We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +48 221041849 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Value management is a vital approach that drives project success and organisational performance. By aligning project objectives with stakeholder expectations and optimising resource allocation, value management maximises value delivery. It enhances Decision-Making, minimises risks, and fosters collaboration among stakeholders.
Embracing the management of value ensures organisations stay competitive, meet stakeholder needs, and achieve long-term success. This blog will elaborate on some of the key pointers that showcase the Importance of Value Management.
Table of Contents
1) A brief introduction to Value Management
2) The importance of Value Management
a) Enhancing project success
b) Optimising resource allocation
c) Improving decision-making
3) Conclusion
A brief introduction to Value Management
Value management is a strategic approach that focuses on maximising value and optimising resources in projects and organisations. It is a systematic process that ensures project objectives align with stakeholder expectations and emphasises the efficient allocation of resources to deliver the best possible outcomes. By incorporating value analysis, Stakeholder involvement, and data-driven decision-making, value management enhances project success, minimises risks, and drives continuous improvement.
Unlock your potential in managing successful projects with our MoV Foundation course - sign up now!
The importance of Value Management
Managing value holds immense importance for businesses across various industries. Let's explore some of the key reasons why it should be an integral part of your strategic Decision-Making Process
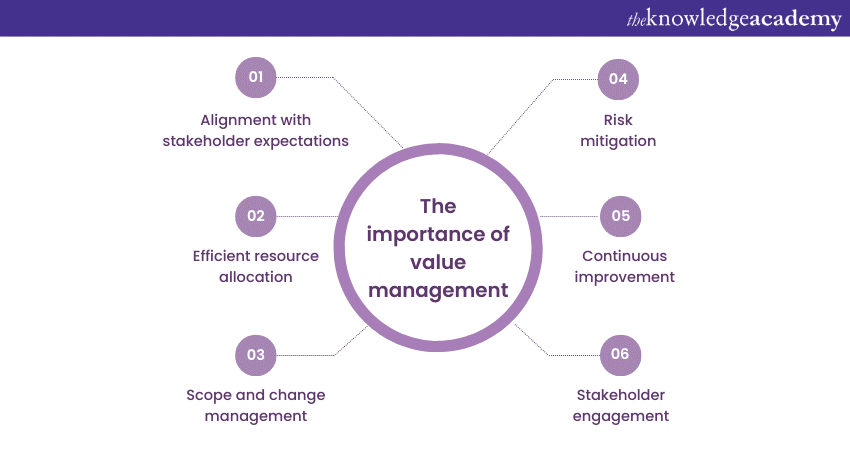
Enhancing project success
Value management plays a crucial role in enhancing project success by ensuring that project objectives align with stakeholder expectations and delivering optimal value throughout the project lifecycle. Here are some key ways in which it contributes to project success:
1) Alignment with stakeholder expectations: It emphasises the importance of understanding stakeholder objectives and expectations. By actively involving stakeholders in the process and seeking their input, organisations can ensure that project goals and deliverables are in line with their needs. This alignment minimises the risk of miscommunication, enhances stakeholder satisfaction, and increases the likelihood of project success.
2) Efficient resource allocation: It helps optimise resource allocation by identifying and prioritising value solutions. Organisations can make the most efficient use of their available resources by focusing resources on activities that create the most value and eliminating unnecessary costs. This improves cost-effectiveness, minimises wastage, and increases the overall efficiency of Project Execution.
3) Scope and change management: Scope creep, which refers to uncontrolled changes or additions to a project's scope, is a common challenge that can negatively impact project success. Value management provides a systematic approach to managing scope and changes effectively.
By continuously evaluating and prioritising value solutions, organisations can ensure that any proposed changes align with the project's objectives and deliver measurable value. This reduces the risk of scope creep, maintains project focus, and enhances the chances of meeting project goals within the defined constraints.
4) Risk mitigation: It incorporates risk analysis as a key tool in decision-making. Organisations can proactively identify and mitigate risks by considering potential risks and their impact on value before they escalate into larger issues. This helps avoid costly delays, rework, or failures, leading to smoother project execution and ultimately enhancing project success.
5) Continuous improvement: It is not limited to only the planning and execution phases of a project. It also emphasises continuous improvement throughout the project lifecycle. By regularly evaluating and monitoring value solutions, organisations can identify improvement areas and promptly implement corrective actions. This iterative approach enables organisations to adapt to changing circumstances, optimise project performance, and maximise the value delivered.
6) Stakeholder engagement: Effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for project success. Value management encourages active involvement and collaboration with stakeholders. By engaging stakeholders throughout the project, organisations can gain valuable insights, manage expectations, and foster a sense of ownership and commitment. This collaborative approach enhances communication, minimises conflicts, and improves overall project outcomes.
Take your project management skills to the next level with our combined MoV Foundation & Practitioner course - Sign up now and become a certified expert!
Optimising resource allocation
Resource optimisation is a critical aspect of value management and is a key component of the Principles of Value Management, playing a vital role in the success of projects and organisations. By effectively allocating resources, organisations can maximise their efficiency, productivity, and overall value delivery. Here's how managing value contributes to optimising resource allocation:
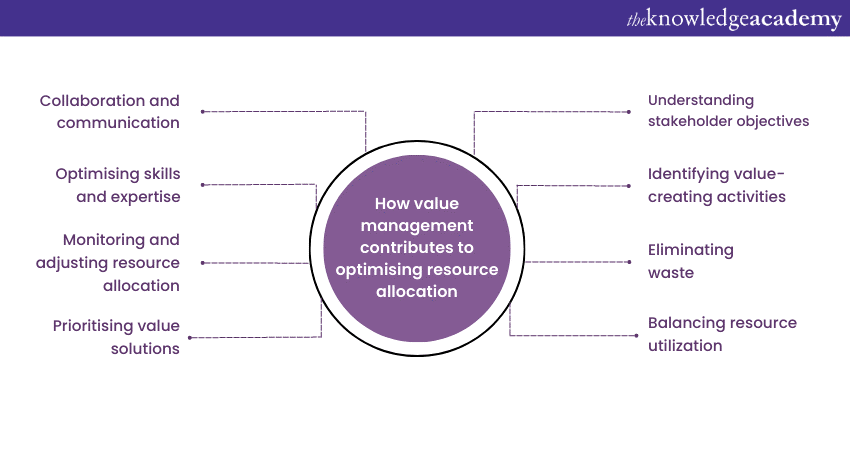
1) Understanding stakeholder objectives: Value management starts with a deep understanding of stakeholder objectives. By identifying the key stakeholders and their priorities, organisations can align their resource allocation strategies with the desired outcomes. This ensures that resources are allocated to activities that create the most value and directly contribute to meeting stakeholder expectations.
2) Identifying value-creating activities: It focuses on identifying and prioritising value-creating activities. By analysing the project requirements and stakeholder needs, organisations can determine which activities impact value delivery most. Allocating resources to these critical activities ensures that the most valuable outcomes are achieved within the given constraints.
3) Eliminating waste: Managing value helps identify and eliminate wasteful practices or redundant activities that do not contribute significantly to value creation. By streamlining processes and optimising resource allocation, organisations can minimise unnecessary costs, reduce time wastage, and increase operational efficiency. This ensures that resources are utilised optimally, and their maximum value is derived.
4) Balancing resource utilisation: It enables organisations to strike a balance in resource utilisation. It ensures that resources are allocated proportionally across different project activities based on their importance and value contribution. This prevents overutilisation of resources in certain areas while neglecting others, leading to a more balanced and effective allocation of resources.
5) Prioritising value solutions: It involves evaluating and prioritising different value solutions. By considering the value criteria and trade-offs associated with each solution, organisations can allocate resources to those solutions that offer the highest value within the given constraints. This enables effective resource allocation, as resources are directed towards initiatives that deliver the greatest value and impact.
6) Monitoring and adjusting resource allocation: Value management is an iterative process that emphasises continuous monitoring and adjustment. By regularly assessing resource allocation and evaluating its impact on value creation, organisations can make informed decisions to optimise their resource allocation strategies. This ensures that resources are constantly aligned with evolving project needs, stakeholder expectations, and changing market dynamics.
7) Optimising skills and expertise: Value management takes into account the skills and expertise required for different project activities. By making sure to match the right resources with the right tasks, organisations can optimise the utilisation of skills and ensure that resources are allocated to activities that align with their capabilities. This improves efficiency, reduces rework, and enhances overall project performance.
8) Collaboration and communication: It encourages collaboration and Effective Communication among team members and stakeholders. By fostering a collaborative environment, organisations can leverage the collective knowledge and expertise of their resources. This enhances coordination, minimises duplication of efforts, and maximises the productivity of resources.
Explore the Benefits of MoV® in our blog and discover how it can help improve the value management in your projects!
Improving decision-making
Effective decision-making is a cornerstone of successful projects and organisations. Value management plays a crucial role in improving decision-making processes by providing a structured framework that considers value, stakeholders, and various factors influencing project outcomes. Here's how it contributes to enhancing decision-making:
1) Systematic approach: Value management provides a systematic approach to decision-making. It makes sure that any decision made by the organisation is made based on a clear understanding of stakeholder objectives, value criteria, and project requirements. This structured approach eliminates guesswork and biases, enabling decision-makers to evaluate options objectively and make informed choices.
2) Value analysis: It incorporates value analysis as a fundamental element of decision-making. It involves assessing the value of different options against predefined value criteria. By considering factors such as cost, quality, time, functionality, and stakeholder preferences, organisations can evaluate the potential value that each option offers. This analysis helps in comparing alternatives and selecting the option that maximises value.
3) Risk assessment: It integrates risk assessment into the decision-making process. By considering potential risks and their impact on value, organisations can make risk-informed decisions. This involves evaluating the likelihood and consequences of risks associated with each option and factoring them into the decision-making process. By addressing risks proactively, decision-makers can mitigate potential negative impacts on value and project success.
4) Trade-off analysis: It facilitates trade-off analysis during decision-making. It recognises that project constraints may require making trade-offs between different value criteria. For instance, there may be a trade-off between cost and quality or between time and functionality. Value management enables decision-makers to weigh these trade-offs and make decisions that strike the right balance based on project objectives and stakeholder priorities.
This blog offers a step-by-step guide on How to add your MoV® Certification to your CV and LinkedIn Profile, enhancing your career prospects!
5) Stakeholder involvement: Managing value encourages stakeholder involvement in decision-making. By engaging stakeholders throughout the process, organisations can gather diverse perspectives, insights, and expertise. This collaborative approach ensures that decisions take into account the needs, preferences, and concerns of all relevant stakeholders. Involving stakeholders fosters buy-in, improves decision acceptance, and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
6) Data-driven decision-making: Value management promotes data-driven decision-making. It emphasises the collection and analysis of relevant Data to support decision-making processes. By using data, organisations can objectively evaluate options, identify trends, and make evidence-based decisions. Data-driven decision-making reduces reliance on subjective opinions and improves the accuracy and reliability of decisions.
7) Scenario analysis: It incorporates scenario analysis into decision-making. It involves considering different possible scenarios and their potential impact on value. By exploring various scenarios, decision-makers can anticipate potential outcomes, risks, and opportunities associated with each option. This helps in making decisions that are robust, adaptable, and future-proof.
8) Alignment with strategic objectives: It ensures that decisions align with strategic objectives. It considers the broader context of the project or organisation and evaluates how each decision contributes to achieving these objectives. This alignment ensures that decisions are in line with the long-term vision, mission, and values of the organisation, providing clarity and direction in decision-making processes.

Conclusion
All in all, value management is a powerful approach that enhances project success, optimises resource allocation, and improves decision-making processes. Organisations can achieve efficient outcomes and maximise project value by aligning with stakeholder objectives, prioritising value, and involving stakeholders.
With its systematic and data-driven approach, value management drives success, reduces risks, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Embracing the Importance of Value Management provides organisations with a competitive edge and ensures long-term success in delivering optimal results.
Accelerate your career in project management? Register for our comprehensive MoV Training courses today and gain the skills to excel!
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 MoV® Foundation & Practitioner
MoV® Foundation & Practitioner
Tue 27th May 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


