We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Agile and Kanban are two popular Project Management methodologies that have gained significant traction in the business world. Both approaches aim to improve efficiency and deliver value, but they differ in their core principles and practices. Project Managers can make an informed decision about which approach is best suited for their Project Management needs, by understanding these differences between Kanban vs Agile.
According to the State of Kanban report of 2022, more than 85 per cent of organisational teams reported the Kanban Board as more effective than other methods. Another report by Digital.ai reveals that about 90 per cent of Agile teams have robust people-centric values and empowerment principles. Check out this blog on Kanban vs. Agile, where you will learn about the key differences between Agile and Kanban methodologies.
Table of Contents
1) A brief look at Kanban Methodology
a) Kanban principles
2) A brief look at Agile methodology
a) Agile principles
3) Key Differences between Kanban and Agile
4) Conclusion
A brief look at Kanban Methodology
Kanban is a visual and Agile approach to Project Management that prioritises continuous flow and limits Work In Progress (WIP). Inspired by Lean manufacturing, Kanban aims to eliminate bottlenecks and streamline workflow. Kanban boards, composed of columns and cards, display the project’s status, making it simple to monitor and manage tasks.
Kanban differs from Agile in that it does not define specific roles, events, or fixed iterations. It enables teams to adjust to changing demands without interrupting ongoing work. Kanban enhances flow by implementing clear rules, restricting WIP, and constantly improving the workflow.
There are many Benefits of Kanban. It fosters continuous improvement by motivating teams to frequently evaluate and improve their workflow, ensuring effective delivery of value. With its adaptable nature and emphasis on flow, Kanban is ideal for projects with uncertain or evolving requirements, allowing teams to cope and respond efficiently.

Kanban principles
Kanban Principles emphasize a focus on visualizing workflow, limiting work in progress, and encouraging continuous improvement. Here are the key principles of Kanban methodology:
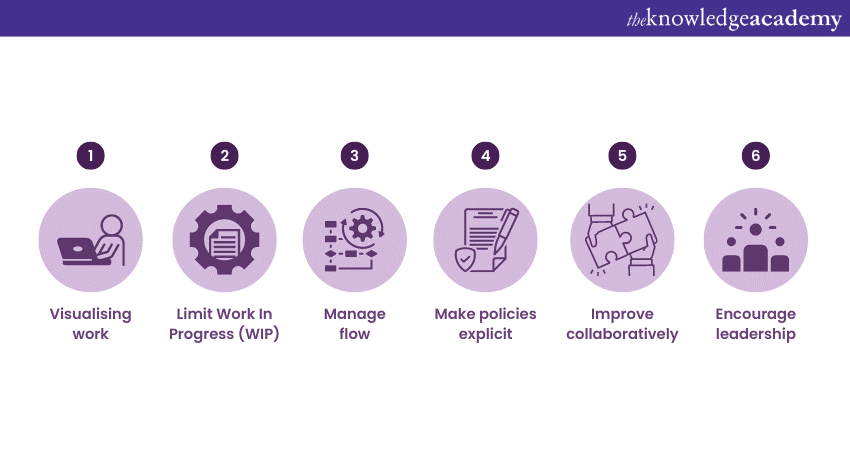
1) Visualise the workflow: Kanban emphasises the workflow by using visualisations on a Kanban board, which consists of columns representing different stages of work and cards representing individual tasks.
2) Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Kanban advocates for limiting WIP, so teams can focus on completing existing work before taking on new tasks, reducing multitasking and improving overall efficiency.
3) Manage flow: Kanban focuses on optimising the flow of work by identifying and addressing bottlenecks and obstacles that impede progress.
4) Make policies explicit: Kanban encourages teams to define explicit policies and rules that govern the workflow.
5) Improve collaboratively: Kanban promotes continuous improvement by encouraging collaboration and learning.
6) Encourage leadership: Kanban encourages leadership at all levels of the organisation.
Learn and apply Kanban to boost your business, by signing up for the Kanban Practitioner Certification Course now!
A brief look at Agile methodology
Agile methodology is a Project Management approach that uses iterative and incremental cycles called sprints. It allows for flexibility and adaptability by splitting projects into smaller, achievable tasks.
Agile aims to deliver functional software early and often through regular cooperation among cross-functional teams. The core values of Agile are expressed in the Agile Manifesto, which highlights individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change.
Scrum is the most popular Agile framework, where work is organised into fixed-duration periods called sprints. Each sprint involves planning, daily stand-up meetings, and retrospectives to evaluate progress and make necessary changes. The product backlog, sprint backlog, and burndown charts are key artefacts used in Agile.
Acquire the skills to work on an Agile project, by signing up for the Agile Project Management Foundation Course now!
Agile principles
Here, we will discuss the key Agile principles:
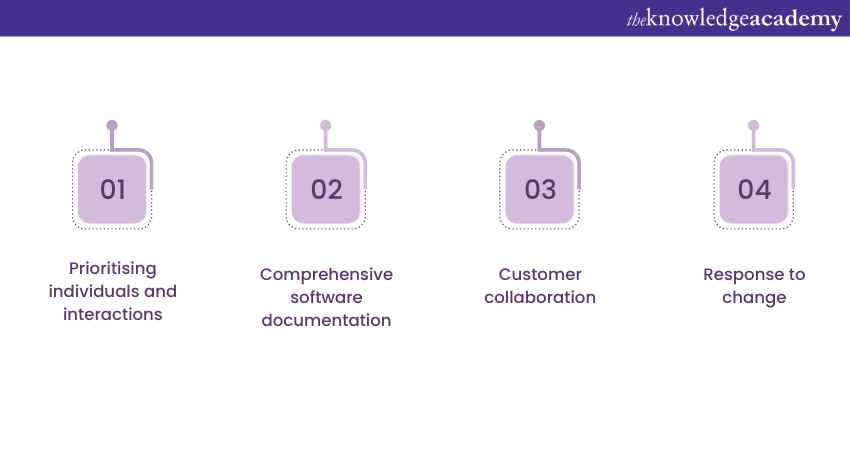
1) Prioritising individuals and interactions: Agile values human interactions and effective communication within a project.
2) Comprehensive software documentation: Agile prioritises delivering working software or tangible value to customers over extensive documentation.
3) [p--Customer collaboration: Agile encourages close collaboration with customers and stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Response to change: Agile embraces change and acknowledges that requirements may evolve during a project.
Adapt an appropriate Kanban initiative, by signing up for the Certified Kanban Foundation Course now!
Key Differences between Kanban and Agile
In this section, we will explore the differences between Kanban vs Agile. Below are the key points of comparison between the Agile and Kanban methodologies:
|
Key Differences |
Kanban |
Agile |
|
Methodology |
Continuous flow with visualised work and emphasis on limiting WIP. |
Iterative framework with time-boxed iterations (sprints) and focus on collaboration and feedback. |
|
Roles and Ceremonies |
No predefined roles or ceremonies, allowing teams to adapt as needed. |
Defined roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, Development Team) and specific ceremonies (sprint planning, daily stand-ups, retrospectives). |
|
Timeboxing |
No fixed time boxes, work is continuously delivered. |
Fixed-duration iterations (sprints) typically ranging from one to four weeks. |
|
Work Prioritisation |
Explicit policies and visualisation on the Kanban board to prioritise and manage work in progress. |
Product backlog used to prioritise and refine work for upcoming sprints. |
|
WIP Limits |
Strictly limits work in progress to maintain a smooth workflow and avoid overburdening the team. |
No explicit WIP limits, allowing teams to pull in new work as ongoing tasks are completed. |
|
Flexibility |
Provides flexibility to respond to changing priorities and adapt the workflow as needed. |
Promotes adaptability through regular feedback and collaboration, but within the boundaries of the fixed sprint duration. |
|
Focus |
Emphasises optimising flow and minimising bottlenecks in the workflow. |
Focuses on collaboration, customer satisfaction, and delivering working software early and frequently. |
Improve your workflow management by downloading the Kanban Rules PDF Guide. Learn the key rules for implementing Kanban effectively.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understood the differences between Kanban vs Agile. This blog highlights the key strengths and differences of Kanban and Agile methodologies, to help managers choose the right approach for their Project Management needs. Agile's time-boxed iterations and defined roles promote collaboration and predictability, making it suitable for complex projects with changing requirements. Kanban, with its emphasis on flow and continuous improvement, is ideal for teams that require flexibility and frequent reprioritisation.
Apply Kanban methodology to your business, by signing up for the Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between Kanban and Agile?

Kanban and Agile are both iterative Project Management methods, but they differ in focus, use case, roles, tasks, workflow, systems, method, and timeframe. For instance, Kanban improves processes and flows continuously, while Agile delivers products and cycles iteratively. Kanban has no specific roles, while Agile has Scrum Master or Product Owner.
How do you choose between Kanban and Agile for your project?

The choice depends on your project’s nature, scope, complexity, uncertainty, change, team skills, and customer feedback. Generally, Kanban suits projects with incremental changes, stable workflows, and low coordination. Agile suits projects with larger-scale changes, dynamic workflows, and high collaboration.
What are the other resources provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related Business Improvement Courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Kanban Courses, including Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Business Improvement methodologies.
Our Business Improvement blogs cover a range of topics related to Kanban, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Training
Certified Kanban Foundation and Practitioner Training
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


