We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever wondered how devices within a computer network exchange data and communicate? The answer lies in network topology—the structural arrangement of cables, nodes, and other elements that form the network’s infrastructure. One of the most commonly used topologies is Ring Network Topology, which is characterised by its circular configuration that interconnects all devices within the network.
In this blog, we will explore the fundamentals, intricacies, and technical aspects of Ring Network Topology, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this elegant and efficient networking framework. Get ready to unravel the beauty of seamless connectivity in action!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Ring Topology?
2) How Does Ring Topology Work?
3) Applications of Ring Topology?
4) Advantages of a Ring Topology
5) Disadvantages of a Ring Topology
6) Devices using Ring Topology
7) Devices Using Ring Topology
8) Data Transmission Steps in Ring Topology
9) How Does Data Travel in Ring Network Topology?
10) What Happens if a Node Fails in Ring Network Topology?
11) Conclusion
What is a Ring Topology?
Ring Topology is a network configuration where devices are connected in a circular pattern, with data passing sequentially between neighbours. It efficiently handles high traffic loads and is more reliable than bus topology. Typically unidirectional, some versions use bidirectional communication to enhance redundancy.
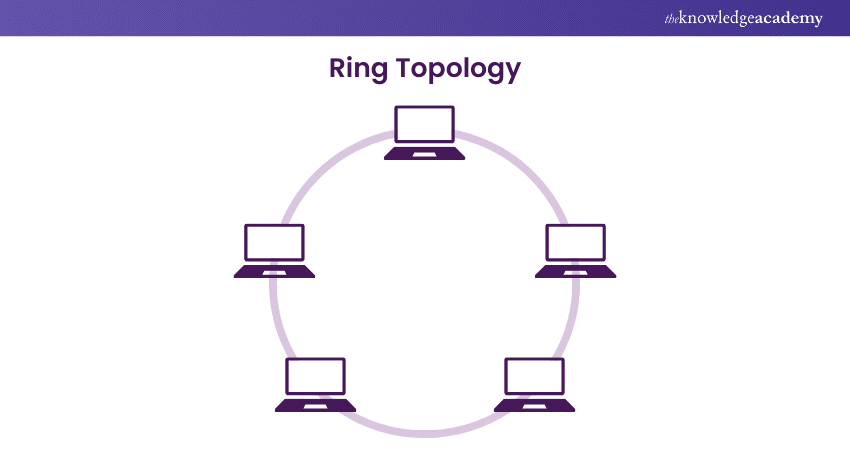
Common in LANs and WANs, it operates without a central hub, relying on network cards and cables like RJ-45 or coaxial. While easy to install and troubleshoot, a single node failure can disrupt the network. Dual-ring structures mitigate this risk, making Ring Topology a key concept in CCNA certification and network design.
How Does Ring Topology Work?
Ring Topology is a network configuration where each node is connected to two others, forming a circular data path. Here’s a refined explanation of how data transmission occurs in a Ring Topology:
a) Token Circulation: When no data is being sent, a token, which is a special data packet, circulates around the ring. The network can operate at speeds ranging from 16 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
b) Token Acquisition: When a node wants to send data, it captures the circulating empty token, fills it with the data frame, and includes the destination node’s MAC address and identifier.
c) Data Transmission: This filled token is then passed along the ring to the next node.
d) Token Reception: Each node examines the incoming token to see if it is the intended recipient. If so, it copies the data from the token, marks the token as read, and forwards it to the next node.
e) Data Delivery: This process continues until the token reaches its intended destination.
f) Acknowledgement: Once the original sender node gets the token back and sees that the data has been read, it removes it from the token, rendering it empty again.
g) Token Reuse: The now empty token is released back into the ring for any node that needs to transmit data.
h) Fault Tolerance: If a node fails or is not transmitting data, and if the network supports a dual-ring structure, the data can be sent in the reverse direction to reach its destination.
This system ensures efficient and orderly data transmission, with the token acting as a ‘baton’ that nodes pass to communicate within the network. These processes are crucial for understanding key responsibilities outlined in a network engineer job description.
Do you want to learn how you can design, install and support business critical network switches? Register now for our CCNA Certification Course now!
Importance of Ring Topology
Ring Topology is chosen for its distinct characteristics that align with specific network requirements and constraints. Here, Ring Topology is used, considering various factors:
Factors Influencing Topology Choice:

a) Budget Allocation: Financial resources available for network setup and maintenance.
b) IT Complexity: The intricacy of the existing IT infrastructure.
c) Operational Model: How the organisation functions and its networking needs.
d) End-user Performance: The expected level of network service for the end-users.
Reasons for Selecting Ring Topology:
a) Minimal Collision Risk: The unidirectional data flow in a Ring Topology greatly reduces the chances of data collisions.
b) No Central Control: It eliminates the need for a central network server to manage data transmission, simplifying the network structure.
c) Speed: Data transmission is swift, facilitating faster communication between nodes.
d) Cost-effectiveness: Ring Topology networks are economical, making them a budget-friendly option.
e) Ease of Expansion: Adding new nodes or making changes is straightforward, simplifying network administration.
These reasons highlight the practicality of Ring Topology in scenarios where budget, simplicity, and efficient data handling are key considerations. Understanding these aspects is key to appreciating the importance of CCNA, as it helps professionals make informed network design decisions.
Applications of Ring Topology
Ring Topology is versatile and finds application in various network configurations, including both Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs). Here’s a refined description of its applications:
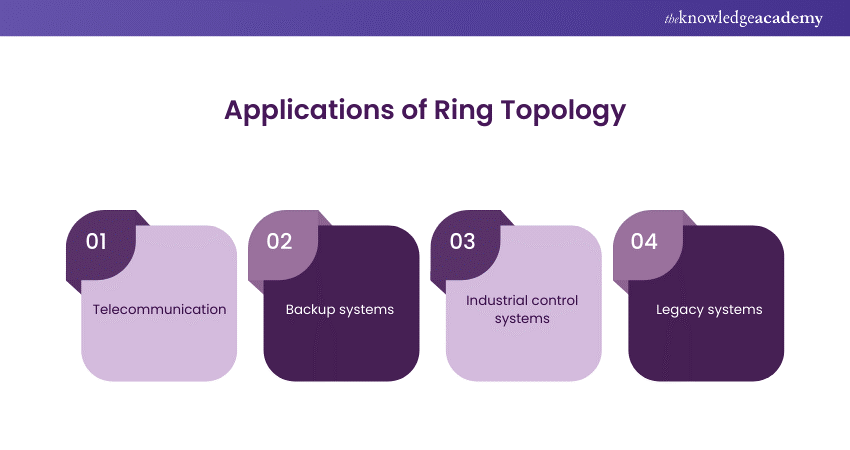
a) Telecommunications: Due to its high bandwidth and fault tolerance capabilities, it is widely used in the telecommunications sector, particularly in Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) fibre optic networks.
b) Backup Systems: Organisations often implement Ring Topology as a secondary, fail-safe network arrangement to support their primary network infrastructure.
c) Industrial Control Systems: In industrial settings, Ring Topology connects devices like sensors, controllers, and actuators. Its reliability ensures uninterrupted communication and control by rerouting data in case of a break.
d) Legacy Systems: While Ethernet dominates modern networks, older systems might still use Ring Topology. Upgrading these systems is often not cost-effective, but ring topology remains functional for specific purposes.
Overall, Ring Topology’s ability to handle high-speed data transfer and provide a reliable backup makes it a practical choice for various networking needs. Understanding the difference between CCNA and CCNA Security improves the effective use of Ring Topology by covering different network management and security aspects.
Do you want to learn the essentials of interconnecting CISCO Networking Devices? Sign up now for our Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Course now!
Advantages of a Ring Topology
Ring Topology offers several benefits, which are listed below:
a) Unidirectional Data Flow: Data moves in a single direction, minimising the likelihood of data packet collisions.
b) Decentralised Management: No central node or server needs to manage the connectivity between workstations.
c) High-speed Transfers: Workstations can exchange data at high speeds.
d) Scalability: Adding more workstations doesn’t significantly affect the network’s performance.
e) Efficiency Under Load: It outperforms bus topology, especially under heavy network traffic.
Disadvantages of a Ring Topology
Here is the list of Disadvantages:
a) Dependency on Continuity: The biggest drawback is the dependency on the integrity of the ring; if one workstation or connection fails, it can disrupt the entire network. Implementing a dual ring or switches can mitigate this risk.
b) Throughput Delays: Since data must pass through every workstation, it can be slower than in a star topology.
c) Higher Costs: The hardware required to connect each workstation, such as network interface cards and switches, is typically more costly than those used in Ethernet networks.
d) Network Fragility: The addition, movement, or reconfiguration of devices within the ring can potentially disrupt network operations.
While Ring Topology is efficient and scalable, it requires careful management to ensure network resilience and optimal performance.
Learn in-depth about GNS3 Architecture with our GNS3 Training – Sign up now!
Devices Using Ring Topology
Here are a few examples of Ring Topology Devices:
a) Token Ring: This popular network technology employs Ring Topology for Local Area Networks (LANs).
b) Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI): Utilised mainly for high-speed data transfer over fibre optic cables in a Ring Topology.
c) Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH): Telecommunications networks that use Ring Topology for redundancy and efficient data transfer.
d) Industrial Control Systems: Many automation and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems rely on Ring Topology for stable communication between devices.
e) Metro Ethernet Networks: Service providers sometimes implement Ring Topology to enhance reliability and network resilience.
f) Distributed Computer Systems: Some distributed networks and cluster computing setups use Ring Topology for synchronised communication.
Data Transmission Steps in Ring Topology
Here is how you can transmit data in Ring Topology
1) Initiation: You start the data transmission from your device.
2) Propagation: The data packet moves sequentially along the ring's path from one device to the next.
3) Reception Check: Each device examines the incoming data to determine if it is the addressee.
a) If not, the data is sent onward to the subsequent device in the ring.
4) Receipt and Processing: Once the data arrives at the correct recipient, it is accepted and processed.
This process ensures that data circulates the ring until it reaches its intended destination.
How Does Data Travel in Ring Network Topology?
In a Ring Network Topology, data travels in a unidirectional or bidirectional circular path. Each device (node) is connected to two adjacent nodes, forming a closed loop. Data packets move sequentially from one node to another until they reach their destination. A token-based system is often used to control data transmission, ensuring that only one device sends data at a time, preventing collisions and improving efficiency.
What Happens if a Node Fails in Ring Network Topology?
If a node fails in a traditional unidirectional Ring Topology, the entire network can be disrupted since data cannot bypass the failed node. However, in a dual-ring or fault-tolerant Ring Topology, data can reroute in the opposite direction, minimising disruption. Modern ring networks often include redundancy mechanisms to enhance reliability and maintain connectivity even in the event of a failure.
Conclusion
The Ring Network Topology is more than just a configuration - it’s a structured, efficient system ensuring seamless data transmission. Its resilience and efficiency make it valuable for both small and large networks. With every node playing a crucial role, this topology showcases the power of connectivity in a circular design.
Learn how you can navigate and use the Meraki Dashboard with our Cisco Meraki Training- Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Where is Ring Network Topology Used?

Ring network topology is used in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs), fibre-optic networks, token ring LANs, and industrial automation systems. It is preferred where predictable data transmission and reliability are essential.
Which Protocol is Used in Ring Topology?

The Token Ring protocol is commonly used in Ring Topology, ensuring collision-free data transmission by passing a token. Other protocols include Fibre Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) for high-speed fibre-optic networks.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various CCNA Training, including Cisco Packet Tracer Course, CCNP Collaboration Training Course, and Cisco Meraki Training Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Star Topology.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to Networking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Networking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CCNA Certification
CCNA Certification
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


