We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Looking to give your finances a boost based on last year’s figures? Want to shield your budget from unexpected twists and turns? Look no further—Incremental Budgeting is your financial safeguard!
Incremental Budgeting is a no-fuss, practical approach to financial planning. It’s all about tweaking your next budget with small changes from the last one, keeping in mind any anticipated shifts. Its ease of use and clear-cut process are a hit with organisations that have steady operations.
Dive into this blog, and we’ll unravel the ins and outs of Incremental Budgeting. We’ll shine a light on its perks and pitfalls and dish out some handy tips for making it work wonders for you. By the end, you’ll be clued up on how Incremental Budgeting ticks and how to harness it to polish your financial strategy and command.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Incremental Budgeting?
2) How does Incremental Budgeting work?
3) Steps to Formulate an Incremental Budget
4) Benefits of Incremental Budgeting
5) Limitations of Incremental Budgeting
6) Operational Mechanism of Incremental Budgeting
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Incremental Budgeting?
Incremental Budgeting is a systematic approach to financial planning that builds upon the foundation of the preceding period’s budget. It involves methodically adjusting the prior Budget’s numbers to reflect anticipated shifts, such as inflationary trends, new projects, or other foreseeable developments.
Incremental Budgeting is appreciated for its simplicity and the facility with which it can be implemented, particularly by entities with stable and foreseeable financial activities. However, while widely adopted, this approach may perpetuate pre-existing inefficiencies and lack the impetus for a comprehensive evaluation of current expenditures. Consequently, this might lead to missed chances for cost reduction and improved resource distribution.
How does Incremental Budgeting work?
Budgeting approaches vary in their complexity; some are more adaptable, while others rely on incremental changes.
Incremental Budgeting is of the latter type, offering a straightforward method for projecting future budgets. It uses the current period’s figures as a baseline and adjusts them incrementally to formulate the next period’s budget.
For instance, consider a company that allocated £312,000 for salaries last year. In the upcoming year, they plan to raise salaries by 10% and recruit six additional employees at a base salary of £11,700 each.
The formula for the upcoming year’s budget increase through Incremental Budgeting would be:
|
Next period’s budget=Previous year’s salary× (1+percentage increase) + (Number of new employees×Base salary of new employees) |
This method is particularly effective for educational institutions, government bodies, and large corporations that distribute funds across departments or long-term projects and typically see only minor variations year over year.
Conversely, it may not be the ideal solution for small businesses that need a more agile budgeting system to accommodate rapid changes and innovative shifts.
Steps to Formulate an Incremental Budget
Let’s look at some steps that can be used to formulate an Incremental Budget:
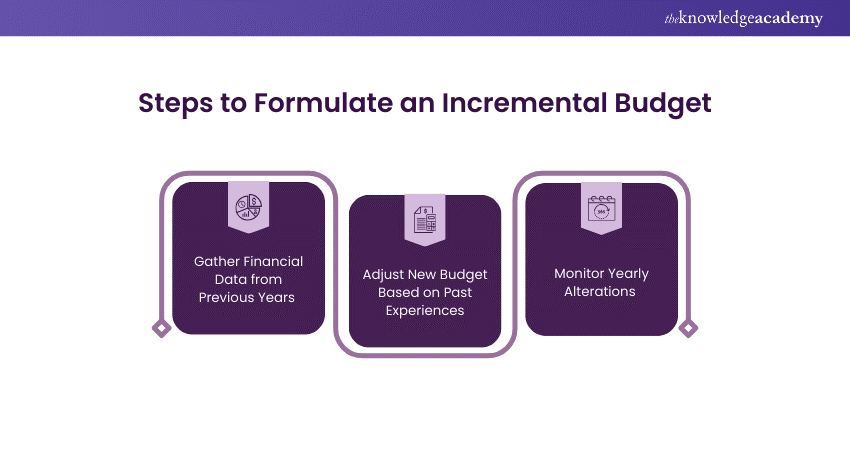
1) Gather Financial Data from Previous Years
Initiate the process by amassing comprehensive financial records from preceding years, including income statements, expense ledgers, and other pertinent financial documentation.
This archival data lays the groundwork for the forthcoming budget, offering a transparent view of previous financial outcomes. A thorough analysis of this data will reveal patterns, consistent costs, and potential areas requiring adjustment.
2) Adjust New Budget Based on Past Experiences
Leverage the accumulated historical data to fine-tune the new budget. Consider various elements like inflationary pressures, shifts in market demand, and the introduction of new ventures or programs.
For instance, if an increase in certain costs is anticipated, adjust the budget to accommodate this expected rise. This phase guarantees that the new budget mirrors projected changes while retaining ties to historical financial experiences.
3) Monitor Yearly Alterations
Maintain vigilant oversight of the budget throughout the fiscal year to confirm its unity with the actual financial performance. Regularly juxtapose the budgeted amounts against the actual expenses and implement adjustments where necessary.
This continuous scrutiny helps pinpoint any variances, facilitates prompt rectifications, and assures that the budget remains pertinent and efficacious in stewarding financial resources.
Are you interested in learning how to prepare for an interview? Then register now for our Interview Skills Training!
Benefits of Incremental Budgeting
There are several benefits of Incremental Budgeting. Let’s have a look at these benefits:
1) Ease of Implementation
Incremental Budgeting stands out for its ease of adoption compared to alternative budgeting methodologies. It utilises the preceding period’s budget as a template, introducing modifications based on projected developments. This streamlines the Budgeting workflow and diminishes the need for extensive time and resources during the budget preparation phase.
2) Consistency and Stability in Operations
This Budgeting approach ensures operational consistency and stability by using the prior budget as a reference point. It enables organisations to sustain ongoing programs and activities with minimal interruption, promoting uninterrupted service provision and operational continuity.
3) Predictable Funding
With its basis in historical budgets adjusted incrementally, Incremental Budgeting offers a predictable financial framework. Predictability aids organisations in planning and resource distribution, mitigating uncertainty and fostering improved fiscal governance.
4) Reduction in Internal Competition
Incremental Budgeting circumvents the need for departmental competition over funding based on performance metrics or needs, thereby reducing internal rivalry. This can cultivate a more collaborative organisational culture, with departments uniting to pursue shared objectives instead of vying for finite resources.
5) Ease of Tracking Changes
With Incremental Budgeting, tracking budgetary shifts is more straightforward due to its application of gradual changes to the existing budget. This clarity in tracking facilitates a better understanding of financial adjustments, promoting transparency in budget administration.
Learn how to create a Budget with our Introduction to Managing Budgets Course- join now!
Limitations of Incremental Budgeting
Even though there are several benefits of Incremental Budgeting, there are certain limitations that you need to look into before you put this into use. Here are some of these limitations:
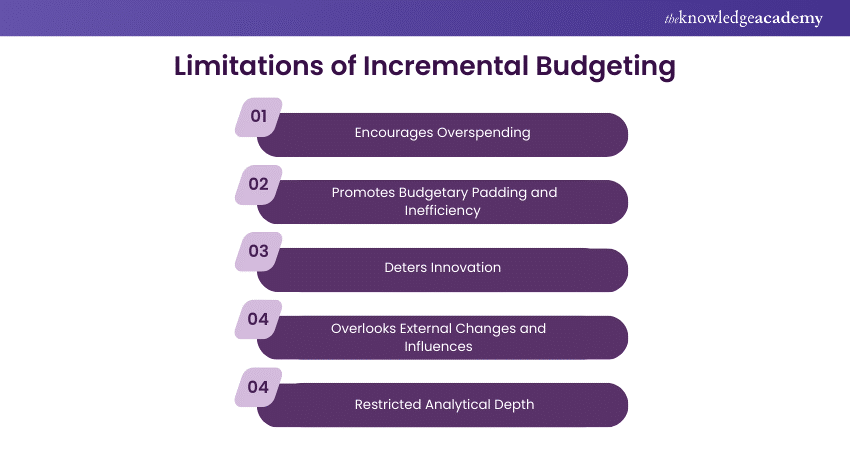
a) Encourages Overspending
Incremental Budgeting can inadvertently lead to a cycle of increased spending. As the new budget is incrementally adjusted from the previous one, departments might overlook a rigorous evaluation of their fiscal needs, potentially incurring extra costs.
b) Promotes Budgetary Padding and Inefficiency
Departments might inflate their budget requests to guarantee ample funding, a practice known as budgetary padding. This behaviour can foster fiscal inefficiency and unnecessary outlays, as securing a larger budget becomes a priority over efficient resource utilisation.
c) Deters Innovation
The nature of Incremental Budgeting, with its emphasis on sustaining current operations, may stifle the pursuit of innovation. Budget allocations, rooted in historical spending, offer limited flexibility for investing in novel projects or seeking inventive solutions to organisational challenges.
d) Overlooks External Changes and Influences
Incremental Budgeting might fail to reflect significant external economic shifts or regulatory updates. This oversight can lead to budgets that are misaligned with the prevailing economic landscape, resulting in suboptimal resource distribution.
e) Restricted Analytical Depth
The Incremental Budgeting methodology, centred on minor adjustments to past budgets, may not provide the depth of analysis required for extensive financial planning. This could restrict an organisation’s capacity to uncover cost-reduction avenues and maximise resource efficiency.
Operational Mechanism of Incremental Budgeting
Incremental Budgeting hinges on systematic adjustments to the preceding period’s budget to accommodate anticipated shifts. It commences with the prior budget as a reference and modifies values to reflect inflation, demand fluctuations, and new projects.
This method streamlines the Budgeting procedure by utilising established financial records and presumptions, curtailing the time and resources necessary for budget formulation.
Conclusion
Incremental Budgeting is like the trusty old recipe you rely on for a family dinner—it’s easy to follow and you know exactly what you’ll get. But just like sticking to the same recipe every time might mean missing out on trying new flavors, relying solely on Incremental Budgeting can lead to splurging where you don’t need to and sticking to the same old ways, even when they’re not working so well.
Do you want to learn how to adapt to working routines or environment changes? Then register now with our Stress Management Course!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which companies use Incremental Budgeting?

Incremental Budgeting is a favoured financial planning method among large organisations, educational institutions, and government agencies.
What is the principle of Incremental Budget?

The principle of Incremental Budgeting revolves around using the existing budget as a baseline and adjusting by adding or subtracting incremental changes for the next period.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses , including the Introduction to Managing Budgets, Time Management Training, Attention Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into How to Create a Marketing Budget.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Budgeting, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Budgeting skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Managing Budgets
Introduction to Managing Budgets
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


