We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +48 221041849 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

2024 brought an exciting twist to GCSE coursework. The grading system not only evaluated performance but also redefined how brilliance was recognised. In this blog, we delved into the intriguing 9-1 structure and the latest GCSE Grades boundaries that shook up the status quo. Whether you were eagerly awaiting your results or simply curious about the changes, you explored a realm where precision met potential.
Ready to decode the secrets behind the numbers and uncover what lay ahead in this new academic frontier? Let’s embark on this journey together!
Table of Contents
1) What were the 9-1 GCSE Grades and their Grade Equivalents?
2) How Were Grade Boundaries Determined?
3) Why Did the Grading System Change?
4) What to Do If Your Results Were Unexpected?
5) How Were GCSEs Graded in Northern Ireland?
6) How Were GCSEs Graded in Wales?
7) Conclusion
What were the 9-1 GCSE Grades and their Grade Equivalents?
The 9-1 grading system for GCSEs in England was introduced to better reflect the revised, more challenging curriculum and to provide greater differentiation among students. Here’s a breakdown:
a) Grade 9: The highest grade awarded for exceptional performance.
b) Grade 8: Very high achievement, just below Grade 9; roughly equivalent to an A*.
c) Grade 7: Strong performance, equivalent to the old A grade.
d) Grade 6: Good performance, equivalent to a high B under the old system.
e) Grade 5: Known as a strong pass; equivalent to a low B or high C.
f) Grade 4: A standard pass, equivalent to the old C grade; the minimum required for many post-16 courses.
g) Grade 3: Roughly equivalent to a D, indicating below the standard pass level.
h) Grade 2: Equivalent to the old E grade, showing a lower level of achievement.
i) Grade 1: The lowest grade, equivalent to the old F and G grades, indicating minimal understanding.
j) U (Ungraded): Indicates that the student did not achieve the minimum required to be awarded a grade.
How Were Grade Boundaries Determined?
Grade boundaries for GCSEs were established through a blend of statistical analysis and expert assessment. These boundaries are not fixed and can vary each year based on overall student performance. Here’s a detailed look at the process:
1)Statistical Predictions
Exam boards used historical data and students' prior performance to forecast the expected distribution of grades. By analysing trends and patterns from previous years, they could estimate the grade boundaries needed to maintain consistency and fairness across different cohorts.
2) Expert Judgment
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) reviewed a selection of exam scripts around critical grade boundaries, such as 4, 5, and 7. They evaluated the quality of responses to determine the level of performance required for each grade. This review process ensured that the grades reflected the actual standards of student work.
3) Adjustments
Grade boundaries were adjusted based on the relative difficulty of the exam compared to previous years. If an exam was notably more challenging or easier, the boundaries were modified to account for these variations. This adjustment process was designed to ensure that students were assessed fairly and that the results accurately reflected their abilities.
Learn about the rating prediction method with our Sentiment Analysis Training - Join now!
Why Did the Grading System Change?
The GCSE Grading system transitioned from letters (A-G) to numbers (9-1) to improve differentiation, especially among top performers, and to reflect a more challenging curriculum.
a) Greater Differentiation
The new scale offers finer distinctions among high-achieving students, providing clearer differentiation.
b) Reflecting a Rigorous Curriculum
The numerical grades better align with the advanced curriculum, ensuring an accurate representation of students' knowledge.
c) Alignment with International Standards
The change brings GCSEs in line with global grading practices, enhancing international comparability.
d) Enhanced Clarity for Employers and Educational Institutions
The system provides clearer insights into student capabilities, aiding better assessment by employers and institutions.
e) Maintaining Relevance
The updated grading system ensures that assessments are relevant in today’s competitive global education landscape.
Learn problem-solving techniques with our Soft Skills Engineering Course– Join today!
What to Do If Your Results Were Unexpected?
Receiving GCSE results that don’t meet your expectations can be disheartening, but there are several proactive steps you can take to address the situation:
1) Talk to Your School or College
Reach out to your school or college for guidance. They can help you understand your options, including the possibility of appealing a grade, resitting exams, or exploring alternative qualifications such as apprenticeships or vocational courses.
2) Consider Resits
If you did not achieve a grade 4 in English or maths, you will need to resit these subjects. Resits can be scheduled for the autumn or the following summer, giving you an opportunity to improve your grades.
3) Appeal the Results
If you believe there has been an error in marking, you can request a review or re-mark of your exam papers through your school. Be aware of the deadlines set by exam boards for submitting appeals.
4) Explore Alternative Pathways
If your grades do not meet the entry requirements for your preferred A-levels or college courses, consider alternative routes such as vocational qualifications, apprenticeships, or other educational pathways that may better align with your goals.
How Are GCSEs Graded in Northern Ireland?
In Northern Ireland, GCSEs were graded using either the 9-1 system or the traditional A-G system, depending on the exam board selected by the school. Here's a comparison of the two grading systems:
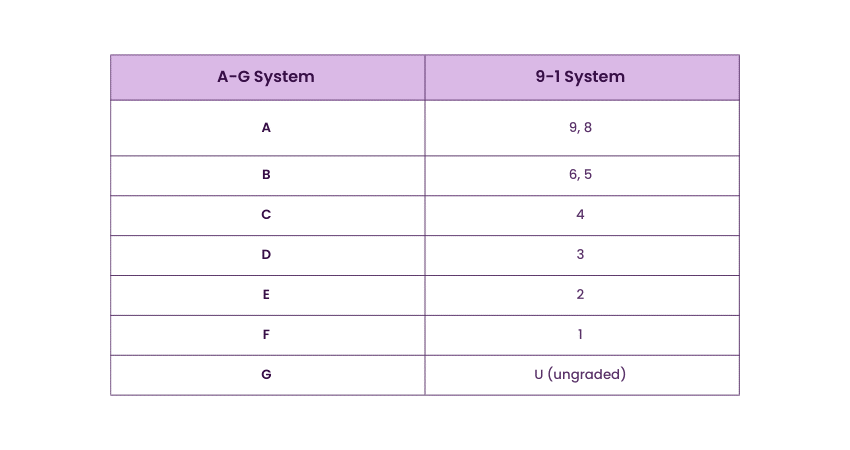
Learn how to achieve goals with our Attention Management Training- Register now!
How Were GCSEs Graded in Wales?
In Wales, GCSE Grading systems varied depending on the exam board chosen by the school. The two systems in use were the traditional A-G grades and the more recent 9-1 grades. Here is a detailed comparison between the two grading systems:
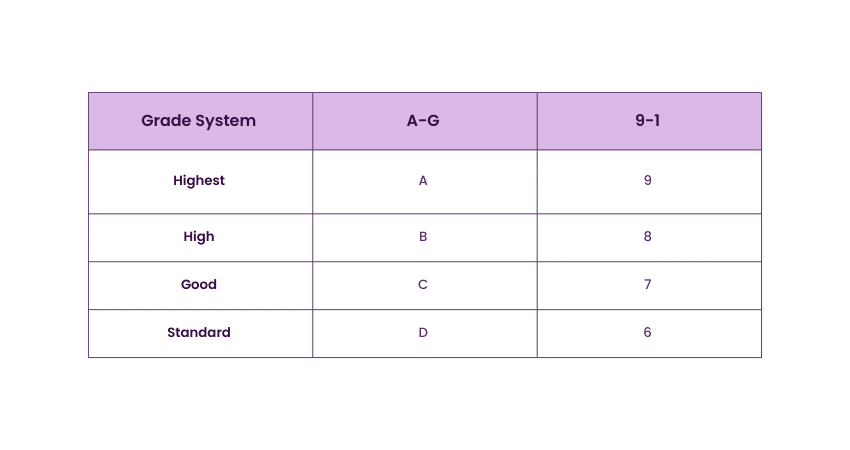
The A-G grading system, where A represents the highest achievement and G the lowest, was used alongside the 9-1 system. In the 9-1 system, a grade of 9 denotes the highest level of performance, with grades descending to 1, which represents the lowest. The mapping indicates that while both systems are designed to reflect student performance, the 9-1 system allows for greater differentiation among higher-achieving students.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the 2024 GCSE results, it’s evident that the new grading system has reshaped our understanding of academic excellence. The 9-1 structure and updated GCSE Grades boundaries provided a more nuanced assessment of student performance, highlighting each learner’s potential. This year’s results set a new benchmark, inspiring students and educators to strive for greater heights. As we move forward, let’s embrace these changes, recognising that every GCSE Grade tells a story of hard work, resilience, and brilliance.
Understand the career development challenges with our Career Development Course – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

GCSE stands for General Certificate of Secondary Education. It is a set of exams taken by students in the UK, typically at the end of compulsory education, around age 15-16, covering various subjects.

GCSE Results Day 2024 was on Thursday, 22 August 2024. Students were able to collect their results from around 8:00 AM at their schools, with specific times varying by institution.

In India, the GCSE equivalent is the Class 10 board exams, such as those administered by the CBSE or ICSE. These exams assess students' knowledge in various subjects at the end of secondary education, similar to GCSEs.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses, including the Career Development Course, Soft Skills Engineering Course, and Attention Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Ethics vs Morals
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Personal Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your career development knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Career Development Course
Career Development Course
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


