We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In a world where nearly every aspect of our lives is touched by technology, have you ever paused to wonder What is a Computer Network? This invisible force connects our devices, powers our communications, and drives the digital experiences we take for granted every day. But how does it work, and why is it so essential to modern life?
As you delve into the fascinating world of Computer Networks, you'll uncover the complexity behind what seems so effortless. But what exactly goes into building these networks? How do they manage to connect billions of devices globally, ensuring data flows smoothly from one point to another? Let’s explore the complexities of What is a Computer Network and how it shapes our digital reality.
Table of Contents
1) Decoding What is a Computer Network?
2) How Does a Computer Network Work?
3) Components of Computer Networks
4) Types of Computer Networks
5) Key Objectives of Establishing a Computer Network
6) Network Topologies
7) Conclusion
Decoding What is a Computer Network?
A Computer Network is a system where multiple devices, such as computers and servers, connect to share resources and data. These devices communicate using wired cables, wireless signals, or fibre optics. The main objective of a Computer Network is to enable efficient communication and collaboration between users by sharing files, applications, and internet access.
Networks can be small, like those in homes, or large and complex, like those in businesses or across the globe. The internet is the largest example, connecting millions of networks worldwide and allowing for global communication and resource sharing.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
A Computer Network is a sophisticated web of interconnected devices, and understanding how it works involves grasping the basics of data transmission, protocols, and network devices. The process begins with data encapsulation, where information is wrapped in multiple layers (headers and trailers) that contain crucial routing and control information.
Protocols, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP), govern this communication. TCP ensures data integrity and reliable transmission, while IP handles addressing and routing across the network.
Routing plays a pivotal role in directing data through the network. Routers, the traffic controllers of the digital highway, analyse destination addresses and determine the most efficient path for data packets. Switches further facilitate this journey by managing the flow of information within local segments, whereas hubs, now largely outdated, were once used to distribute data to multiple devices.
Essential network devices, including routers, switches, and hubs, collaborate to enable seamless connectivity. Routers connect different networks, switches facilitate communication within a network, and hubs serve as central points for data distribution. Each device contributes to efficient data flow, creating a dynamic network ecosystem.
Ultimately, a Computer Network operates as a collaborative orchestra, with each device playing a distinct role in ensuring that data travels swiftly and accurately from source to destination. This orchestrated symphony of protocols and devices forms the backbone of our interconnected digital world, enabling the instantaneous exchange of information that defines modern communication and collaboration.
Unlock your potential in Linux Server management with our expert-led Ubuntu Linux Server Administration Training – join now!
Components of Computer Networks
A Computer Network comprises several critical components, each playing a distinct role in shaping the network's functionality, efficiency, and security.
1) Network Devices
Network devices are the backbone of any Computer Network, facilitating communication and resource sharing. These devices include routers, switches, hubs, and access points. Routers direct data between different networks, while switches manage data flow within a network.
Though less common today, Hubs serve as central points for connecting devices. Access points enable wireless connectivity. Collectively, these devices create a cohesive network infrastructure that enables seamless communication and resource utilisation.
2) Links
Links form the physical or logical connections between network devices. Physical links involve cables, such as Ethernet or fibre optics, directly connecting devices. Logical links, on the other hand, are established through protocols and address assignments, creating a virtual connection. The quality and speed of links significantly impact the network's overall performance.
3) Communication Protocols
Communication protocols are rules governing data exchange between devices on a network. Protocols define how data is formatted, transmitted, received, and acknowledged.
Common protocols include Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Internet Protocol (IP), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Adhering to standardised protocols ensures interoperability among diverse devices and systems, fostering efficient and secure communication.
4) Network Security
Network security is important as it protects data and resources from unauthorised access, attacks, and breaches. This includes implementing firewalls, encryption mechanisms, and intrusion detection systems.
Security protocols like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Virtual Private Network (VPN) are crucial in securing data during transmission. Robust network security ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information, safeguarding the network against potential threats.
Unlock the secrets of domain names and web hosting with our Introduction To Domain Names and Web Hosting Training - empower your online journey now!
Types of Computer Networks
Computer Networks come in diverse forms, each tailored to specific needs and scale. The array of Types of Computer Networks can be categorised based on their geographical scope and purpose.
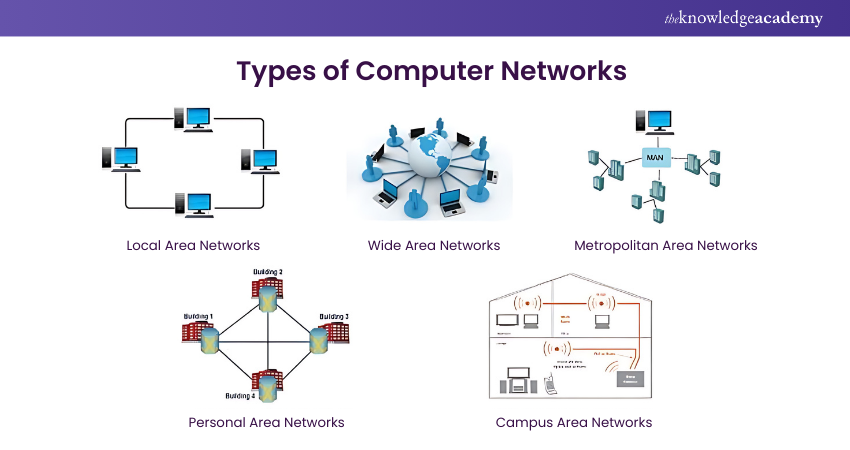
1) Local Area Networks (LANs)
A LAN connects devices within a small geographic area, such as a home, office, or school. It enables fast data sharing and communication between connected devices, typically using Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
2) Wide Area Networks (WANs)
A WAN spans a large geographic area, connecting multiple LANs across cities, countries, or even continents. It uses various transmission technologies and is often managed by telecommunications providers.
3) Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs)
A MAN covers a city or large campus, bridging multiple LANs within a metropolitan area. It offers high-speed connections for public or private use, often using fibre-optic or wireless links.
4) Personal Area Networks (PANs)
A PAN is a small network designed for personal devices, like smartphones, tablets, and laptops, typically within a range of a few meters. Bluetooth and USB are common technologies used in PANs.
5) Campus Area Networks (CANs)
A CAN connects multiple LANs within a limited geographic area, such as a university or corporate campus. It provides high-speed communication between buildings and is managed internally by the organisation.
6) Storage Area Networks (SANs)
A SAN is a specialised network that provides access to consolidated, block-level storage. It enables multiple servers to access shared storage devices, enhancing storage efficiency and data management.
7) Enterprise Private Networks (EPNs)
An EPN is a private network built and maintained by an organisation to securely connect various locations and departments. It ensures secure communication and resource sharing across the enterprise.
8) Service Provider Networks
These networks are managed by companies that lease network capacity and services to customers. They typically include telecommunications companies, data carriers, internet service providers, and cable television providers, offering essential connectivity and communication services.
9) Cloud Networks
A type of WAN, cloud networks utilise infrastructure provided by cloud-based services, like Amazon Web Services. This approach has become a standard for modern networking, offering scalable and flexible network solutions delivered through the cloud.
10) Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
By using a VPN, one can establish a private, encrypted connection across a public network, like the internet. It allows users to safely and remotely access a private network, protecting data from unauthorised access.
Secure your network with our VPN Training and enhance your Cyber Security skills today - register now!
Key Objectives of Establishing a Computer Network
In Computer Networks, establishing connectivity goes beyond mere technological interlinking; it revolves around achieving objectives that enhance overall system efficiency and foster collaboration. Here are the key objectives:
1) Shared Resource Utilisation
One of the primary objectives of a Computer Network is the efficient utilisation of shared resources. These resources can include hardware components like printers, scanners, and storage devices. By interconnecting devices, networks enable multiple users to access and use these resources simultaneously, optimising their utilisation.
2) Ensuring Resource Accessibility and Reliability
Networks are designed to ensure seamless resource accessibility, promoting data retrieval and utilisation reliability. Whether accessing files on a shared server or utilising a centrally connected printer, the objective is to guarantee that resources are readily available and dependable for all network users.
3) Efficient Performance Oversight
Computer Networks incorporate mechanisms to monitor and manage network performance. This involves tracking data transfer speeds, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring consistent performance across the network. Efficient oversight contributes to a smooth and responsive network experience.
4) Economical Operations
Networks aim to streamline operations by reducing redundancy and optimising resource usage. This objective aligns with cost-effectiveness, ensuring the network infrastructure operates efficiently without unnecessary expenditures. Consolidating resources and centralising management contribute to economical network operations.
5) Expanded Storage Capability
Networks provide expanded storage capabilities through centralised servers and cloud solutions. This objective addresses the growing need for scalable storage solutions, allowing organisations to accommodate increasing data volumes without resorting to individual device upgrades.
6) Enhanced Collaboration and Communication Streamlining
A fundamental goal of Computer Networks is to enhance collaboration and streamline communication. Shared access to files, collaborative document editing, and real-time communication tools are integral. The network acts as a facilitator for efficient teamwork, breaking down geographical barriers.
7) Error Minimisation
Networks incorporate error detection and correction mechanisms to minimise data transmission errors. Robust protocols and algorithms ensure data integrity during transmission, contributing to the reliability and accuracy of information exchange.
8) Secure Remote Access
Enabling secure remote access is a crucial objective, especially in the modern work landscape. Networks implement security protocols to safeguard data during remote access, allowing users to connect securely to the network from different locations.
Enhance your IT expertise by mastering CloudFlare Training - secure, optimise, and accelerate your web applications today!
Network Topologies
Network Topologies define the physical or logical layout of interconnected devices in a Computer Network, influencing communication, scalability, and fault tolerance. Several common Network Topologies are employed based on specific requirements and considerations:

1) Point-to-point Network Topology
Two devices are directly connected in a point-to-point Network Topology, creating a dedicated communication channel. It's a simple and efficient setup used in telecommunications, providing a direct link for data exchange.
2) Bus Topology
In a bus topology, devices share a single communication line or "bus." Data travels along this central cable, and each device on the network receives the data. While simple and cost-effective, bus topologies can experience performance issues as the number of connected devices increases.
3) Star Topology
Each device is connected directly to a central hub or switch in a Star Topology. The hub acts as a central point for data exchange. Star topologies offer easy scalability and efficient fault isolation since the failure of one connection doesn't affect others. However, they may require more cabling.
4) Ring Topology
In a Ring Network Topology, devices form a closed loop, and data travels in one direction. Each device is connected to precisely two neighbours. While this structure simplifies network management, a failure in any single connection can disrupt the entire network.
5) Tree Topology
Tree topology is a hierarchical network structure where devices are arranged in a tree-like format. A central hub connects multiple secondary hubs or devices, forming a branching structure. This design enhances scalability and allows for efficient data flow and network expansion.
6) Mesh Topology
Mesh topologies involve direct connections between every device, creating redundancy and multiple communication paths. This redundancy enhances fault tolerance, as data can take alternative routes if one path fails. However, the extensive cabling and setup complexity are considered.
7) Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topologies combine elements of two or more topologies to meet specific needs. For example, a network might incorporate aspects of both star and bus topologies. This approach allows organisations to tailor their networks to balance efficiency, scalability, and fault tolerance.
Empower your IT career by gaining crucial skills through our expert-led IT Support and Solution Training – Sign up today!
Conclusion
Uncovering What is a Computer Network reveals the powerful web connecting our world. These systems, from their core components to diverse types and topologies, are the heartbeat of modern communication. As our reliance on connectivity grows, understanding networks is key to navigating and shaping the future.
Gain insights into Networking with our Introduction to Networking Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Computer Networks enable seamless communication, resource sharing, and connectivity. They form the backbone of our digital world, powering everything from online services to global collaboration.

Network components like routers, switches, and protocols ensure efficient data transmission, secure connections, and seamless communication. Every component plays an essential role in maintaining the network's stability, speed, and reliability.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various IT Support and Solution Training, including Introduction to Networking Training, Ubuntu Linux Server Administration Training and VPN Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Star Topology.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to Computer Network, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Knowledge of Computer Networks, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Networking Training
Introduction to Networking Training
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


