive updates, and new features become available, ensuring Photographers always have the best tools at their disposal.
Explore your passions with our diverse range of Hobbies & Interests Courses.
Digital Photography Examples and Genres
Digital Photography offers a vast range of styles and genres. Here's a glimpse into some popular categories and their typical subjects:
a) Portraits:Focuses on capturing the essence of a person or group. Examples include selfies, family shots, and professional headshots, often enhanced with creative Photography Captions to add context and personality.
b) Landscape: Emphasises the vastness and beauty of nature. Think serene beaches, majestic mountains, or dense forests.
c) Macro: Highlights small details not visible to the naked eye. Shots of dew on a leaf or patterns on an insect fall here.
d) Wildlife: Captures animals in their natural habitat. Lions on a hunt or birds in mid-flight are classic examples.
e) Sports: Freezes fast-paced action moments. It can range from a basketball dunk to a sprinter crossing the finish line.
f) Street Photography: Documents everyday life on the streets. A bustling market, a lone pedestrian, or kids playing can be subjects.
g) Architectural: Focuses on buildings, structures, and design. From ancient ruins to modern skyscrapers, it showcases man-made wonders.
h) Night Photography: Explores scenes under low light conditions. Star trails, city skylines at dusk, and lit-up monuments are typical examples.
i) Documentary: Tells real-life stories through pictures. Photographers might cover social issues, events, or the daily life of a community.
Master creative editing with our Photoshop course! Learn pro techniques and unlock your design potential. Join today to excel!
Conclusion
Mastering the proper techniques and tools in Digital Photography can turn ordinary moments into extraordinary visual stories. This blog is a detailed exploration on What is Digital Photography including its exciting history and the various genres it offers. Its cutting-edge nature lets you experiment with different visual flavours tailored to everything, ranging from fast-paced adventure photography to high-resolution wedding photography.
Unlock Your filmmaking potential with our Filmmaking Course. Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Mode Should I Use for My Pictures?

To achieve the best print results, the digital camera should be set to the highest megapixel and finest resolution. If you are unsure how to do this, refer to your instruction manual. Remember that the finer the quality setting, the more room each photo requires on your memory card. Most cameras will be configured to save files as .jpg.
Is Photography a Good Career?

Photography is a great career choice if you have a passion for life stories and have a keen eye for detail. In the age of diverse photo and video content (thanks to social media), photography can offer high-income potential and excellent job satisfaction. You will need a formal photography education to start this career path.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Hobbies & Interests Courses, including Photography Course and Filmmaking Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Photography.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Photography, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Photography skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Photography Course
Photography Course
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


