We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you a tech enthusiast who is fascinated by the power and potential of Quantum Computing? Or maybe you are a researcher or a developer who wants to explore the applications and challenges of this emerging field. Perhaps you are curious how Quantum Computing can revolutionise domains such as cryptography, artificial intelligence, and physics. Then, this blog is for you. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantum Computing extend beyond all the previously mentioned aspects.
Want to know more about them? Keep Reading. This blog will provide an overview of the various Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantum Computing, including speed, scalability, security, complexity, and cost, along with some helpful tips.
Table of Contents
1) What is Quantum Computing?
2) Importance of Quantum Computing
3) Advantages of Quantum Computing
4) Disadvantages of Quantum Computing
5) Conclusion
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum Computing utilises the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in ways classical computers cannot. Unlike classical bits, quantum bits or qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling parallel computation. This enable Quantum Computers to solve complex problems exponentially faster, from simulating molecular interactions for drug discovery to optimising logistics.
Quantum Computing holds the potential to revolutionise industries by tackling challenges beyond the reach of classical computing. As we unravel its mysteries, the transformative impact of Quantum Computing on technology and innovation becomes increasingly apparent.
Importance of Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing is important because it has the power to change almost everything in our daily lives. Quantum Computing offers unprecedented computational power, enabling us to solve complex problems that are presently beyond the capabilities of classical computers. This includes simulating molecular interactions for drug discovery, optimising supply chains, designing new materials with specific properties, and enhancing cybersecurity through advanced encryption methods.
Furthermore, Quantum Computing has the potential to accelerate scientific research and innovation across various disciplines. It can facilitate breakthroughs in climate modelling, renewable energy optimisation, and artificial intelligence. By providing faster and more accurate simulations, Quantum Computing can help scientists better understand the fundamental laws of nature and develop innovative solutions to global challenges.
Moreover, the impact of Quantum Computing extends beyond scientific research and technological innovation. It has implications for economic competitiveness, national security, and societal well-being. Countries and organisations investing in Quantum Computing research and development are positioning themselves at the forefront of the next technological revolution, gaining a competitive advantage in the global economy.
Advantages of Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing offers many advantages that promise to revolutionise various industries and domains. Below are the key advantages of Quantum Computing elaborated:
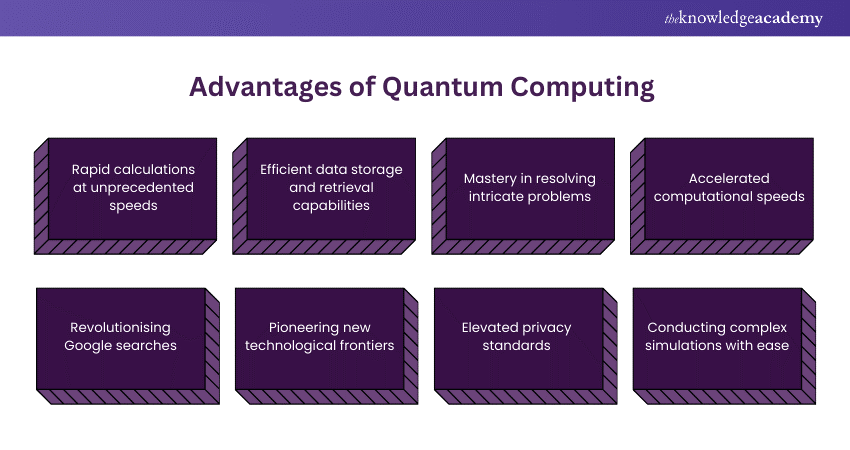
1) Rapid calculations at unprecedented speeds
Quantum Computers can perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. They harness the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in parallel, allowing for rapid execution of complex algorithms. This capability enables Quantum Computers to tackle problems currently infeasible for classical computers due to their computational limitations.
2) Efficient data storage and retrieval capabilities
Quantum Computing offers efficient data storage and retrieval capabilities through quantum memory systems. Quantum bits, or qubits, can store and manipulate vast amounts of data in quantum states, allowing for high-density data storage and faster access times than classical storage systems. This enables Quantum Computers to handle large datasets more effectively, facilitating data-intensive tasks such as machine learning and data analysis.
3) Mastery in resolving intricate problems
Quantum Computing solves intricate problems involving complex mathematical calculations, optimisation, and simulation. Quantum algorithms utilises the unique properties of quantum mechanics to find optimal solutions to optimisation problems, simulate quantum systems with high accuracy, and solve cryptographic challenges efficiently. This mastery over intricate problems opens new avenues for scientific research, engineering, and innovation.
4) Accelerated computational speeds
Quantum Computers offer accelerated computational speeds, enabling organisations to perform computations at unprecedented rates. This speed advantage translates into faster decision-making, reduced time-to-market for products and services, and increased productivity across various industries. Quantum Computers can solve computational tasks in minutes or hours that would take classical computers days, weeks, or even years to complete.
5) Revolutionising Google searches
Quantum Computing has the potential to revolutionise search algorithms and information retrieval systems, including Google searches. Quantum algorithms can process large amounts of data more efficiently, providing users with more accurate and relevant search results. This could enhance user experiences, improve search engine performance, and enable new functionalities such as personalised recommendations and predictive search.
6) Pioneering new technological frontiers
Quantum Computing is paving the way for the development of new technological frontiers and innovations. It enables researchers and engineers to explore previously uncharted territories in materials science, drug discovery, artificial intelligence, and quantum communication. Quantum Computers are strong machines that help us discover new things and go beyond what we currently know and can do.
7) Elevated privacy standards
Quantum Computing offers elevated privacy standards through advanced encryption and cryptographic techniques. Quantum cryptography uses the rules of quantum mechanics to create safe ways to send messages that are very hard for others to spy on or hack into. This enhances privacy and data security in digital communication networks, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorised access and interception.
8) Conducting complex simulations with ease
Quantum Computing facilitates the simulation of complex systems and phenomena with ease. Quantum simulators can accurately model quantum systems, chemical reactions, biological processes, and physical phenomena that are challenging to simulate using classical computers. This capability enables researchers to gain insights into complex systems, predict their behaviour, and optimise their performance for real-world applications.
Disadvantages of Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing holds immense promise but has several challenges and disadvantages that must be addressed. Below are the key disadvantages of Quantum Computing explained:
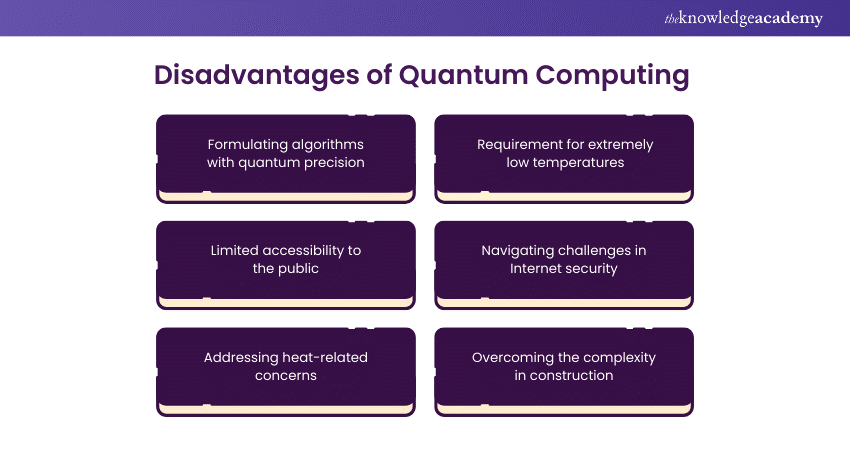
1) Formulating algorithms with quantum precision
Developing algorithms for Quantum Computers requires a deep understanding of quantum mechanics and specialised expertise. Quantum algorithms must be formulated with precision to effectively leverage qubits' unique properties effectively. This is a significant challenge for researchers and developers, as Quantum Computing concepts can be complex and abstract. Additionally, debugging and optimising quantum algorithms can be challenging due to the non-intuitive behaviour of quantum systems.
2) Requirement for extremely low temperatures
Quantum Computers operate using qubits, which are highly sensitive to external disturbances such as temperature fluctuations and electromagnetic interference. To maintain the intricate quantum states of qubits, Quantum Computers require extremely low temperatures close to absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0 Kelvin). Achieving and maintaining these ultra-low temperatures using cryogenic systems adds complexity and cost to Quantum Computing infrastructure, limiting scalability and accessibility.
3) Limited accessibility to the public
Quantum Computing resources are limited and primarily available to academic institutions, research laboratories, and large technology companies. Accessing Quantum Computers for experimentation and research purposes can be challenging for individuals and smaller organisations due to cost constraints and limited availability. This lack of accessibility impedes widespread adoption and hinders innovation in Quantum Computing.
4) Navigating challenges in Internet security
Quantum Computing potentially threatens existing cryptographic systems used to secure digital communication and data storage. Quantum algorithms like Shor's can factor large prime numbers efficiently, compromising widely-used encryption methods like RSA and ECC. Addressing this challenge requires the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms and deploying quantum-safe encryption technologies to ensure cybersecurity in the quantum era.
5) Addressing heat-related concerns
Quantum Computing systems generate significant heat during operation due to the energy dissipation associated with qubit manipulation and control. Managing heat dissipation and thermal management in Quantum Computers is essential to prevent qubit decoherence and ensure reliable operation. Heat issues create technical problems and can stop Quantum Computing systems from becoming larger and more efficient.
6) Overcoming the complexity in construction
Building and scaling Quantum Computing hardware is a highly complex and resource-intensive process. Quantum systems require precise control over qubits and sophisticated error correction and fault-tolerance mechanisms to mitigate decoherence and errors. Designing, fabricating, and calibrating quantum processors involves intricate engineering and manufacturing processes, making achieving reliable and scalable Quantum Computing systems challenging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantum Computing unveils both the transformative potential and the challenges associated with this revolutionary technology. While its benefits promise to reshape industries, addressing its limitations will be crucial for realising its full potential in the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions

While Quantum Computing involves complex concepts, there are resources available for individuals to learn and understand the basics. However, mastery often requires a deep understanding of quantum mechanics and programming skills.

Quantum Computing poses challenges to traditional encryption methods, as quantum algorithms can potentially break cryptographic systems used to secure data. To address this, researchers are developing quantum-resistant encryption techniques to ensure data security in the quantum era.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. By tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies courses, including Quantum Computing Training and 5G Wireless Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Latest Technology Trends.
Our Advanced Technologies blogs cover a range of topics related to Quantum Computing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Quantum Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 5G Wireless Training
5G Wireless Training
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


