We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Effective risk management is crucial when it comes to operating a successful business. Success entirely depends on how well you manage risks and threats in your business. Learning the various Types of Risk Management can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your management strategies.
According to Statista, cyber incidents were the biggest threats to global businesses. Implementing proper management strategies is vital to overcome such issues. In this blog, you will learn what risk management is, it's different types and its importance respectively. Continue reading below to find out more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Risk Management?
a) Purpose of Risk Management
2) Importance of risk management
3) What are the various Types of Risk Management?
a) Financial risk management
b) Operational risk management
c) Strategic risk management
d) Compliance risk management
e) Reputational risk management
4) Conclusion
What is Risk Management?
Risk management involves the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and controlling potential risks that may impact an organisation's ability to achieve its objectives and goals. It involves identifying potential risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and implementing measures to minimise or eliminate them.
Purpose of Risk Management
By effectively managing risks, businesses can enhance their decision-making processes, protect their assets, and create a solid foundation for sustainable growth. Below are the purposes of Risk Management:
a) Risk avoidance: Eliminating or avoiding activities with potential risks to minimise harm or losses. This is useful when risks outweigh rewards. Risk avoidance involves taking proactive measures to steer clear of high-risk situations.
b) Risk reduction: Implementing appropriate measures to mitigate potential risks, such as Identifying risks, assessing severity, and implementing preventive actions. Additionally, enhanced safety protocols, improved processes, and implementing redundancy systems are performed to minimise the impact of risks.
c) Risk transfer: It is shifting the financial burden of risks to another party through insurance or contracts. Sharing responsibility for potential losses and liabilities and transferring risks to insurers or other entities to mitigate the financial impact.
d) Risk retention: Accepting and managing risks internally. Retaining a certain level of risk and develop strategies to handle them effectively. Using reserves, contingency plans, and internal expertise to manage and mitigate potential risks.
Understanding risk avoidance, reduction, transfer, and retention enables businesses to mitigate risks and enhance overall business strategy proactively. And taking necessary actions based on the nature and magnitude of risks is done to ensure long-term success and resilience.

Importance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is vital for organisations across all industries. Here are the key reasons why it holds immense significance:

Protection against financial loss
By identifying and managing risks, businesses can avoid costly financial setbacks caused by unforeseen events. Proper risk management helps in mitigating the impact of potential threats, ensuring financial stability and sustainability.
Enhanced decision making
Risk management provides organisations with valuable insights into potential risks associated with different courses of action. This information empowers decision-makers to make informed choices that align with the organisation's objectives and risk appetite.
Improved business resilience
A robust risk management framework equips organisations to navigate through crises and unexpected challenges. By having a comprehensive understanding of potential risks, businesses can develop strategies to proactively respond and recover from disruptions
Stakeholder confidence
Effective risk management demonstrates a company's commitment to responsible business practices. This, in turn, fosters trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and partners, leading to stronger relationships and long-term success.
Opportunity identification
Risk management goes beyond risk avoidance. It aids in opportunity identification by assessing risks, allowing businesses to take calculated risks for competitive advantage. This proactive approach fosters innovation, market expansion, and staying ahead of the competition.
Risk management is of utmost importance in today's dynamic business landscape. By prioritising risk management, businesses can navigate uncertainties effectively, ensure long-term success, and thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Unlock your potential in risk management with our Management Of Risk (MoR®) Foundation training and gain the skills to navigate challenges and seize opportunities. Sign up now!
What are the various Types of Risk Management?
Risk management encompasses various categories of risks that organisations encounter. Here are the key Types of risk management:
1) Financial Risk Management
Financial risk management involves identifying and mitigating financial transactions and investment risks. This type of risk management aims to safeguard the organisation's financial assets and maintain stability in the face of market fluctuations and uncertainties.
Definition: Financial risk management is the process of assessing and controlling risks related to financial activities, such as market risk and credit risk etc.
Examples:
1) Credit risk: It involves the risk of financial loss arising from the failure of a borrower to meet their obligations. This includes the potential default on loans, unpaid invoices, or non-payment by customers.
2) Market risk: The potential for financial loss due to fluctuations in stock prices, interest rates, or foreign exchange rates. Market risk encompasses risks associated with investments, like interest rate risk, equity risk and currency risk.
3) Liquidity risk: It involves the risk of not being able to meet short-term financial obligations. It involves challenges in accessing sufficient cash or liquid assets to cover immediate financial needs, potentially leading to financial distress.
4) Operational risk: It involves the risk of loss resulting from insufficient internal processes, systems, or human errors. Operational risks include fraud, technology failures, supply chain disruptions, or legal and regulatory compliance issues.
2) Operational Risk Management
Operational risk management focuses on identifying and mitigating risks associated with an organisation's operational processes, procedures, and systems. It aims to minimise disruptions, errors, and inefficiencies in day-to-day operations, ensuring smooth business functioning.
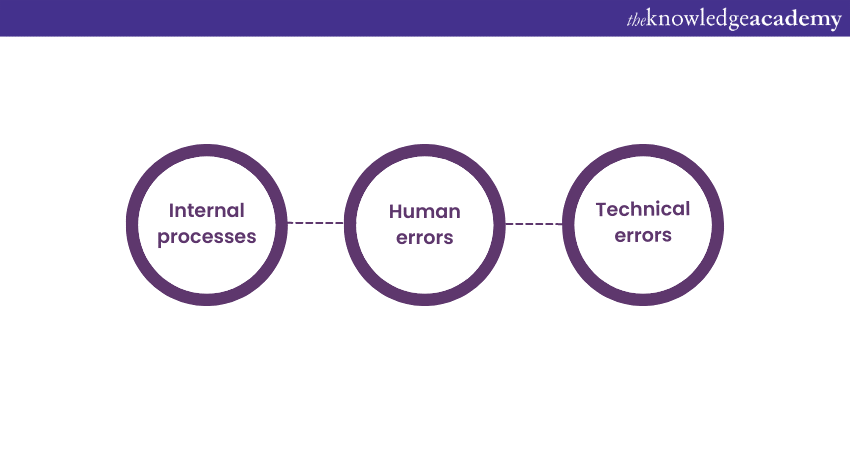
Definition: Operational risk management involves detecting, assessing, and mitigating organisational risks. These risks could arise from internal processes, people, and systems that could potentially lead to financial loss or reputational damage.
Examples:
a) Process risk: Risks associated with inadequate or flawed processes, which can lead to errors, delays, or inefficiencies.
b) People risk: Risks associated with human actions or behaviour, such as employee errors, misconduct, or insufficient training.
c) Systems risk: Risks related to technology systems, including IT failures, cybersecurity threats, or data breaches.
d) Supply chain risk: Risks arising from dependencies on suppliers, including disruptions in the supply chain, quality issues, or geopolitical factors.
3) Strategic Risk Management
Strategic risk management focuses on identifying and addressing risks that may impact an organisation's long-term strategic objectives. It involves evaluating risks associated with business strategies, market dynamics, competitive landscape, and emerging trends.
Definition: Strategic risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could hinder the achievement of strategic goals and objectives.
Examples:
a) Market risk: Risks associated with changes in market conditions, customer preferences, or competitive dynamics that could affect the organisation's market share or profitability.
b) Technological risk: Risks related to the adoption, implementation, or reliance on new technologies, including obsolescence, security vulnerabilities, or disruptive innovations.
c) Reputation risk: Risks associated with damage to the organisation's reputation due to negative publicity, customer dissatisfaction, or ethical misconduct.
d) Strategic decision risk: Risks arising from strategic decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions, market entry, diversification, or product development, may not yield the expected results.
4) Compliance Risk Management
Compliance risk management focuses on identifying and addressing risks associated with non-compliance with laws, regulations, industry standards, and internal policies. It aims to ensure that the organisation operates within legal and ethical boundaries.
Definition: Compliance risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating internal risks and external risks.
Examples:
a) Regulatory risk: Risks associated with non-compliance with regulatory requirements, such as data protection regulations, financial reporting standards, or environmental regulations.
b) Legal risk: Risks related to legal actions or disputes, including lawsuits, contractual breaches, intellectual property infringements, or violations of antitrust laws.
c) Ethical risk: Risks associated with unethical behaviour or actions that may damage the organisation's reputation or lead to legal repercussions.
5) Reputational Risk Management
Reputational risk management focuses on preserving and enhancing the organisation's reputation. It involves identifying potential risks to the organisation's image and implementing strategies to maintain a positive public perception.
Definition: Reputational risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could damage the organisation's reputation, brand value, or public perception.
Examples:
a) Public relations risk: Risks associated with negative media coverage, social media backlash, or public scrutiny of the organisation's actions, products, or services.
b) Customer perception risk: Risks arising from poor customer experiences, product failures, or unethical business practices that could result in losing customer trust and loyalty.
c) Social responsibility risk: Risks associated with the organisation's social and environmental practices, including issues related to sustainability, corporate social responsibility, or ethical supply chain management.
Overall, they help address specific categories of risks that organisations face. By understanding and effectively managing these risks, businesses can protect their financial stability, optimise operations, make informed strategic decisions, comply with regulations, and maintain a positive reputation in the market.
Supercharge your risk management skills with our MoR® 4 Practitioner Risk Management Certification and learn how to mitigate risks effectively and protect your business.
Conclusion
After reading this blog, we hope you understand the Types of Risk Management in detail, including their significance and importance. Embracing various risk management approaches equips organisations with the tools to seize opportunities, innovate, and navigate the ever-changing business landscape.
Sign up for our courses on MoR® Management of Risk courses to gain the essential skills to identify, assess, and manage risks confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP
Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP
Thu 27th Feb 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 24th Jul 2025
Thu 23rd Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


