We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Are you preparing for a Blockchain interview? Mastering Blockchain Interview Questions demands a deep understanding, as they can range from fundamental concepts to real-world applications.
This blog is your ultimate preparation guide. We've compiled a list of the most common Blockchain Interview Questions to help you ace your next interview. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced Blockchain professional, these questions will test your understanding of the technology and its applications. Get ready to impress potential employers with your Blockchain expertise!
Table of Contents
1) Beginner-Level Blockchain Interview Questions
2) Intermediate-Level Blockchain Interview Questions
3) Advanced-Level Blockchain Interview Questions
4) Conclusion
Beginner-level Blockchain Interview Questions
In this section, we will explore the beginner-level Blockchain Interview Questions:
1) What do you Understand by Blockchain Technology? How Does it Work?
Blockchain is a decentralised, immutable record of economic activity that may be used to record nearly any exchange of value, not just money.
A Blockchain is a continuously expanding digital ledger that maintains an unalterable, secure record of all transactions that have ever occurred.
Simply described, it is an immutable distributed database that is administered by a group of computers but is not owned by any one organisation. Blockchain data is kept as flat files or databases. Without the need for a third-party middleman like a bank or the government, it may be used for the secure transfer of money, property, contracts, etc.
2) What are the Key Features of Blockchain?
The key features of Blockchain Technology are as follows-
a) Decentralised systems
b) Distributed ledger
c) Faster settlements
d) Low transaction fees
e) Immutability
f) Safe and secure ecosystem
g) Minting
3) State the Different Types of Blockchains.
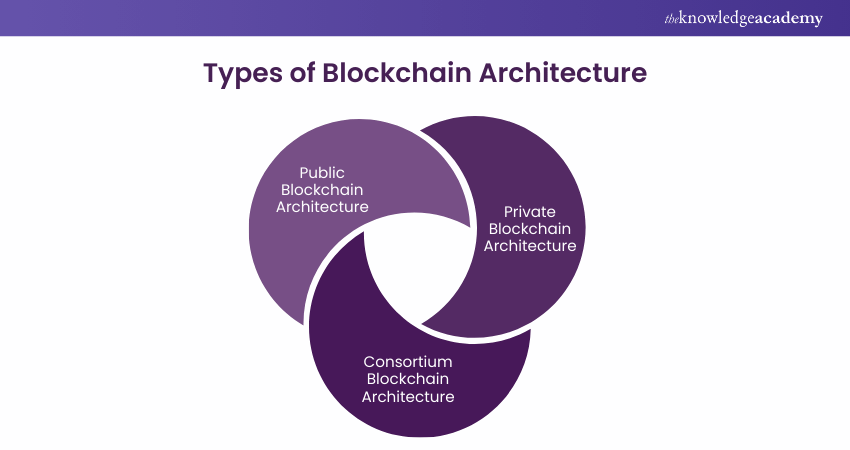
Public, Private, and Consortium Blockchain are the three different types of Blockchain.
a) Public Blockchain ledgers are visible to all web users, and any user can authenticate and add a block of transactions to the Blockchain. Bitcoin and Ethereum are two examples
b) Private Blockchain ledgers are visible to internet users, but only certain employees of the company have the ability to validate and add transactions. It is a permissioned Blockchain, meaning that even while the data is accessible to everyone, the organisation itself chooses who gets to control it. Blockstack is an example.
c) In Consortium Blockchain, only specific nodes are in charge of the consensus process. Ledgers, however, are accessible to everyone through the consortium Blockchain. Ripple is an example.
4) Differentiate between Ethereum Blockchain and Bitcoin Blockchain.
|
Criteria |
Bitcoin |
Ethereum |
|
Consensus mechanism |
Proof of work |
Proof of stake or work |
|
Concept |
P2P currency |
P2P currency and smart contract |
|
Hashing Algorithm |
SHA-256 |
Ethash |
|
Time taken to mine a block |
10 Minutes (approx.) |
12-15 seconds |
|
Reward |
12.5 BTC |
3 ETH |
|
Transaction fee |
Optional |
A fee is calculated in gas |
|
Value |
1 BTC = 6934.34 USD |
1 ETH = 278.98 USD |
5) What do you Understand by a Block in Blockchain Technology? How is it Recognised?
Every block in this online ledger essentially consists of transaction information, a time stamp, and a hash reference that serves as a connection to the block that comes before it.
6) Where is a Blockchain Stored?
A flat file or a database can be used as a storage platform for Blockchain.
7) What are the two Types of Records Available in the Blockchain Database?
A Blockchain database has two different kinds of records.
a) Transactional Records
b) Block Records
The finest aspect is that without using complicated algorithms, it is possible to combine both of these records with one another.
8) What is a Smart Contract in Blockchain?
This is an important question in the list of Blockchain Interview Questions.
Self-executing contracts, known as "smart contracts ", include the terms and conditions of an agreement between peers.
Some application examples include:
a) Transportation: Smart contracts make it simple to track the delivery of products.
b) Protecting copyrighted content: Smart contracts can safeguard ownership rights for things like music or books.
c) Insurance: False claims can be detected via smart contracts, and they can also be stopped.
d) Employment contract: Smart contracts can be useful in facilitating wage payments
9) Where and how do Nodes run Smart Contract Code?
On the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), nodes execute smart contract code. It is a virtual machine created to function as a runtime environment for smart contracts built on Ethereum.
EVM is used in a sandboxed setting (isolated from the main network). This setting is ideal for testing.
Once your smart contract has been tested and verified, you can deploy it on the main network after downloading the EVM and running it locally in an isolated environment.
10) How can you Identify a Block?
Each block contains four fields:
1) The block's prior hash value (thereby getting linked in a Blockchain)
2) Details of numerous transaction data are included
3) The nonce is one of its values. A nonce is a random number that is used to change the hash value in order to get a hash value that is less than the target
4) Hash of the block itself. It serves as both a block's alphanumeric identification value and digital signature
The block can only be identified by its hash address. It is a 64-character hex value that contains both letters and digits. The SHA-256 algorithms are used to obtain it.
11) Discuss the Elements of a Block in Blockchain.
These are the vital elements that every block should consist of:
a) A hash pointer to the previous block
b) Timestamp
c) List of transactions
12) How does Blockchain Differ From Relational Databases?
The difference between Blockchain and Relational Database is shown in the below table:
|
Point of Difference |
Blockchain |
Relational Database |
|
Data unit |
Measured in Block |
Measured as a Table |
|
Failure occurrence |
No chance of occurrence of failure |
Chances of failure can happen |
|
Centralised Control capability |
Blockchain has the feature of Centralised control |
Relational Database lacks this capability |
|
Possibility of Data Modification |
Data Modification is not possible in this technology |
Data Modification is possible in Database. |
|
Existence of single point of Failure |
Single point of failure does not exist here |
Single point of Failure exists in relational database |
13) What is the Principle on Which Blockchain Technology Is Based on?
It makes it possible to share information across users without it being duplicated.
14) What are the Benefits of Blockchain Technology?
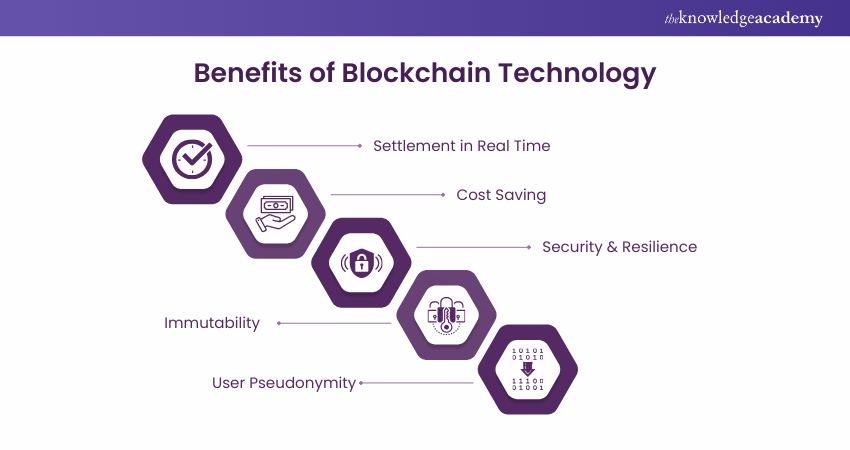
a) Settlement in Real-Time: Blockchain accelerates trade settlement in the financial sector by providing a single, mutually agreed-upon version of data. This eliminates the need for lengthy verification, settlement, and clearance processes.
b) Cost-Saving: By removing the need for third parties like banks in peer-to-peer transactions, Blockchain reduces overhead expenses associated with trading assets.
c) Security and Resilience: Blockchain employs advanced cryptography to safeguard data from fraud and hacking attempts, ensuring robust security.
d) Immutability: Transactions are recorded chronologically, making the Blockchain's operations unchangeable. Once a block is added to the ledger network, it cannot be altered or deleted.
e) User Pseudonymity: Users interact using a consistent, detectable identifier without revealing their real names, maintaining privacy while allowing administrators to access genuine identities.
15) Discuss whether it is possible in Blockchain to remove one or more blocks from the networks.
Yes, it is possible. Sometimes, only a particular section of this online ledger should be taken into account. This may be accomplished quickly and easily without putting in a lot of work with the use of default choices and filters.
16) What is cryptography? What is its role in Blockchain?
Blockchain secures users' identities using cryptography and with a hash function, ensures that transactions are secure.
To encrypt and decrypt data, cryptography employs public and private keys. A public key in the Blockchain network can be shared with all Bitcoin users, but a private key (similar to a password) is kept secret from the users.
Blockchain employs SHA-256, which is secure and generates a unique hash output for each input. The basic feature of this algorithm is that it will return a standard alphanumeric output of 64 characters regardless of the input. It is a one-way function that can generate an encrypted value from input but not vice versa.
Learn the fundamentals of Blockchain 101 and Ethereum. Sign up for our Ethereum Developer Training now!
17) What is a Genesis Block?
1) The genesis block, also known as block ‘zero’, is the first block in the Blockchain.
2) It is the only block in Blockchain that does not refer to the block before it.
3) It determines the parameters of the Blockchain, such as the level of difficulty, consensus process, and so on, in order to mine blocks.
18) What is a Dapp and How is it different from a Normal Application?
1) A Dapp is a Decentralised Application that is launched utilising smart contracts.
2) A Dapp's back-end code (smart contract) runs on a decentralised peer-to-peer network.
3) Its process consists of the following:
a) Front-end
b) The smart contract (backend)
c) Blockchain (P2P contract)
Normal application:
1) A normal application has back-end code that runs on a centralised server.
2) It is a computer software application that is hosted on a central server.
3) Its process is made up of the following:
a) Front-end
b) API
c) Database
19) What is the very first thing you must specify in a Solidity file?
A version number of Solidity is necessary to be defined at the start of the code as it removes the chances of incompatibility errors that can arise when compiling with another version. This is an essential clause that needs to be at the top of any Solidity code one writes.
20) What is the nonce and how is it used in mining?
In Blockchain, a process known as mining is used to validate transactions by solving a difficult mathematical puzzle, called Proof of Work (PoW). This process is used to find a number (nonce) along with a cryptographic hash algorithm to produce a hash value lower than a calculated target. To ensure that the final hash value meets the hash conditions, the nonce is a random value used to vary the value of the hash.
21) Why is Blockchain a trusted approach?
A Blockchain is considered to be a trusted approach due to the following reasons:
1) Due to the open-source structure, it is simply compatible with other business applications.
2) Encrypted, safe, and hacking-proof.
3) No central authority is present to control it.
4) How transactions get inserted into the Blockchain, is agreed upon by all Participants.
5) The transaction is immutable i.e., once the transaction is inserted into the Blockchain, one cannot change it.
22) What do you mean by DAO?
A Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO) is an entity that operates both autonomously and decentralised, guided by rules encoded in a transparent computer program. Controlled by shareholders and independent of central government influence, DAOs represent the most complex form of smart contracts. They exist autonomously online but rely on people for tasks beyond their capabilities.
DAOs' financial transactions and rules are recorded on a Blockchain, enabling various parties to exchange value and reach agreements. Whether devices communicate with people or other devices, DAOs function automatically and immutably as programmed in their smart contracts, ensuring seamless and autonomous operations.
23) What do you Mean by Coinbase transaction?
The first transaction in a block is called as a Coinbase transaction. It is known to be a unique type of bitcoin transaction that is created by a miner. For their work, they use this transaction to collect the block reward, and in addition, any other type of transaction fees collected by the miner is also sent into this transaction.
Learn how bitcoins work and how to secure bitcoins. Register for our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course now!
Intermediate-level Blockchain Interview Questions
1) List Some Popular Platforms for Developing Blockchain applications
Some of the most popular platforms for developing Blockchain applications are:
a) Ethereum
b) Hyperledger Sawtooth
c) Quorum
d) Ripple
e) R3 Corda
f) Qtum
g) IOTA
h) EOS
2) Can you Modify the Data in a Block?
You cannot change the data within a block. You must also remove the data from any other related blocks if any update is necessary.
3) What do you Understand About the Security of a Block?
Well, a block or the whole Blockchain is secured by a strong cryptographic hash algorithm. Every block has a different hash pointer. The block's hash identification will change whenever any of the block's components are altered. As a result, it provides a prominent level of security. The safety and security of the data contained in a block are, thus, not a concern.
4) What is the Merkle Tree? How is it Important for Blockchains?
A block is verified using a data structure called a Merkel Tree. It has the shape of a binary tree and contains the block's individual cryptographic hashes. The leaf node of a Merkle tree is a hash of a block of transactional data, and each non-leaf node is a hash of its leaf node. This system is similar to that of a binary tree. The resulting hash root of all transaction hashes is known as the Merkel root. It includes all the transactions supporting every non-leaf node.
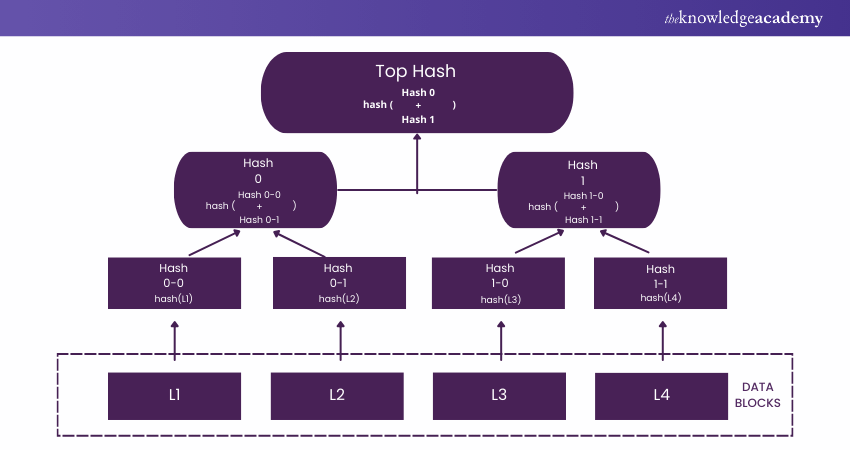
An essential component of Blockchain technology is the Merkle tree. There is no need to download the full block to verify a single transaction in a block if someone only needs to confirm its presence. It is limited to downloading the block header chain. It enables downloading a collection of the transaction's branch from the tree, which is sufficient. The hashes that are pertinent to your transactions are checked.
5) What is a ledger? List the different types of ledgers in Blockchain.
A ledger is a continuously expanding file. All the exchanges between two parties on the Blockchain network are permanently recorded by it.
Users of the Blockchain can take into account one of three popular types of ledgers:
1) Centralised Network
2) Decentralised Network
3) Distributed Network
6) Which cryptographic algorithm is used in Blockchain?
SHA-256 Hashing Algorithm is used by Blockchain. This algorithm was developed by the National Security Analysis (NSA) in the USA.
7) In what order are the blocks linked in the blockchain?
Each block is linked in backward order in the Blockchain. It means each block is linked with its previous block.
8) What is Double Spending? Is it possible to double spend in a Blockchain system?
Double spending implies spending the same money more than twice. The double-spending problem can never arise in a physical currency, whereas in digital money like Bitcoin, this problem can arise. Therefore, in Bitcoin transactions, there remains a possibility of copying and rebroadcasting, resulting in the possibility that the same bitcoin could be spent twice or more by its owner. Blockchain technology’s primary aim is to eliminate the approach up to the greatest possible extent.
9) Blockchain vs Hyperledger - What's the Difference?
Blockchain is a decentralised system made up of immutable records, or blocks, that are encrypted and safeguarded. A platform or organisation called Hyperledger enables the creation of private Blockchains.
While Hyperledger only allows for the creation of private Blockchains, Blockchain allows for the creation of both public and private Blockchains.
Hyperledger is a private Blockchain technology with access to Blockchain data and is restricted to predetermined users, configurations, and programming. Blockchain is separated into public, private, and consortium Blockchains.
While Hyperledger is largely utilised for enterprise-based solutions, Blockchain can be used in a variety of sectors, including business, government, healthcare, etc. Public Blockchain refers to the use of Blockchain over the internet in all contexts, while Hyperledger-based Blockchain solutions are designed for intranet use within an organisation.
10) Is Blockchain Different From Banking Ledgers?
Blockchain is thought to be incorruptible. Not to forget the energy needed to power the computers required for the Blockchain system to function; should that occur, the person would take all reasonable measures to avoid being recognised.
11) How are Blockchain Distributed Ledgers Different From Traditional Ledgers?
|
Properties |
Distributed Ledger |
Traditional Ledger |
|
Operations |
Only Insert Operations |
Performs C.R.U.D. |
|
Replication |
Replication of every block on each peer |
Multi Master and Master- Slave |
|
Consensus |
Most of the peers agree on the outcome of transactions |
Distributed Transactions |
|
Invariants |
Anybody can validate transactions across the network |
Integrity Constraints |
12) Do you know the difference between Blockchain and Database?
|
Blockchain |
Database |
|
Blockchain is Decentralised. Because there is no administration present, everyone is in charge. |
It has a centralised database. All of the data is within the authority of administrators. |
|
Reading and writing are rights for everyone. |
Only those with permission are able to read and write. |
|
Peer-to-peer technology. |
Server-client architecture |
|
Only the append operation is permitted here. |
It is possible to use a CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) mechanism. |
|
Digital records with historical information. |
No ownership records exist. |
|
Blockchains are completely private |
Databases are not completely private. |
|
Blockchain is inefficient since it is reliant on hash rate. |
Because there are fewer individuals managing the database, it is quick. |
|
Blockchain is an open network. |
The database is password-protected. |
13) Name some of the universally used Cryptographic algorithms in Blockchain.
Below are a few universally used Cryptographic algorithms in Blockchain:
a) SHA - 256
b) Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
c) Triple DES
d) Ethash
e) Blowfish
14) Explain what happens when you try to deploy a file with multiple contracts.
In Blockchain, deploying a file with multiple contracts is not possible. The compiler only deploys the last contract from the uploaded file, and the remaining contracts are neglected.
15) How will you handle the risk management when it comes to securing the transaction records?
Risk Management is the process of locating all the threats and vulnerabilities to the financial records of an organisation. With this approach, one best thing that can be done is taking the right countermeasures against them immediately.
A second approach is to pay attention to a backup plan. Based on the value of information, other approaches like buying new risk management software can be simply considered. The main risk to information is from the black-hat hackers.
16) What are the core requirements for a Business Blockchain?
The core requirements of a Business Blockchain includes, a shared ledger, smart contract functionality, trust and privacy.
17) How is the Hash or Block Signature Generated?
The process of generating a block signature involves the following steps:
a) Hashing Transaction Details: Pass the transaction details through a one-way hash function, such as SHA-256.
b) Creating the Digital Signature: Run the resulting hash through a signature algorithm (e.g., ECDSA) using the user’s private key.
The final output, an encrypted hash along with additional information (such as the hashing algorithm used), forms the digital signature.
18) What is the Difference Between Ethereum and Bitcoin?
|
Bitcoin |
Ethereum |
|
Introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 |
Introduced by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 |
|
Primarily a Cryptocurrency |
A Cryptocurrency that also supports executable codes and smart contracts for DApps |
|
Average block time is 10 minutes |
Average block time is 10-15 seconds |
|
Turing incomplete |
Turing complete |
|
Uses Proof of Work (PoW) |
Transitioned from PoW to Proof of Stake (PoS) in September 2022 |
|
Native Cryptocurrency is Bitcoin (BTC) |
Native Cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH) |
Learn to create and deploy your Private Blockchain on Multichain. Check out our Blockchain Training Course today!
Advanced-level Blockchain Interview Questions
1) What are the steps involved in the Blockchain Project Implementation?
This process involves 6 steps, which are:
1) Requirement identification
2) Screen ideas consideration
3) Project development for Blockchain
4) Feasible study on the security
5) Implementation
6) Controlling and monitoring the project
2) Differentiate between Centralised Network, Decentralised Network and Distributed Ledger.
1) Distributed ledger: It is a shared ledger that is not under the control of a single entity. It functions as a database for financial, legal, or electronic assets and is decentralised by nature.
2) Centralised network: A network with centralised authority can operate more efficiently.
3) Decentralised network: Each node in a decentralised network has a complete copy of the network configurations and is not reliant on a single server point.
6) What are the Important Elements of the Blockchain Ecosystem?
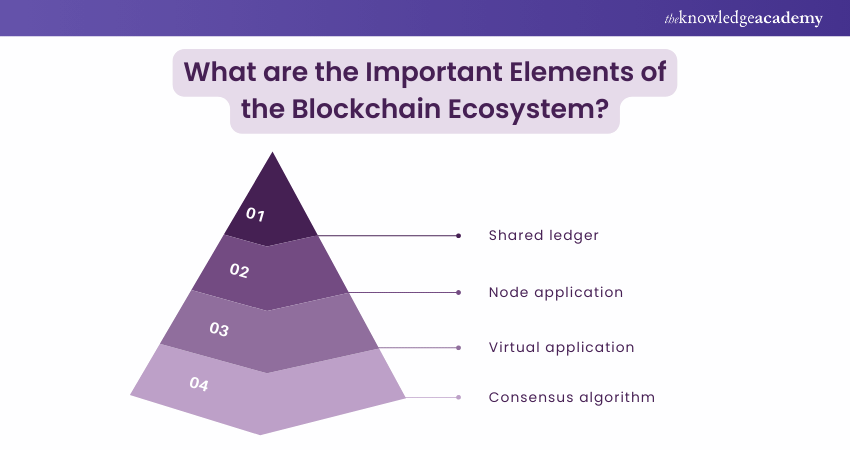
The Blockchain has four major elements:
a) Shared Ledger - It's a key element of the Blockchain and is decentralised in nature.
b) Node Application - It is software that lets your computer connect with the Blockchain. Ex: Bitcoin uses the bitcoin wallet application to detect each mode on the network.
c) Virtual Application - It handles all the tasks that Blockchain undertakes.
d) Consensus Algorithm - This is used to control the Blockchain's rules, which determine how each node can conclude.
5) What are some of the popular Cryptocurrencies?
Some of the well-known Cryptocurrencies are:
a) Bitcoin (BTC)
b) Ethereum (ETH)
c) Ripple (XRP)
d) Litecoin (LTC)
e) Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
6) What are Blockchain Durability and robustness?
In the year 2008, Bitcoin was established. Since then, there has been no damage done to the Bitcoin network. For close to 30 years, the internet proved to be a trustworthy resource. It’s a track record that shows a bright future of Blockchain technology.
7) Name some of the popular consensus algorithms?
Some of the well-known Consensus Algorithm includes:
a) Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
b) Proof-of-work (POW)
c) Proof-of-stake (POS)
d) Delegated proof-of-stake
e) Proof of elapsed time
8) Explain the Difference Between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof of Work (PoW):
In Blockchain, PoW is the method used to solve a complicated mathematical puzzle called mining. The amount of computation a miner performs determines the likelihood of mining a block in this case. The cryptographic puzzle requires a lot of processing power, which miners invest in hardware to solve.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
PoS is a PoW substitute in which Blockchain tries to achieve distributed consensus. The quantity of tokens you possess determines your likelihood of validating a block. The more opportunities you have to validate a block, the more tokens you possess. It was developed as a way to reduce the consumption of costly resources used in mining.
9) Describe a Real-life use Case of Blockchain Technology.
Smart contracts in supply chain management offer ongoing validation and transparency of transactions handled by numerous supply chain parties.
10) Explain the Various Parts of EVM Memory.
An EVM has three distinct types of memory:
1) Storage
a) The Blockchain network permanently retains storage values.
b) It is incredibly costly.
2) Memory
a) Memory is a transitory, customisable storage.
b) It is only accessible when a contract is being executed. Upon completion of the execution, its data is lost.
3) Stack
a) A stack serves as transient, immutable storage.
b) In this case, the content is lost when the execution is finished.
11) Why does Blockchain Need Coins or Tokens?
A Blockchain needs tokens or coins because they are used as a medium of exchange between the states. Within a Blockchain, these are digital assets built to perform a particular function. For instance, when a transaction is carried out by someone, there is a change of state, and coins are moved from one address to another one. In addition, transactions carry some additional data, which can be mutated through the change of state.
Because of this reason, to incentivise the participants to join their network, Blockchains need tokens or coins.
12) What is Mining?
Mining, in reference to Blockchain Technology, is defined as the process of addition of transactions to the large distributed public ledger by giving the proof of work to the network, i.e., validating the generated block. Mining also adds new coins to the generated block. Mining as a term is best known for its association with bitcoin.
13) What do you Understand by a 51% attack?
A miner or group of miners seeking to control more than 50% of a network's mining power, computational power, or hash rate is known as a "51 per cent attack" on a Blockchain network. The attacker of this attack has the ability to prevent the confirmation or execution of additional transactions. Moreover, they can undo transactions that have already been confirmed when they were in charge of the network, which creates a problem with double-spending.
14) Differentiate Between Off-chain Transactions and On-chain Transactions?
On-chain transactions:
All nodes on the Blockchain network can see these transactions because they are available on the Blockchain. It involves a predetermined number of parties authenticating and validating a transaction.
Off-chain transactions:
These transactions, which can be executed in a variety of ways, deal with values outside the Blockchain.
15) What is a Public Key?
A Public Key is made consists of line of alphanumeric characters. These are specifically related to a particular address or node. In a Blockchain, a Cryptographic algorithm facilitates peers to obtain funds in their blockchain wallet using a Public Key.
When a public key connects with a private key are connected, pair of keys are created. The usage of private-public key pair is to ensure that the Blockchain’s security is maintained.
16) What is a Private Key?
A private key, consisting of an alphanumeric term is used to encrypt and decrypt data associated with a public key. A private key is also a component of the cryptographic algorithms in Blockchain security.
The key is allocated to the key generator and can only be used by the user. If the user fails, somebody else can gain access to the wallet’s information as well as the address for which the private key is stored.
17) What is Transparent and Incorruptible in Blockchain?
Once in, every 10 minutes, a Blockchain network checks itself to ensure that is in state of consensus. The network functions as a digital value’s self-auditing ecosystem that conforms to any transaction that occurs in ten-minute intervals. A “block” is a collection to these transactions.
Transparency data as a definition is available as it is embedded in the network as a whole. It is not easy to tamper because a change in every single unit of data will require an extensive amount of computational power to evade the entire network.
18) What are Function Modifiers in Solidity? Name the Most Extensively Used Modifiers.
Utilising function modifiers in Solidity, you can quickly change how your smart contract functions behave. Basically, it can offer new functionality or impose constraints on how well smart contracts work. The following are the most frequently used function modifiers in Solidity:
a) View, which are operations that have no influence over a smart contract's state and have read-only capabilities.
b) Pure, are operations that do not read or write a smart contract's state. They both provide the same outcome based on their input values.
19) What is the Fork? Explain its Types.
The phrase "forking" refers to the process of altering a cryptocurrency system or code. A fork indicates that a Blockchain separates into two branches. It may take place if the networks' users are unable to agree on the consensus method and new guidelines for transaction validation.
Three different forking types are:
1) Hard forks
2) Soft forks
3) Accidental forks
20) What Happens if the Execution of a Smart Contract Costs More Than the Specified Gas?
Your transaction will initially be carried out, but if the cost of carrying out a smart contract exceeds the allotted gas, the miners will stop verifying your contract. The transaction will be marked as unsuccessful on the Blockchain, and the user will not receive a refund.
21) What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is defined as a digital asset (currency) that can be used to exchange value between parties. It uses strong cryptography to verify and secure financial transactions and also control the creation of new units of that currency. Since it is a digital currency, it doesn’t exist physically. Examples of popular cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Litecoin, Z-Cash, Monero, Dash, etc.
It is well known that government prints fiat currencies like Dollars, Euros, or Rupees. That implies, there is a centralised institution that can create thousands or millions more of that currency. Bitcoin, unlike the fiat currencies, is created by the same mathematical formulae which make cryptography work.
Therefore, cryptocurrencies use decentralised control, that works through distributed ledger technology which serves as a public financial transaction database.
22) What are the Limitations of Blockchain?
The major shortcomings of Blockchain include the following:
a) Shortage of Technical Talent: Blockchain technology suffers from a lack of skilled developers. While other fields have abundant talent, Blockchain expertise is scarce, hindering its development.
b) Size of Network: Blockchain's effectiveness relies on a vast network of users. However, this distributed grid of nodes can make the system less resistant to attacks and slower to respond.
c) Consensus Mechanism: Achieving consensus in Blockchain requires significant time and resources due to the dependency on the network size and the number of nodes, slowing down block creation.
d) Transaction Speed and Costs: As Blockchain networks grow, transaction costs increase, making it less efficient for money transfers. By 2016, transactions cost around £0.17 and processed seven per second.
e) Security Flaw: The 51% attack is a major security flaw where a group of miners controlling over half the network's computing power can manipulate transactions, posing a significant risk.
23) What is Encryption? What is its Role in Blockchain?
Encryption is defined as the process of converting data or information into a code to prevent unauthorised access. It helps organisations to secure their data. In this technique, data or information is encoded or changed into an unreadable format to some extent before it is sent out of a network by the sender. The only thing that a receiver can understand is how to decode the same.
This approach is very useful in Blockchain Technology as it makes the overall security and authenticity of blocks and help to keep them secure.
24) How Does the Security of a Block Works?
A chain of blocks in a Blockchain contains a record of transactions. A block is considered to be the most secure part of a Blockchain. Through a cryptographic hash algorithm, the record of a blockchain is protected. The connection of each block with all other blocks before and after it is done through a distinctive hash pointer which also adds security to the block.
This hash is basically a security identifier that provides a reasonable level of security to the whole Blockchain. If within a block the value is modified, there will be a change in the hash value.
To make changes to the block information, hackers also need to know the hash key of the previous block. For such hackers, Blockchains are decentralised across peer-to-peer networks that get continuously updated and keep syncing. These records are not contained in a centralised location, hence Blockchain don’t have a single point of failure and also can't be changed from a single computer.
25) What is the Difference Between Public and Private Key?
A private key is used to lock or encrypt a message sent on a Blockchain Network. Using the public key of the receiver, a sender can send a message. On the other hand, using a private key, a receiver can decrypt the message or the transaction. By using the public and private keys, any communication or transaction is kept tamper-proof and safe.
26) How Does Bitcoin use Blockchain?
A transaction happens when there is a value transfer between Bitcoin wallets that gets included in the Blockchain. A secret piece of data known as a private key is kept by Bitcoin wallets. The usage of this private key is to sign transactions and provide mathematical proof that have come from the owner of the wallet.
27) What is Consensus Algorithm?
The method of achieving consensus on a change of data over the system or distributed network is termed a Consensus Algorithm. This algorithm is extensively used in Blockchains as they permit the network of unknown nodes so that it reaches a consensus on the data that is being shared or stored through the blockchain.
28) What are the Types of Consensus Algorithms?
There are different types of consensus algorithms widely known, out of which the popular ones are listed below:
a) Proof-of-Work (PoW)
b) Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
c) Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
d) Proof-of-Authority (PoA)
e) Proof-of-Elapsed Time (PoET)
f) Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Conclusion
Armed with these Blockchain Interview Questions, you're well-prepared to impress potential employers. Practice your answers, showcase your understanding of Blockchain technology, and confidently step into your blockchain career!
Become a Blockchain expert with our in-depth Blockchain Trainings. Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Blockchain Training Course
Blockchain Training Course
Thu 6th Feb 2025
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


