We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Artificial Intelligence Techniques spark major changes in many areas of life and work. They empower data-driven decision-making, automate tasks, and personalise experiences, enhancing efficiency and precision. In healthcare, AI aids in diagnosis and drug discovery, while natural language understanding and computer vision technologies revolutionise communication and visual data interpretation.
AI also catalyses scientific discoveries, benefits the financial sector, aids in environmental conservation, and ensures accessibility for all. It fortifies cybersecurity, revolutionises education, and sparks creativity in various fields. In this blog, we'll explore how Artificial Intelligence Techniques significantly impact innovation and shape our future in profound and transformative ways.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Artificial Intelligence Techniques
2) Types of Artificial Intelligence Techniques
a) Supervised learning
b) Unsupervised learning
c) Reinforcement learning
d) Deep learning
e) Natural Language Processing (NLP)
f) Computer vision
3) Exploring the landscape of AI Techniques
4) Conclusion
Understanding Artificial Intelligence Techniques
Understanding AI Techniques is important to grasp the inner workings of AI systems, which aim to replicate human-like cognitive functions. These techniques offer several fundamental aspects, each playing a significant role in AI's ability to learn, reason and comprehend human language.
Learning is the bedrock of AI. It is the process by which AI systems accumulate knowledge from data and experiences. Through learning, AI systems discern patterns and relationships within data, enabling them to make predictions and decisions autonomously.
Reasoning is the cognitive process in which AI systems employ logical thinking to draw conclusions, make inferences, and solve complex problems. This aspect allows AI to make informed decisions based on available information, much like human thought processes.
Problem-solving is a critical facet of AI Techniques. AI employs algorithms, mathematical procedures, and computational methods to tackle specific challenges efficiently. Whether optimising delivery vehicle routes or solving intricate mathematical equations, AI's problem-solving capabilities are instrumental in many applications.
Perception equips AI systems with the ability to interpret their environment. Through various sensors and data sources, AI perceives the world around it. This sensory input is vital for tasks such as image recognition, where AI processes visual data to identify objects, and speech recognition, where it translates auditory input into meaningful information.
Language understanding, often achieved through Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, is pivotal for effective human-computer interaction. AI systems equipped with NLP can comprehend human language, including nuances, context, and sentiment. This enables them to converse seamlessly with humans, making possible chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation applications.
Elevate your business analysis skills with Artificial Intelligence (AI) For Business Analysts– Register now to gain a competitive edge!
Types of Artificial Intelligence Techniques
AI Techniques are the building blocks for creating intelligent systems that mimic human-like cognitive functions. By categorising AI Techniques, we can better understand how AI systems operate and how they impact our world.
Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning is a foundational AI Technique that plays a pivotal role in tasks requiring pattern recognition and prediction. In this method, AI systems learn from a labelled dataset, where each data point is associated with a known outcome. The primary goal is for the AI to identify patterns within the data that can be used to map input to the correct output.
Supervised Learning finds extensive use in various applications, such as image classification, speech recognition, and recommendation systems. For instance, it enables email spam filters to distinguish between spam and legitimate emails based on learned patterns.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning takes a different approach compared to Supervised Learning. In this technique, AI systems analyse unlabelled data, where no predefined outcomes are provided. The objective is to uncover inherent structures or patterns within the data without any prior knowledge.
Clustering and dimensionality reduction are common applications of Unsupervised Learning. For instance, it can group similar customer behaviour data to identify customer segments for targeted marketing strategies.
Reinforcement Learning
Unsupervised Learning takes a different approach compared to Supervised Learning. In this technique, AI systems analyse unlabelled data, where no predefined outcomes are provided. The objective is to uncover inherent structures or patterns within the data without any prior knowledge.
Clustering and dimensionality reduction are common applications of Unsupervised Learning. For instance, it can group similar customer behaviour data to identify customer segments for targeted marketing strategies.
Deep Learning
At its core, Deep Learning relies on neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks) to model intricate patterns and representations within data.
The impact of Deep Learning is evident in image and speech recognition and even in playing games like Go and Chess at a superhuman level.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing focuses on allowing machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP techniques enable AI systems to process, analyse, and respond to text or speech data in a way that resembles human language comprehension.
NLP powers applications like chatbots, language translation, sentiment analysis, and virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. It has transformed how we interact with computers, making human-computer communication more intuitive.
Computer vision
Computer vision is an AI Technique dedicated to helping machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world. It involves the analysis of images and videos to recognise objects, people, and scenes.
Applications of computer vision range from autonomous vehicles that perceive and navigate their surroundings to facial recognition systems used for security and image analysis tools that detect defects in manufacturing processes.
Supercharge your career with AI and Machine Learning – Sign up now for our Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Courses and stay ahead in the digital age!
Exploring the landscape of AI Techniques
In this section, we will talk about various AI Techniques, each with distinct characteristics and practical applications:
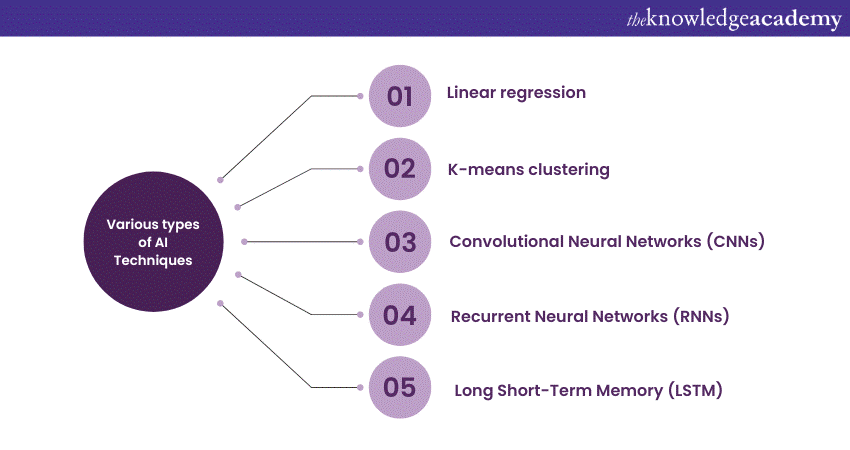
a) Linear regression: A Supervised Learning method for predicting continuous outcomes, widely used in fields such as economics for trend prediction and healthcare for estimating patient outcomes.
b) Random forest: An Ensemble Learning technique known for its high accuracy in classification and regression tasks. It finds applications in finance for credit risk assessment and ecology for species classification.
c) K-means clustering: An Unsupervised Learning approach that groups similar data points. It is employed in customer segmentation strategies and image compression.
d) Q-learning: A Reinforcement Learning algorithm where agents learn to make decisions through trial and error in dynamic environments. It is instrumental in robotics path planning and game-playing agents.
e) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These Deep Learning models are tailored for image and video analysis and are essential in applications like facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, and medical image analysis.
f) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): RNNs excel in handling sequential data such as time series. They find utility in stock price prediction and the development of conversational chatbots.
g) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): An RNN variant designed to capture long-term dependencies in data sequences prominently used in speech recognition and machine translation.
h) Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU): Another RNN variant balancing efficiency and performance, primarily applied in real-time tasks like voice assistants.
i) Transformer models: These are state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) models, including famous examples like BERT and GPT-3. They power applications like chatbots, language translation, and content summarisation.
j) Support Vector Machines (SVMs): They are Supervised Learning techniques used for classification and regression tasks. They are employed in various fields, such as stock market prediction and disease classification.
k) Principal Component Analysis (PCA): This is an Unsupervised technique for dimensionality reduction, essential for applications like image compression and data visualisation.
l) Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These Deep Learning models are used for generating synthetic data, image-to-image translation, and more. They have been pivotal in creating deepfake videos, image style transfer, and synthetic data generation for AI training.
Conclusion
The personalisation that Artificial Intelligence Techniques bring to the table is reshaping customer experiences. For e-commerce, streaming services, and marketing, recommendation systems powered by AI analyse user behaviour to provide highly tailored content and products. We are on a journey that invites us to embrace the opportunities while also recognising the responsibilities that come with this incredible transformative force.
Master Machine Learning for boundless opportunities at our Machine Learning Training – Register today and transform your future!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to AI Course
Introduction to AI Course
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


