We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
What helps the projects get completed within budget and on time? Project Controls. If you are new to this domain, you might be wondering, What are Project Controls. It involves a systematic approach to Project Management, integrating various elements such as planning, scheduling, budgeting, and risk management. It also provides a framework that allows Project Managers to track progress, identify deviations, and take corrective actions when necessary. In this blog, you are going to learn about Project Controls, key components, their importance and some real-life scenarios showing their successful implementation.
Table of Contents
1) What are Project Controls?
2) Importance of Project Controls
3) Key components of Project Controls
4) Project Controls vs. Project Management
5) When to use Project Controls?
6) Challenges in Project Controls
7) Conclusion
What are Project Controls?
Project Control is the strategic and systematic approach to managing projects throughout their lifecycle. It involves a series of processes, methods, and tools aimed at ensuring that a project achieves its objectives effectively and efficiently. It encompasses various activities, including detailed planning, continuous monitoring, and timely adjustments to align the project's actual progress with the planned trajectory.
This proactive approach enables Project Managers to identify deviations from the project plan, assess their impact, and implement corrective measures promptly. It also empowers Project Managers with the insights needed to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, optimise resource allocation, and ensure that the project is delivered within the defined constraints. It acts as a comprehensive framework, allowing organisations to navigate the complexities of projects, fostering efficiency, accountability, and, ultimately, successful project outcomes.
Importance of Project Controls
Project Controls serve as the guiding mechanism in Project Management, which ensures that projects are executed smoothly, within budget, and on schedule. The importance of Project Controls can be understood through various vital points:
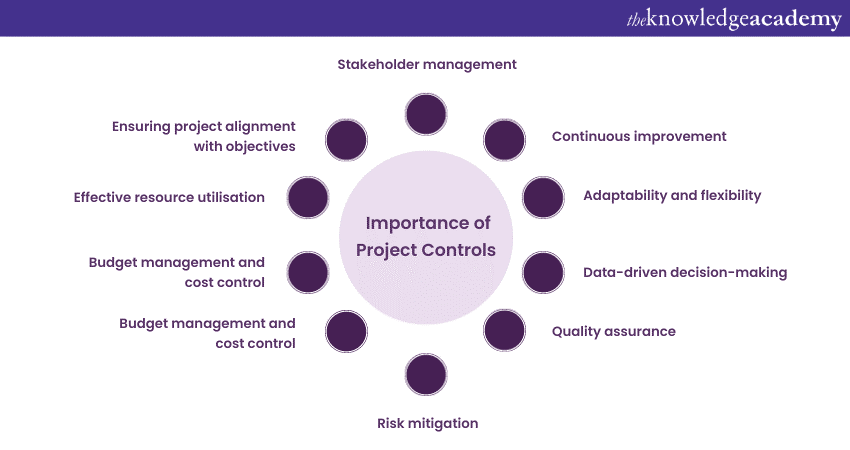
a) Ensuring project alignment with objectives: Project Controls ensure that the project's objectives are clearly defined, aligning the team towards a common goal. By constantly referring to these objectives, the project stays focused and on track.
b) Effective resource utilisation: It helps in optimising resource allocation. Through systematic Project Planning and monitoring, resources are allocated efficiently, preventing overallocation or underutilisation. This ensures maximum productivity and cost-effectiveness.
c) Budget management and cost control: Effective Project Controls involve budget planning and continuous cost monitoring. This prevents budget overruns, enabling financial stability within the project. Controlling costs ensures that the project remains financially viable and sustainable.
d) Timely project delivery: Through meticulous scheduling and monitoring, it facilitates the timely completion of tasks and milestones. This convenient delivery is critical, especially in industries where time-to-market is a competitive advantage.
e) Risk mitigation: It includes robust Risk Management strategies. By identifying potential risks early, project teams can proactively develop mitigation plans. This prevents minor issues from escalating into significant problems, enhancing project resilience.
f) Quality assurance: Ensuring quality standards is a core aspect of Project Controls. By defining quality parameters and conducting regular inspections, the project team can maintain high-quality deliverables. This not only satisfies clients but also safeguards the project's reputation.
g) Stakeholder management: Clear communication and transparency are facilitated by Project Controls. Regular reporting and updates keep Stakeholders informed about the project's progress, minimising misunderstandings and enhancing trust between the project team and stakeholders.
h) Data-driven decision-making: It generates valuable data and metrics. Analysing this data provides insights into the project's performance. Project Managers can make informed decisions based on real-time information, leading to better outcomes.
i) Adaptability and flexibility: It enables the project team to adapt to changes effectively. When unexpected challenges arise, Project Controls provide a framework for evaluating options and choosing the best course of action. This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments.
j) Continuous improvement: Through post-project evaluations and analysis of Project Control data, lessons learned can be identified. These insights contribute to the constant improvement of Project Management Processes, ensuring enhanced efficiency and effectiveness in future projects.
k) Client satisfaction: Projects that are well-controlled are more likely to meet or exceed client expectations. Client satisfaction is not just about delivering the project on time and within budget but also about having a high-quality product or service. Satisfied clients are more likely to provide positive referrals and repeat business.
l) Legal and compliance requirements: It helps ensure that the project complies with legal regulations and industry standards. By tracking and verifying compliance at every stage, the project avoids legal complications and fines, safeguarding the organisation's reputation and financial standing.
Elevate your skills and lead successful projects even without a Project Management background. Register now for our Project Management for Non-Project Managers Course!
Key components of Project Controls
Project Controls consist of several integral components that collectively form the backbone of effective Project Management:
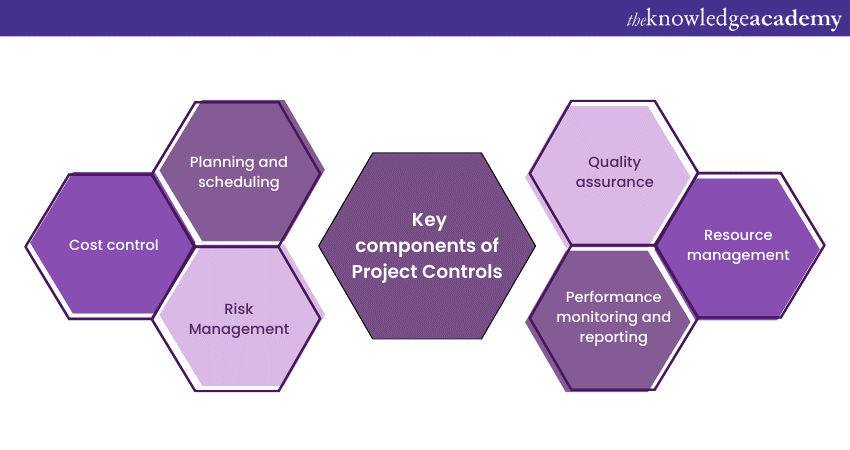
1) Planning and scheduling: Detailed project planning involves breaking down tasks, setting timelines, and establishing dependencies. Scheduling ensures a logical sequence of activities, highlighting the critical path and facilitating efficient resource allocation.
2) Cost control: Monitoring expenditures against budgets is crucial. It involves tracking costs in real-time, analysing variances, and implementing strategies to prevent budget overruns, ensuring financial stability.
3) Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks are fundamental. Project Controls employ Risk Management techniques to anticipate potential issues, enabling proactive measures and minimising disruptions.
4) Quality assurance: Maintaining high-quality standards in projects is paramount. It establishes quality benchmarks, ensuring that deliverables meet predefined criteria and enhances client satisfaction and project reputation.
5) Resource management: Efficient utilisation of resources, including human capital and materials, is vital. It optimises resource allocation, preventing bottlenecks, ensuring productivity, and avoiding overburdening specific resources.
6) Performance monitoring and reporting: Real-time tracking of project progress allows for immediate corrective actions. Regular reports, metrics, and dashboards enable stakeholders to stay informed, facilitating transparency and informed decision-making.
Master the essentials of Project Management with our Introduction to Project Management Certification Course
Project Controls vs. Project Management
The intersection in function between Project Controls and Project Management can at times cause certain confusion. These two disciplines can at times make it difficult to differentiate between them. At times many organisations assign the role of a Project Controller to one of the Project Managers. This often makes their roles even more confusing. However, it’s important to discern the differences between these two to fully appreciate the role of Project Controls.
Project management is a holistic function. It involves managing people, processes and deliverables in a project. This is done through various sub-functions. Its focus is on quality assurance and scope, in addition to cost. The objective of Project Management is more exhaustive as it aims to successfully complete a project with available resources and given time.
Project Controls, on the other hand, are sub-functions. The focus is on just two parameters: cost and schedule. People Management and quality control, for example, does not fall under its purview. The main objective of project controls is to minimize the variance in costs and schedule from what was originally planned.
It acts as a safety harness to Project Management. Sometimes Project managers can focus almost solely on delivery, which leaves less space to examine costs, deviation from the project plan and other variables involved.
When to use Project Controls?
Project Controls help Project Managers track and control project constraints. Project Controls are most used while planning a project. Before every project begins, teams need to be assembled, tasks must be broken down and stakeholders need to be identified. When deciding on the costs and the duration of the project, Project Controls are used.
Project Planning
Project controls are needed at the beginning of the project, as you make your schedule, assemble a team, break down tasks, identify stakeholders and figure out the project objective. It’s in the estimation of costs and duration of the project where controls are essential. These two constraints are some of the greatest risks to your project and they’re key to making accurate estimates.
Project Execution & Project Monitoring
Executing the project means keeping the team focused to prevent slipping off schedule and imploding your budget. This requires accurately monitoring and tracking your progress.
Project controls act as a means to identify when there are problems and bottlenecks. Whether balancing resource allocation to match team capacity or quality issues, you need project controls to break down data on the team’s hours worked against the budget spent and more to see where there are problems and resolve them quickly.
Case studies: Successful implementation of Project Controls
Examining real-life case studies provides valuable insights into the challenges faced, strategies employed, and the ultimate triumph of implementing Project Controls. Here are two compelling case studies that demonstrate the successful implementation of Project Controls in diverse contexts:
a) Case study 1: Construction of a high-rise skyscraper
A construction company undertook the ambitious task of building a high-rise skyscraper in a bustling urban area. The project faced numerous challenges, including limited space, complex architectural designs, and stringent safety regulations. To navigate these challenges, the project team implemented comprehensive Project Controls.
Implementation of Project Controls:
1) Detailed planning: The project team created a meticulous project plan outlining tasks, milestones, and dependencies. Utilising specialised software, they developed a 4D Building Information Modelling (BIM) model, integrating scheduling information with architectural designs.
2) Cost management: A robust cost management system was established, tracking expenses, monitoring budgets, and analysing cost variances. Regular audits ensured financial transparency.
3) Risk mitigation: The team identified potential risks, such as adverse weather conditions and supply chain disruptions. Contingency plans were developed, and risk response strategies were in place.
4) Quality assurance: Quality benchmarks were set, and inspections were conducted at every stage of construction. Non-compliance issues were immediately addressed to maintain high-quality standards.
5) Real-time monitoring: Advanced monitoring tools provided real-time data on project progress, enabling the team to track construction activities, identify bottlenecks, and ensure timely completion of tasks.
6) Stakeholder engagement: Clear communication channels were established with stakeholders. Regular progress reports were shared, addressing concerns promptly and maintaining stakeholder confidence.
Outcome: The implementation of Project Controls ensured that the construction project proceeded smoothly. Timelines were met, costs were contained within the budget, and the quality of work exceeded industry standards. The skyscraper stood tall as a testament to effective Project Controls, showcasing the company's expertise in managing complex projects.
b) Case study 2: Implementation of an enterprise software system
A large corporation aimed to implement a comprehensive enterprise software system to streamline its operations. The project involved integrating various modules, training employees, and ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing business processes. Project Controls were instrumental in managing this complex IT project.
Implementation of Project Controls:
a) Comprehensive project planning: The project team developed a detailed project plan outlining the implementation phases, milestones, and resource requirements. Each step was meticulously planned to avoid overlaps and conflicts.
b) Change Management: Recognising the impact on employees, a robust Change Management strategy was devised. Training sessions, workshops, and communication campaigns were conducted to prepare employees for the new system.
c) Budget and resource management: A stringent budget was established, and resources were allocated based on project priorities. Regular monitoring ensured that expenses were controlled, and resources were utilised efficiently.
d) Data migration and testing: A data migration plan was formulated to transfer existing data seamlessly. Rigorous testing protocols were established, including User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and System Integration Testing (SIT), to identify and resolve issues promptly.
e) Real-time reporting: Project Management software generated real-time reports on project progress. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) were tracked, allowing the team to identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions.
f) Post-implementation support: A post-implementation support plan was developed to address any issues that arose after the system went live. A dedicated support team was in place to handle user queries and technical glitches.
Outcome: The enterprise software system was implemented successfully, transforming the company's operations. The Project Controls ensured that the implementation was completed within the planned timeline and budget. Employees adapted to the new system seamlessly, and the corporation experienced improved efficiency and productivity across its departments.
Become an expert in Project Management with our course on Project Management Black Belt!
Challenges in Project Controls
While Project Controls play a pivotal role in ensuring successful Project Execution, they are not without their share of challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for effective Project Management. Here are some of the common difficulties in Project Control:
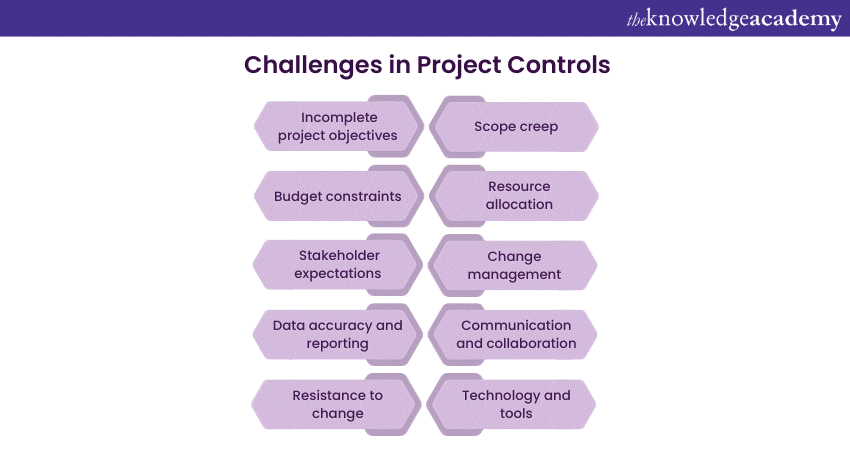
a) Incomplete project objectives: Inadequate project objectives or objectives that need to be clarified can lead to Project Control difficulties. When the end goal is well-defined, it becomes easier to measure progress and ensure that the project remains aligned with its purpose.
b) Scope creep: One of the most prevalent challenges in Project Management is scope creep, where the project's scope gradually expands beyond the original definition. This can lead to increased costs, longer schedules, and strained resources.
c) Budget constraints: Budget limitations are a constant concern in Project Management. Staying within the allocated budget while meeting project objectives can be demanding. Unforeseen expenses and changes can put significant pressure on Project Controls.
d) Resource allocation: Efficiently managing and allocating resources can be complex, especially in larger projects with numerous tasks and team members. Ensuring that the right resources are available when needed is essential for smooth project execution.
e) Stakeholder expectations: Managing the expectations of various stakeholders, including clients, team members, and management, can be challenging. Differing opinions and priorities can lead to communication issues and delays.
f) Change Management: When changes occur during a project, they need to be effectively managed. Failure to do so can disrupt the project schedule, increase costs, and impact overall project performance.
g) Data accuracy and reporting: The accuracy of project data and the timeliness of reporting are vital for informed decision-making. Only inaccurate or untimely data can lead to misjudgements and flawed strategies.
h) Communication and collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration among project team members, stakeholders, and project managers are essential. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and a lack of alignment among team members.
i) Resistance to change: Implementing Project Controls often necessitates changes in processes and practices. Resistance to change from team members can hinder the successful adoption of project control procedures.
j) Technology and tools: The selection and implementation of Project Management tools and software can be a challenge. Integrating new technologies into an organisation's existing processes requires planning and may face resistance.
Advance your Project Management skills with Project Management Certification. Sign up now!
Conclusion
We hope that from this blog you understood What are Project Controls. This blog also discussed the foundation upon which successful projects are built. They provide the structure, discipline, and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of Project Management. It ensures that projects achieve their goals efficiently, effectively, and to the satisfaction of all stakeholders involved.
Drive infrastructure projects forward with confidence. Sign up now for our Project and Infrastructure Financing Training.
Frequently Asked Questions

Industries that highly value professionals with expertise in Project Control include construction, engineering, aerospace, information technology, and energy. These sectors demand precise planning, budget management, and timely delivery of complex projects.

Project Control skills in the technology sector are crucial for managing complex software development, infrastructure rollouts, and innovation projects. Professionals with these skills can ensure projects meet deadlines, budgets, and quality standards, leading to significant cost savings and project success.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various PRINCE2 courses, including PRINCE2 Foundation, Practitioner, and Agile. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Project Management methodologies.
Our Project Management blogs cover a range of topics related to PRINCE2, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Project Management Course
Introduction to Project Management Course
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


