We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the world of Project Management, success often hinges on effective planning. As Project Planning is a crucial aspect of project management and involves a series of phases or steps to ensure that a project is well-defined, organized, and executed effectively.
In this blog, we will dive into the various Project Planning Phases and explore key strategies for ensuring a successful outcome. From initiation to closure, we will explore the Phases of Project Planning and provide you with insights that can be applied to your own projects.
Table of Contents
1) The importance of Project Planning
2) Phases of Project Planning
a) Phase 1: Initiation
b) Phase 2: Planning
c) Phase 3: Execution
d) Phase 4: Monitoring and controlling
e) Phase 5: Closure
3) Key strategies for success in Project Planning
4) Conclusion
The importance of Project Planning
Project Planning is the compass that guides a project from inception to completion, ensuring it stays on course and achieves its objectives efficiently. It provides clarity by defining project goals, scope, timelines, and resource allocation, allowing Stakeholders to understand their roles and responsibilities.
Moreover, effective planning minimises risks, anticipates challenges, and facilitates better Decision-making throughout the project's lifecycle. It saves time and resources by preventing scope creep and reducing the need for corrective actions later on. Ultimately, Project Planning is the foundation upon which successful projects are built, leading to better outcomes, satisfied stakeholders, and enhanced Project Management.
Enhance your Project Management skills with our Project Management Courses | Training & Certifications. Join now and drive project success!
Phases of Project Planning
This section of the blog will expand on the 5 phases of Project Planning below.
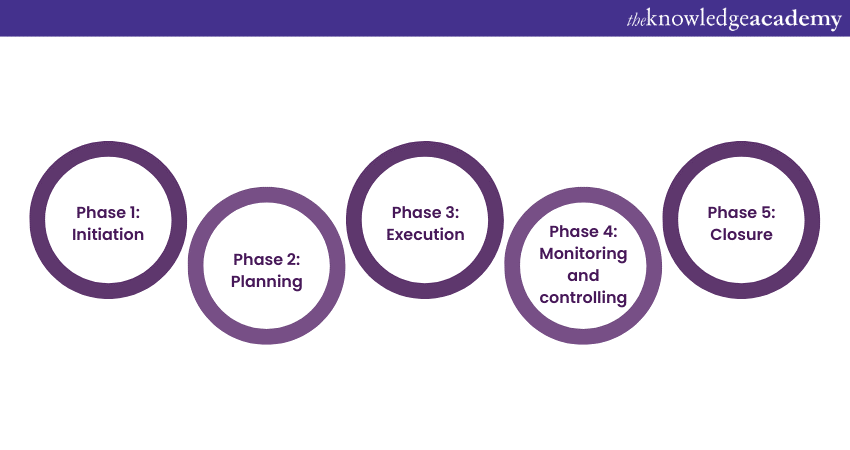
Phase 1: Initiation
The Project Initiation Phase is the project's birth, where the seeds of success are sown. During this critical stage, the project's purpose and objectives are clearly defined. It's about answering the fundamental questions: What are we trying to achieve, and why? Stakeholders are identified, and their specific needs and expectations are assessed.
The development of a Project Charter, a document that encapsulates the project's essence, is a hallmark of this phase. By meticulously laying these foundations, you establish a robust framework for the entire project, ensuring everyone is aligned towards a common goal.
Phase 2: Planning
The planning phase is akin to drawing up the blueprint for a building. Here, you dive into the specifics of how the project will unfold. Key elements such as scope, time, resources, and risks are thoroughly examined. The scope defines what is within the project's boundaries and what isn't.
A detailed project schedule is created, allocating time and resources optimally. Risk assessments are conducted to identify potential pitfalls and develop mitigation strategies. This phase is the backbone of Project Management, providing a roadmap that guides the project from inception to completion, reducing uncertainties and improving control.
Phase 3: Execution
With a solid plan in place, the execution phase is where the project takes shape. It involves mobilising the project team, allocating resources, and putting the plan into action. Effective Communication is paramount during this phase, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and progress is tracked.
Quality assurance measures are implemented to maintain the standard of deliverables. Additionally, Change Management Strategies come into play as unforeseen challenges may arise. Successful execution relies on the coordination of efforts, efficient resource utilisation, and a constant focus on meeting the project's objectives.
Phase 4: Monitoring and controlling
Once the project is underway, the monitoring and controlling phase serves as the compass to keep it on course. Here, progress is rigorously tracked against the project plan. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to measure just how well the project is meeting its goals. Issues and deviations are identified promptly, and corrective actions are taken to address them.
Cost management is integral to ensuring the project remains within budget. Scope changes are carefully managed to prevent "scope creep," which can derail the project. This phase is all about maintaining control and making timely adjustments to ensure the project stays on track.
Phase 5: Closure
The closure phase marks the project's triumphant finale. Here, deliverables are reviewed and accepted by stakeholders, ensuring that they meet the agreed-upon criteria. Knowledge transfer is a crucial component, as the project team imparts their expertise to those who will be responsible for ongoing maintenance or support.
A post-implementation evaluation is conducted to assess the project's overall success and learn valuable lessons for future endeavours. Closure activities include administrative tasks like finalising contracts, releasing project resources, and archiving project documentation. Successfully closing a project not only wraps it up neatly but also paves the way for new beginnings and future successes.
Take your first step into Project Management excellence. Sign up for our Introduction to Project Management Certification Course today!
Key strategies for success in Project Planning
Project Planning is the secret to successful Project Management. It lays the groundwork for all project activities, influencing the project's trajectory and ultimate outcome. To ensure a project's success, here are key strategies that should be integrated into your Project Planning process:
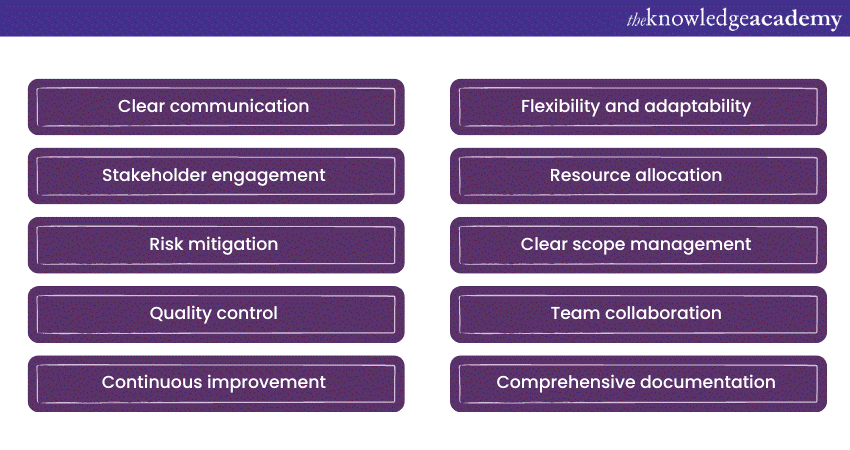
Clear communication
Effective communication is paramount throughout all project phases. Ensure that project goals, objectives, and expectations are clearly articulated to all stakeholders. Encourage open and honest communication channels, fostering an environment where members can share their ideas and concerns. Regular updates and status reports keep everyone informed and aligned.
Stakeholder engagement
Identify and engage with stakeholders early and consistently. Understand their needs, interests, and concerns. Regularly seek their input and feedback to make informed decisions and manage expectations. Engaged stakeholders are more likely to support the project and contribute to its success.
Risk mitigation
Comprehensive risk assessment and management are crucial. Identify potential risks, assess their impact and likelihood, and develop mitigation strategies. Review and update the risk register regularly throughout the project's lifecycle. Being proactive in addressing risks can prevent costly setbacks.
Quality control
Quality should be at the forefront of Project Planning. Establish clear quality standards and procedures from the outset. Regularly monitor and assess deliverables to ensure they meet these standards. Implement quality assurance processes to identify and rectify issues early, preventing rework later in the project.
Continuous improvement
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement. Regularly review and learn from past projects, identifying areas for enhancement in your planning and execution processes. Encourage team members to share lessons learned, promoting a culture of innovation and growth.
Flexibility and adaptability
While a well-defined plan is essential, be prepared to adapt to changing circumstances. Project plans should be dynamic documents that can accommodate unforeseen challenges. Build contingency plans and be open to adjusting Project Management Timelines or resources when necessary.
Resource allocation
Allocate resources judiciously, considering the project's scope and objectives. Ensure that team members have the necessary skills and tools to complete their tasks efficiently. Regularly monitor resource usage and make adjustments as required to maintain optimal productivity.
Clear scope management
Prevent scope creep by rigorously managing project scope. Document all scope changes, assess their impact on the project, and obtain proper approvals. A well-defined scope ensures that the project stays on track and within the agreed-upon boundaries.
Team collaboration
Promote a collaborative team environment where members feel valued and empowered. Encourage cross-functional collaboration, knowledge sharing, and a shared sense of ownership. A cohesive team is more likely to overcome challenges and deliver successful outcomes.
Comprehensive documentation
Maintain thorough project documentation. This includes project plans, schedules, meeting minutes, and decision logs. Well-documented projects are easier to manage, and they provide valuable references for future projects.

Conclusion
Success in Project Management is not just a matter of chance; it's a product of meticulous planning and execution. The Project Planning Phases form the bedrock of this success. By adhering to key strategies like clear communication, stakeholder engagement, risk mitigation, and a commitment to quality, project managers can navigate the complexities of any endeavour, ensuring that projects reach their intended destinations with efficiency and excellence.
Unlock your full potential in Project Management with our Project Planning And Control Training by joining today for comprehensive skill enhancement!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation
Project Planning and Control™ (PPC) Foundation
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


