We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
To connect our devices to the internet, a crucial element is the IP address, serving as a distinct identifier for each device. However, there are two options to consider: IPv4 and IPv6. This blog will shed light on the Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6 and help you make an informed decision on which one is best suited for your system.
IPv6 addresses the limitations of IPv4, primarily addressing the exhaustion of addresses, and introduces enhancements in terms of address space, security, & more. Read more to know more about the Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6!
Table of Contents
1) What is IPv4?
a) Address format of IPv4
2) What is IPv6?
a) Address format of IPv6
3) IPv4 vs IPv6
4) Conclusion
What is IPv4?
IPv4, or Internet Protocol version 4, is an older version of the Internet Protocol that serves as the foundation for how data is transmitted over networks, including the internet. In simple terms, IPv4 is a set of rules that enables communication between devices by assigning unique numerical labels, known as IP addresses, to each device connected to a network.
While IPv4 has been a cornerstone of internet communication, its limitation in available unique addresses has become apparent due to the ever-growing number of internet-connected devices. As a result, the technology industry is gradually transitioning to IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), which uses a 128-bit addressing format to accommodate a significantly larger pool of unique addresses.
Address format of IPv4
IPv4 has been the fundamental backbone of the internet since its early days. The address format comprises four numbers separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Each segment in an IPv4 address ranges from 0 to 255, allowing for roughly 4.3 billion unique addresses.
What is IPv6?
IPv6 is the latest iteration of the Internet Protocol devised by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It identifies and localises endpoint systems within a computer network, directing online traffic. This is aimed at mitigating the issue of IPv4 address exhaustion resulting from prolonged global internet usage.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) operates as a network layer protocol facilitating communication across the network. Each internet-connected device possesses a unique IP address, enabling its identification and location. In the 1990s digital revolution, it became evident that the IP addresses employed by Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) to link devices would fall short of meeting escalating demand.
Improve your networking skills with our Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks Course - visit the link to join!
Address format of IPv6
IPv6, the successor to IPv4, was introduced to address the looming issue of IPv4 address exhaustion. IPv6 features a distinct address format, comprising eight groups of hexadecimal digits separated by colons. An example of this format is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. With many possible addresses, IPv6 aims to future-proof the internet.
IPv4 vs IPv6
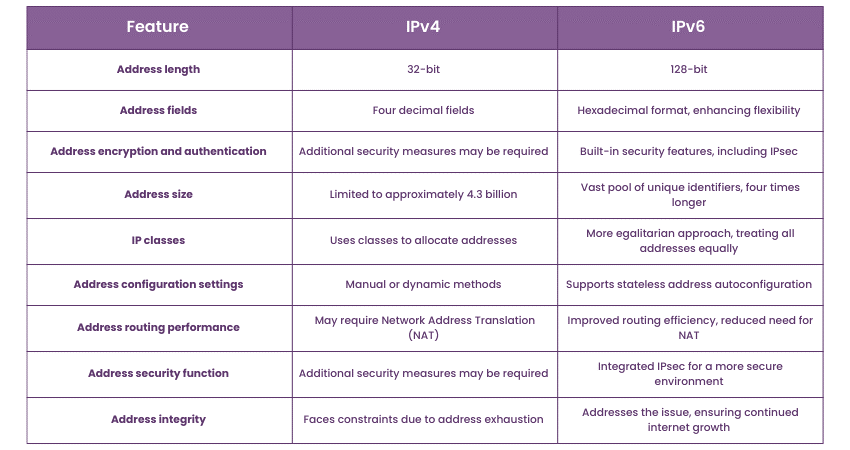
The following provides the Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6:
Address length
The address length is one of the most notable distinctions between IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address, limiting the available addresses to around 4.3 billion. In contrast, IPv6 boasts a 128-bit address, opening an astronomical number of unique combinations.
Address fields
IPv4 has a more straightforward address structure with four decimal fields, while IPv6's hexadecimal format enhances flexibility and allows for a more extensive range of unique addresses.
Address encryption and authentication
IPv6 incorporates built-in security features, including IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), as a standard. IPv4, on the other hand, often requires additional security measures.
Address size
The size of IPv6 addresses, four times longer than IPv4 addresses, allows for a more extensive pool of unique identifiers. This expansion supports the growing number of devices connected to the internet.
IP classes
IPv4 uses classes to allocate addresses, while IPv6 adopts a more egalitarian approach, treating all addresses equally. This simplification enhances address management and allocation.
Address configuration settings
IPv6 supports stateless address autoconfiguration, streamlining the assigning of addresses to devices. IPv4 typically relies on manual or dynamic methods.
Address routing performance
IPv6 benefits from improved routing efficiency, as its larger address space reduces the need for Network Address Translation (NAT). This enhances end-to-end connectivity and simplifies network configuration.
Master the basics of networking concepts by signing up for our Cisco Certified Network Professional Boot Camp Week 1 Course now!
Address security function
IPv6 prioritises security by integrating IPsec, offering a more secure communication environment. IPv4 often requires additional security measures to achieve comparable levels of protection.
Address integrity
IPv6 addresses the issue of address exhaustion, ensuring the continued growth of the internet without the constraints faced by IPv4. The integrity of the IPv6 address space allows for sustained innovation and expansion.
Explore the fundamentals of IPv6 with IPv6 Basics Course. Join today!
Conclusion
We have explored the essential role of an IP address within a system. Subsequently, we have delved into a comprehensive analysis of the distinctions between two types of IP addresses, guiding the selection process for your network device. We hope you have now understood the Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6!
Explore our expert-led Cisco Training courses for advanced networking skills. Sign up now!
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 IPv6 Basics
IPv6 Basics
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 13th Mar 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


