We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today’s digital world, we cannot fail to look at the importance of Information Security. Information Security is the practice of safeguarding data from unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. The usage of technology in business and personal lives is getting higher, which has led to an increase in the need for us to be aware of the principles of Information Security, its best practices and its measures. It is all because of protecting confidential data from theft or manipulation.
If you are curious to know What is Information Security in detail, read this blog. In this blog, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of Information Security and its vital role in protecting sensitive data in today's digital age.
Table of contents
1) Defining Information Security
2) Principals of Information Security
3) Types of Information Security
4) Difference between Cybersecurity and Information Security
5) Policies of Information Security
6) Measure of Information Security
7) What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
8) Conclusion
Defining Information Security
Information Security, often known as InfoSec, is a comprehensive discipline focused on safeguarding an organisation's data, information systems, and technology infrastructure from unauthorised access, disclosure, disruption, alteration, or destruction. The primary goal of Information Security is to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, ensuring that it remains secure and reliable. Information Security is considered the base whose objectives are to goal create Security tools and policies and ensure the protection of confidential data such as financial details, cognitive data and more.

Principals of Information Security
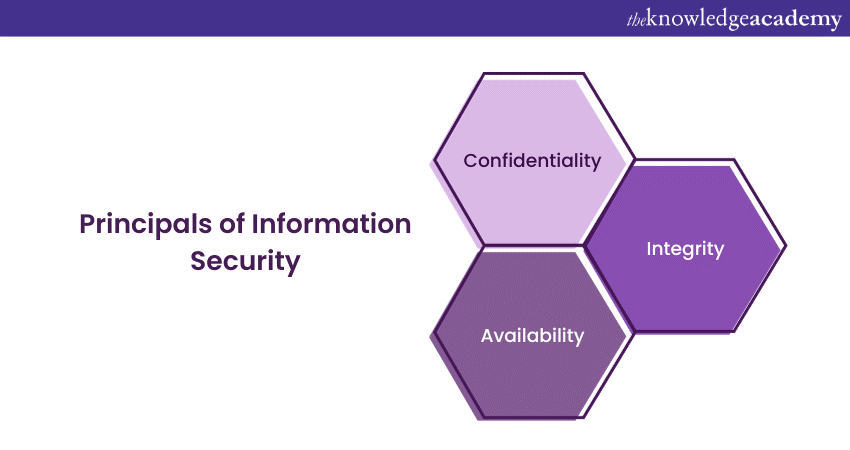
Information Security is mainly based on three building blocks. Confidentiality, integrity and availability which is often termed the CIA triad. Let's understand what the CIA triad is and how it is helpful in protecting data.
1) Confidentiality: Confidentiality ensures that information is only accessible to those who have the proper authorisation. It involves restricting access to sensitive data, such as personal information, trade secrets, and financial data, to authorised personnel or systems.
2) Integrity: Integrity focuses on the accuracy and reliability of data. It ensures that data remains unaltered and reliable during its entire lifecycle. Techniques such as data validation, checksums, and digital signatures help maintain data integrity.
3) Availability: Availability makes sure that information and resources are accessible when needed. This principle is about minimising downtime, ensuring system resilience, and maintaining continuity of operations. It includes measures like redundancy, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery planning.
Types of Information Security
Information security includes various types or aspects of security measures designed to protect information and data. Here are some common types of Information Security.
1) Application Security: Application security involves securing software and applications to prevent vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers. It includes secure coding practices, application firewalls, and regular security testing.
2) Infrastructure Security: Infrastructure security involves safeguarding an organisation's physical and virtual assets, including servers, networks, and data centres. This type of Security is essential to protect the foundational components that support the IT environment.
3) Cloud Security: With the growing adoption of cloud computing, cloud security has become crucial. It involves securing data and applications hosted in cloud environments through measures like encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and security assessments.
4) Cryptography: Cryptography is the process of encoding information to protect its confidentiality and integrity. It's used to encrypt data in transit and at rest, as well as to authenticate users and devices.
5) Network Security: This type of Security focuses on protecting an organisation's data during transmission over networks, including the Internet and internal networks. There are some measures which include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs).
6) Data Security: Data Security is all about protecting the integrity and confidentiality of data at rest. Encryption, access controls, data classification, and data masking are some of the techniques used to safeguard data.
7) Endpoint Security: Endpoint security focuses on protecting individual devices (endpoints), such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. Antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, and mobile device management (MDM) are common tools used for endpoint security.
Secure your future with our Information Systems Security Management Training. Join us and learn to protect vital information in the digital age!
Difference between cybersecurity and Information Security
Cybersecurity and Information Security are closely related but have distinct focuses within the broader field of safeguarding an organisation's information assets. Here are the key differences between the two.
|
Cyber Security |
Information Security |
|
Cybersecurity primarily deals with protecting an organisation's digital assets, particularly in the context of the Internet and cyberspace. |
Information Security has a broader scope encompassing the protection of all forms of information, regardless of its format, whether it's digital or printed. |
|
Cybersecurity is more narrowly focused on safeguarding against cyber threats, which include a wide range of digital threats such as malware and hacking. |
Information Security addresses a wide variety of threats, including not only digital threats but also physical threats. |
|
It specifically addresses the Security of networks, servers, endpoints (devices), and the protocols and technologies that underpin digital communication. |
Information Security takes a holistic approach that includes not only technology but also policies, processes, physical Security, access control, and personnel training. |
|
Professionals in the field of cybersecurity often have titles like "Cybersecurity Analyst," "Ethical Hacker," or "Security Engineer." |
Professionals in Information Security may have titles like "Information Security Manager," "Data Privacy Officer," or "Security Compliance Analyst." |
Policies of Information Security
An Information Security policy is a critical document that outlines an organisation's approach to Information Security. It serves as a foundational framework for defining the rules, responsibilities, and procedures related to safeguarding an organisation's data, information systems, and technology resources. The policy's primary goal is to make sure the confidentiality, availability and integrity of information assets and to establish a security-conscious culture within the organisation. Here are the key elements typically found in an Information Security policy.
1) Purpose and scope: Clearly define the purpose of the policy and its scope, indicating the boundaries of the policy's application. It should specify which information and systems are covered.
2) Policy statement: Present a clear and concise statement of the organisation's commitment to Information Security and the importance of safeguarding information assets.
3) Roles and responsibilities: Outline the key responsibilities of individuals and teams involved in Information Security, including top management, IT staff, and end-users.
4) Information classification: Define a classification scheme for categorising information based on its sensitivity and explain how different classifications should be handled and protected.
5) Access control: Detail access control mechanisms, including user authentication, authorisation, and the principle of least privilege.
6) Data encryption: Specify when and how data encryption should be used to safeguard sensitive information, both in transit and at rest.
7) Incident response: Describe procedures for detecting, reporting, and responding to security incidents and breaches.
8) Password management: Set password policies and guidelines, including password complexity requirements, expiration, and best practices.
9) Physical Security: Address physical security measures such as access control, surveillance, and visitor policies for securing facilities and hardware.
10) Network Security: Define network security measures, including the usage of firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and secure configurations.
Elevate your cybersecurity career with CISSP Training. Join now to become a certified expert in information security!
Measures of Information Security
Information security measures are the specific actions and safeguards put in place to protect an organisation's information assets from unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. These measures are essential for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Here are some common Information Security measures.
1) Access control: This includes implementing access control policies and technologies to restrict access to information systems, data, and resources to authorised individuals or systems. This includes user authentication, authorisation, and the principle of least privilege.
2) Encryption: Use encryption techniques to protect data both in transit and at rest. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
3) Firewalls: Deploy firewalls to monitor and filter network traffic, allowing or denying access based on predefined security rules. This helps prevent unauthorised access and the spread of malware.
4) Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Employ IDPS for detecting and responding to suspicious or malicious activities on the network. Intrusion detection systems identify potential threats, while intrusion prevention systems take action to block or mitigate those threats.
5) Anti-malware software: Use anti-virus and anti-malware software for identifying and removing malicious software, such as viruses, trojans, and spyware, which can compromise the Security of systems and data.
6) Patch management: Keep all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date and updates to address known vulnerabilities.
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection and privacy regulation that was established by the European Union (EU) in May 2018. GDPR replaced the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC and is designed to harmonise and strengthen data protection laws across the EU member states. It has a significant impact on how organisations handle personal data and the privacy rights of individuals.
Conclusion
This is all about What is Information Security. Information Security is the fastest growing technology that offers complete protection to confidential information and data and makes Internet networks well grounded. Information Security has the basic key factors, which include availability, accountability, integrity, confidentiality and non-repudiation.
Lead the charge in cybersecurity! Check out our Chief Information Security Officer Training to become a guardian of digital assets and data security!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISSP Certification
CISSP Certification
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


