We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +40 316317743 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you interested in simplifying your business procedures and enhancing productivity? Then, PDCA Cycle can help you. But What is PDCA? The PDCA Cycle, consisting of Plan, Do, Check, Act, provides a successful approach for ongoing enhancement in different sectors. It is a flexible instrument utilised in quality management and business strategies to promote innovation and expansion.
This blog will help you understand What is PDCA and how it assists in pinpointing improvement areas, making and applying changes. Learn how this continuous improvement methodology helps optimise processes, enhance efficiency, and drive quality in your organisation.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding PDCA
2) The Importance of PDCA
3) The Four Phases of the PDCA Cycle
4) When to Implement the PDCA Cycle?
5) The Benefits of the PDCA Cycle for Maintenance Teams
6) Diverse Applications of PDCA
7) An Example of the PDCA Cycle
8) Conclusion
Understanding PDCA
In the 1950s, a management consultant, Dr. William Edwards Deming, created a technique to uncover the reasons behind underperforming products or processes. His method, now famous as the PDCA Cycle, has emerged as a widely used strategy tool in many organisations. It allows them to develop theories about required changes and experiment with them in an ongoing feedback cycle.
The PDCA Cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle, consists of four steps: Plan, Do, Check, and Act. During the initial phase of planning, teams pinpoint possible issues and devise enhancement plans. The phase of 'Do' includes testing the effectiveness of these strategies on a small scale when implementing them.
The 'Check' step assesses the results, while the 'Act' stage concentrates on implementing needed modifications or expanding effective changes. This ongoing process supports companies in improving their operations consistently. The result is higher efficiency, decreased waste, and improved product quality.
The Importance of PDCA
The PDCA Cycle is a major model for making good decisions to reach business objectives. By incorporating the PDCA model, your company can boost its workflow via a systematic approach to PDCA. The feedback approach allows you to effectively alter your plans by carefully assessing each phase before implementing projects.
Applying the Deming cycle on a tiny scale allows organisations to improve gradually and consistently. It also helps to find mistakes beforehand, leading to waste reduction. The PDCA model supports teams in carefully assessing their activities, learning from feedback, and making data-driven decisions.
The plan, do, check, and act cycle improves productivity and efficiency and thoroughly maintains operations. This instrumental approach aids businesses in embracing changing conditions and staying ahead of the competition.
The Four Phases of the PDCA Cycle
The PDCA Cycle provides a structured method for problem-solving and implementing solutions. We will now explore each of the four stages individually.
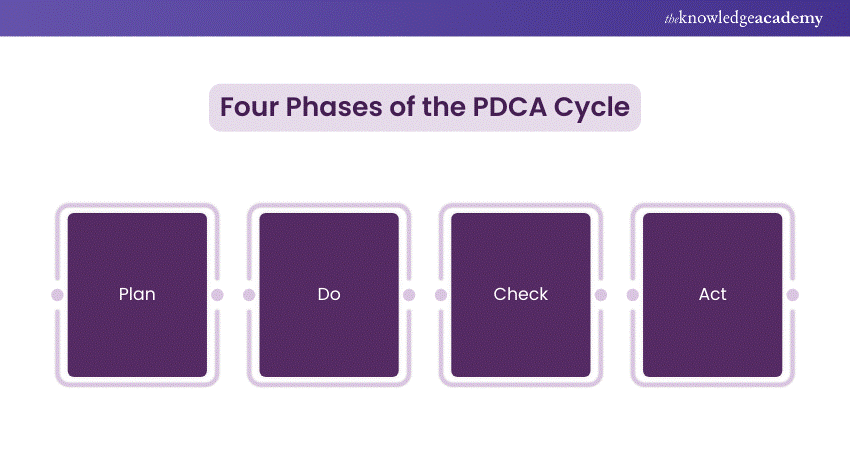
1) Plan
Begin by recognising and comprehending the issue or improvement opportunity in front of you. The finished product may lack quality, or a specific area of your marketing strategy needs enhancing. Carefully investigate all accessible data, generate ideas through brainstorming, and create a detailed plan for execution. Clearly articulate your success indicators and verify they are quantifiable, as they will be reviewed during the Check phase.
2) Do
Have a potential solution ready and carry out a small pilot project to evaluate its efficiency. This trial aims to see if the suggested alterations lead to the expected outcomes, reducing possible disruptions to the overall function in case of failure.
For example, you could conduct the test in a particular department, in a small geographical location, or focus on a specific group of people. Gather information during the pilot phase to assess the effectiveness of the modifications.
3) Check
Evaluate the outcomes of your pilot initiative based on the standards set in the planning stage to ascertain the effectiveness of the modifications. If the results fall short of expectations, return to the Planning stage.
If this is accomplished, proceed to the next stage. You can make extra modifications and iterate through the Do and Check steps to enhance your method even more.
4) Act
Execute the effective resolution on a grander level. Remember that the PDCA Cycle is an ongoing loop, not a single instance. Your upgraded process or product will set a new benchmark, prompting you to pursue more improvements to sustain a continuous enhancement culture consistently.
This cyclic method guarantees that your company always grows and adjusts, promoting a culture of ongoing enhancement and creativity.
Become a certified Lead Auditor with ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course- Sign up now!
When to Implement the PDCA Cycle?
Let’s explore when you can apply the PDCA Cycle. The PDCA Cycle is adaptable and can be used in different scenarios, such as:
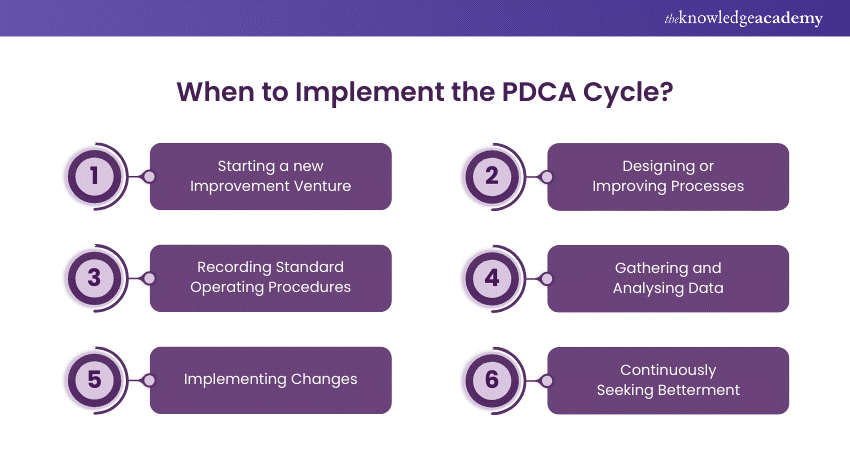
1) Starting a new Improvement Venture: Employ PDCA to decrease defects, improve cycle times, or maximise resource usage.
2) Designing or Improving Processes: PDCA assists in guaranteeing quality and efficiency, whether it involves creating something innovative or improving existing offerings.
3) Recording Standard Operating Procedures: Great for establishing consistency and quality by standardising routine tasks.
4) Gathering and Analysing Data: Collecting and analysing data systematically with the help of PDCA helps identify problems or root causes.
5) Implementing Changes: Whether it's process, organisational, or technological changes, the PDCA Cycle aids in effectively planning and implementing changes.
6) Continuously Seeking Betterment: PDCA promotes a mindset of constant improvement, urging teams to adjust and enhance their efforts consistently.
The Benefits of the PDCA Cycle for Maintenance Teams
The PDCA Cycle, used in maintenance management and other fields, is a popular continuous improvement model. Maintenance workers receive numerous advantages, including:
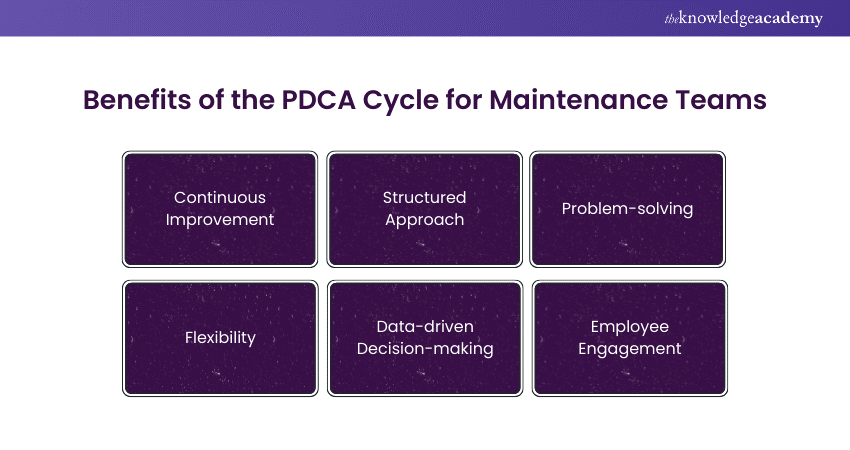
1) Continuous Improvement
The PDCA Cycle promotes a culture of ongoing learning and refining, urging maintenance personnel to seek out opportunities for improvement. This mentality results in superior maintenance results in the long run.
2) Structured Approach
The PDCA Cycle offers a structured method for organising, carrying out, assessing, and making changes to maintenance procedures. This method assists maintenance teams in systematically addressing challenges and enhancing and optimising operations.
3) Problem-solving
The cycle facilitates proactive problem-solving among maintenance personnel by guiding them through in 4 steps. The steps include defining the issue, implementing solutions, evaluating outcomes, and adjusting as needed. This method assists in pinpointing underlying reasons and putting into place successful remedies.
4) Flexibility
The PDCA Cycle enables changes and revisions to be made in response to the outcomes identified in the Check stage. Maintenance staff can enhance processes by implementing needed adjustments when improvements or unforeseen obstacles are identified in the Act phase.
5) Data-driven Decision-making
Data-driven decision-making is highlighted in the PDCA Cycle, allowing maintenance personnel to collect and examine data in the Check phase. This data-based approach allows for well-informed decision-making using facts and evidence, improving maintenance strategies.
6) Employee Engagement
The PDCA Cycle promotes teamwork, fostering participation and involvement of maintenance staff at every level. Enabling team members to share ideas, perspectives, and skills fosters a feeling of ownership, drive, and involvement within the team.
In general, the PDCA Cycle gives maintenance staff a systematic method, a focus on ongoing enhancement, and method for solving problems. It can make data-based decisions, flexibility, uniformity, and increased employee involvement.
It aids in enhancing maintenance procedures and results and cultivating a culture of constant enhancement in the organisation.
Enhance your Auditing skills with ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training- Register now!
Diverse Applications of PDCA
Incorporate the PDCA Cycle as a foundational part of your company's functions and values. It is simple to integrate into various processes, which is why organisations of all sizes and industries favour this approach.
If your organisation is going through a partial Agile transformation, you can begin by implementing PDCA in areas of potential improvement within teams.
One example is implementing the Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle when you:
1) Establish innovative work procedures
2) Start a fresh project to enhance something
3) Improve the design of a product, service, or process
4) Intend to gather and assess information to rank and confirm issues or underlying reasons
5) Create an environment that promotes ongoing enhancement
The PDCA Cycle provides valuable advantages through its transparent, scientific approach to various projects. Empowering the validation of assumptions before acting saves costs and enables testing on a smaller scale, leading to quicker results for teams.
An Example of the PDCA Cycle
Let’s take the example of Regional Blue Hospitals to see how the PDCA Cycle is implemented. Firstly, the hospital forms a team to identify the high frequency of healthcare-related infections (HAIs). In this case, the patients get secondary infections in the hospital. Now, the PDCA team follows this cycle:
a) Plan: The team sets its goals beforehand, such as reducing HAIs by 25%. It also investigates possible causes of the issue, such as a poor air filtration system.
b) Do: The team brief that poor employee training contributes to HAI issues. They plan to apply a complete training program for employees to protect against secondary infections.
c) Check: After a few months, the team creates new training protocols and rules to monitor whether the nurses adhere to them.
d) Act: This cycle will be considered adequate if the training serves perfectly and the PDCA team is satisfied with the outcomes. In contrast, if the training fails to reduce HAIs, the team will revisit and make proper adjustments in strategies.
Conclusion
We trust that this blog has helped you grasp the idea of ‘What is PDCA’ for ongoing improvement. Through strategic and organised methods of preparing, executing, monitoring, and responding to adjustments, businesses can efficiently tackle problems. Also, they can improve operations and promote creativity. The PDCA Cycle facilitates continuous improvement and adaptability in quality management, project development, and daily operations.
Kickstart your journey to ISO 9001 with our ISO 9001 Lead Implementer Certification today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The main aspects of PDCA consist of Plan, Do, Check, and Act. Planning includes recognising issues and creating plans. Implements these strategies in a limited capacity. Check assesses outcomes, while the Act concentrates on implementing required modifications or expanding effective alterations for ongoing enhancement.

The objective of PDCA is to enhance processes, products, or services constantly. Its aim is to systematically identify and address issues, improve standards, and increase efficiency through iterative planning, implementation, evaluation. It also adjusts using data and results.

The PDCA approach is applied for continual enhancement in different areas, such as quality control, project advancement, and operational procedures. It aids companies in methodically recognising problems, executing fixes, and improving procedures. Furthermore, it promotes a mindset of flexibility and continuous improvement.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 9001 Certification, including the ISO 9001 Foundation Course, ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels and provide comprehensive insights into What is ISO 9001.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 9001, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health & Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 17020 Foundation Training
ISO 17020 Foundation Training
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


