We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound goals are known as SMART Goals. This framework is used as a guide to set goals and objectives to attain better productivity and achieve desired targets.
The SMART framework provides a structural approach to attaining personal or professional goals. These SMART Goals are instrumental in monitoring, strategising, and recording the progress of various operations at an organisational level. In this blog, you will understand everything about SMART Goals, their advantages and drawbacks and tips to achieve these Goals for better productivity.
Table of Contents
1) What are SMART Goals?
2) How do SMART Goals Work?
3) How to Write SMART Goals?
4) Why are SMART Goals Important?
5) SMART Goals: Advantages and Drawbacks
6) Tips for Achieving SMART Objectives
7) Examples of SMART Goals
8) How to Track SMART Goals?
9) Conclusion
What are SMART Goals?
A SMART Goal is a method for setting objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This framework helps you establish clear, realistic goals with deadlines, making it easier to stay accountable.
SMART Goals are valuable in all professional sectors and industries, as well as in personal life. By using this framework, you work towards clearly defined goals that you can achieve by a set deadline.
Moreover, the SMART framework reduces uncertainty and back-and-forth between parties. It also enables individuals and teams to track progress using pre-defined success metrics.
How do SMART Goals Work?
Each one of us understands the importance of setting the right goals. However, setting a goal with a relevant objective can be a challenging and confusing task. SMART Goals help you to address the common challenges faced while developing the goals. The following steps will help you understand how these goals work:
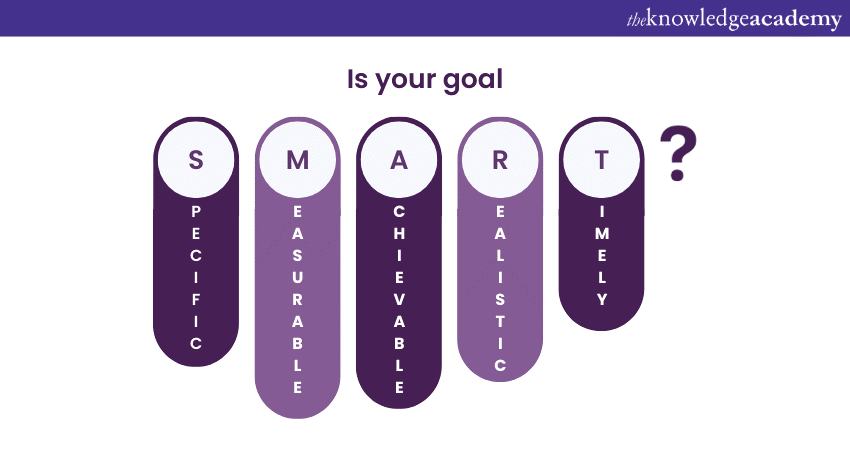
Specific
S in the acronym SMART stands for Specific. This is the first step to begin with the SMART Goals. Being ‘Specific’ while setting your goals will provide clarity and precision in the process from day one till you achieve the goal. Some of the crucial questions which will help you become more specific while setting your goals are:
a) What: Answering the ‘what’ refers to the ultimate objective of the goal. For example, losing 10 lbs in a month can be a goal; in this goal, losing 10 lbs answers the ‘what’ question.
b) Who: The ‘who’ answer helps identify the person, team or organisation that will benefit from these goals. For example, losing 10lbs will help you, so ‘you’ are the ultimate beneficiary of these goals.
c) When: By answering the ‘when’, you can set a deadline to achieve the goal. This will provide urgency and importance to achieving the goal. For example, ‘in the next one month’ can be the answer to this question.
d) Where: The ‘where’ question is mainly used by organisations and projects as it is not always relevant to personal goals. By answering this question, organisations can set location-based goals for their product based on local preferences and more.
e) Why: Answering the ‘why’ will help you identify the core purpose of your goals. This is one of the most important questions to answer before setting up your goals. For example, ‘to maintain well-being or health’ can be a relevant answer to this question based on our weight loss example.
Register for our Communication Skills Course and learn the skills for effective conflict resolution and negotiation today!
Measurable
Measurable goals are targets that you can calculate and track over time. Goals with specific measurements or metrics are more concrete than those based on opinions or anecdotes.
Measurable goals let you and your team track progress and make adjustments over time. They provide a clear and specific picture of success. To make your goal measurable, examine your ultimate goal closely. Ask yourself:
a) How can we control this goal?
b) Is this goal clear and actionable?
c) Is there anything subjective about this goal?
Then, select the metrics that most directly connect to your final goal.
3) Achievable
This is when you give yourself a reality check. Goals should be realistic, not overly ambitious. Ask yourself if your team can reasonably achieve the objective.
Example:
Sam's team is tasked with developing a new software feature. Initially, Sam sets the goal of launching five major updates within the next quarter. However, after reviewing the team's capacity and current workload, Sam realises that this goal is too ambitious. To make it more achievable, Sam decides to scale back the objective to three significant updates, focusing on quality and usability.
This adjustment ensures the goal is realistic and attainable, allowing the team to perform at their best without being overwhelmed. It also highlights the importance of setting goals that match the team's actual capabilities and resources.
4) Relevant
The word ‘R’ in SMART Goals stands for Relevant. The goals you want to set should be relevant to your life in general. By setting an appropriate goal, you can stay focused and disciplined towards the goal.
Based on the previous example, you can set a relevant goal by targeting a specific muscle or activity like cardio-vascular muscles or swimming. After understanding the relevance of your goal, you can iterate your practices and exercises to achieve the desired objectives.
5) Time-bound
The ‘T’ in the SMART Goals stands for ‘Time-bound’. This step is often ignored while setting important goals in personal life. Setting time-bound goals will bring urgency to achieve the goal in the desired time. It also prevents you from procrastinating and overthinking about the target goals.
For example, setting a deadline of one month to lose 10 lbs of weight is very important to give you a clear timeline to begin and end the process.
How to Write SMART Goals?
To write a SMART Goal, clearly define each component of the SMART acronym. Ensure your goal is Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. If your goal doesn’t meet these criteria, refine it step by step until it does.
Here’s a guide to crafting and refining SMART Goals:
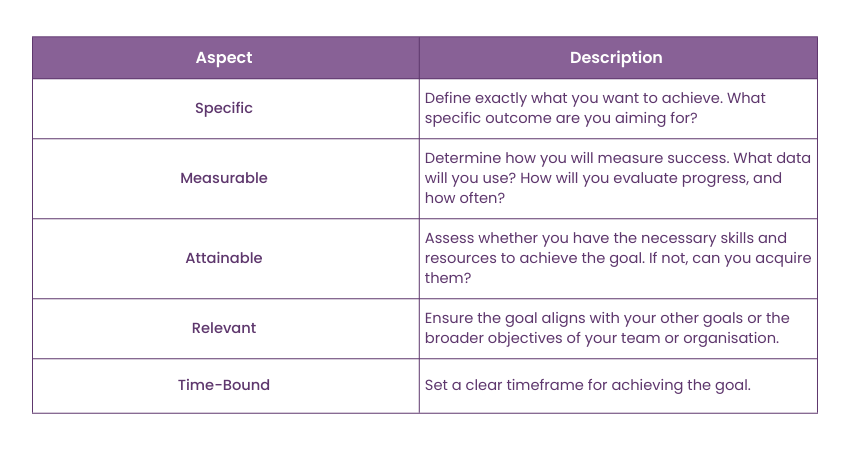
S: Specific – Make Your Goal Clear
Your goal should be precise and outcome-focused. Avoid vagueness, as it can lead to misdirection. Think of this step as the mission statement for your goal. Answer the five W questions:
a) Who: Identify the people involved and assign roles if needed.
b) What: Define what you want to accomplish in detail.
c) When: Outline a general timeline (you’ll refine this further in the "Time-bound" step).
d) Where: Specify a location or event if applicable.
e) Why: Clarify the purpose behind the goal, such as career development or company growth.
M: Measurable – Define Success Metrics
Set clear metrics to track progress and determine success. This makes your goal tangible and helps you stay focused. If your goal spans several months, break it into milestones tied to specific subtasks. Ensure progress can be quantified or clearly indicated. If not, adjust your goal.
A: Attainable – Set Realistic Challenges
Your goal should be ambitious yet achievable with available resources like people, tools, or capital. Review past data or similar projects to assess its feasibility. If the goal isn’t attainable, consider adjusting resources or extending the timeline.
R: Relevant – Align Your Goal with Broader Objectives
Relevance ensures your goal aligns with team or organisational priorities. It should support other initiatives or long-term goals and avoid detracting from existing commitments. A relevant goal adds value and keeps your efforts aligned with larger objectives.
T: Time-bound – Set a Deadline
Define a realistic timeframe for achieving your goal. A hard deadline provides structure, creates urgency, and helps you measure progress. If the goal spans months, set interim milestones to track success. Confirm with stakeholders that the timeline is achievable and adjust as needed.
By following the SMART framework, you’ll create clear, actionable goals. It will keep you focused and accountable while driving measurable progress.
Why are SMART Goals important?
Setting SMART Goals is essential because they:
a) Help you work with clear and specific intentions.
b) Provide benchmarks to measure your success.
c) Ensure objectives are realistic and achievable.
d) Eliminate unnecessary tasks that distract from your main goals.
e) Define a clear start and finish, keeping you on track.
By setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound goals, you increase your chances of success. This approach helps you verify the goal's achievability, identify success metrics, and create a roadmap to reach them. Abstract goals without a clear path or deadline can cause you to lose focus and miss your objectives.
SMART Goals: Advantages and Drawbacks
Setting goals based on the SMART framework is considered an effective exercise to achieve the desired outcomes. Although this framework has a number of benefits, there are certain limitations of this framework as well. Let’s understand some of the most significant advantages and drawbacks of the SMART framework.
Advantages
Setting and achieving goals effectively is crucial for both personal and professional success. Using the SMART framework provides a clear structure to guide you towards your objectives. Some of its benefits are:
a) Offer Focus and Clarity
Achieving goals is often more complex than it appears. Distractions, side tasks, and other projects can easily divert your attention from completing your tasks. SMART Goals enhance focus by simplifying your to-do list and providing an immediate reminder of why each specific task is important.
b) Boost Motivation
Feeling stressed or overwhelmed at work is common, often due to a lack of clear goals. This can significantly impact your motivation. SMART Goals can boost energy, provide direction, and motivate you and your team by:
a) Increasing involvement in the process
b) Helping employees understand the importance of their work
c) Offering new challenges and direction for those feeling stuck.
Drawbacks
In order to completely understand any concept or strategy, you need to have a good understanding of its drawbacks. One of the most discussed drawbacks of SMART Goals is its over-emphasis on quantitative progress rather than qualitative progress. The SMART framework is also arguably considered to become irrelevant when it comes to long-term goals.
Tips for Achieving SMART Objectives
Now that you know the process and key components of the SMART Goals framework. Some of the tips to help you achieve the objectives with the SMART framework are as follows:
Setting Small Goals
Start by setting small goals. This will help you maintain the momentum and motivation throughout the process. Setting small goals will make the task manageable and reduce the stress of achieving the bigger goal. While setting these small goals, always remember that these smaller goals should align and add up with the bigger goal.
Set Milestones
Setting milestones keeps the process more engaging and enables you to time frame your goals. These milestones provide a sense of accomplishment and allow you to take feedback on your progress to adjust if required. Once the milestones are reached, you should celebrate the achievement, and it will add more enthusiasm to work for the ultimate goal.
Time Management
Managing time is one of the most crucial tips while talking about goal setting. Not everyone has the same schedule or routine, which makes time management an essential aspect of successfully achieving your goals. Setting the right time to work on your objectives will help you work on your progress consistently.
Examples of SMART Goals
You can apply SMART Goals in any professional setting, industry, or personal life. Below are real-world examples of initiatives and how to format them as SMART Goals.
Improving Employee Performance and Retention
Ritchie Tendencia, CEO of CSV Now, wanted to enhance employee satisfaction and performance. Initially, his goal was too vague to be actionable. Using the SMART framework, he refined it to:
SMART Goal: Reduce employee turnover rates by at least 10% in the next quarter.
This clear and measurable goal led to a 15% reduction in turnover rates and improved client satisfaction through a structured training program, demonstrating the effectiveness of SMART Goals.
Decreasing Customer Churn Rate
Axel Lavergne, Founder of ReviewFlowz, aimed to reduce customer churn by increasing satisfaction and retention. He and his team defined their goal with a timeline and metrics:
SMART Goal: Reduce customer churn rate by 10% in six months.
They exceeded this goal by improving their onboarding process, providing comprehensive training resources, and regularly checking in with new customers, resulting in stronger customer relationships and significantly reduced churn.
Becoming a Better Leader
Jake Munday of Custom Neon wanted to improve his leadership skills. He focused his efforts by setting a tangible SMART Goal:
SMART Goal: Complete a leadership development course in three months by dedicating two hours every week to study.
This goal was specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, enhancing his leadership skills as a CEO within a set period.
Increasing Business Knowledge
Axel Lavergne sought to broaden his business knowledge by reading more books. He used the SMART formula to define his goal:
SMART Goal: Read one business book per month for a year.
This goal was specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, helping him stay disciplined and informed, ultimately improving his business strategies and effectiveness as a leader.
How to Track SMART Goals?
It's essential to track SMART Goals to measure progress and determine success. Because SMART Goals require you to define metrics and timeframes upfront, they are relatively easy to track and report on. Here are some expert tips for tracking SMART Goals:
a) Ensure Measurability
Ensure your goals are actually measurable. Set quantifiable criteria to track progress and determine when the goal is achieved. For example, rather than aiming to "improve customer satisfaction," set a goal to "achieve a customer satisfaction score of 90% as measured by our end-of-service surveys."
b) Stick to Defined Metrics
Part of defining a SMART Goal is choosing how you will measure success. To effectively report on your performance, don't change these metrics midway through.
c) Set Up a Tracking System
Use project management software or another goal-tracking tool to monitor progress. This ensures that all team members have a single source of truth and helps keep everyone accountable for their goals.
d) Consistently Evaluate Progress
Decide how frequently you will track progress. Avoid checking metrics so often that it becomes stressful (e.g., daily), but monitor often enough to catch any issues early. Consistently tracking progress allows for timely communication and collaboration if things go off course.
e) Celebrate Every Win
Celebrate each time a goal is achieved. Recognising hard work and commitment keeps everyone motivated and prevents future goals from feeling like a thankless task.
f) Reflect and Learn
Even if you fall short of a goal, it's valuable to reflect on the process with your team. Identify what went well and what could be improved. Apply these insights to future goals and adjust criteria, such as time or resources, to better meet new objectives.
g) Reassess and Edit Your SMART Goals
Don't be afraid to revisit and refine your SMART Goals. Give yourself time to review their clarity and details and make any necessary tweaks to ensure they are well-defined and achievable. SMART Goals, like any rough draft, benefit from revision and fine-tuning.
What is an Example of a SMART Objective?
A SMART objective could be: "Increase sales by 10% over the next six months by launching a targeted marketing campaign and offering a 15% discount to new customers." This objective is Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
What are SMART Goals at Work?
SMART Goals at work are clear, concise, and structured objectives that help improve performance. They are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Examples include "reduce project completion time by 20% in the next quarter" or "increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% within six months."
Make the most out of your time – Register for our Time Management Training and unlock the potential of time management today!
Conclusion
SMART Goals are one of the most trusted strategies for effective goal setting. This framework will help individuals and organisations to keep track of the progress and keep an account of the limiting factors to achieve the goal. We hope that this blog helped you understand the SMART Goals framework and ways to implement it.
Register for our Personal Development Courses and take your first step towards a better future! Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are SMART Goals in NHS?

SMART goals in the NHS are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives. They guide healthcare professionals in setting clear, realistic targets that improve patient care, streamline processes, and meet organisational priorities while tracking progress effectively.
What is the Best Way to Work on Long-time Goals?

To work on long-term goals, break them into smaller, manageable steps with milestones. Regularly review and adjust plans as needed, maintaining focus and consistency. Use SMART criteria to set clear targets and stay motivated by celebrating progress and visualising the final outcome.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses, including Introduction to Project Management Course, Project Management Office (PMO) Fundamentals Course and Certified Digital Services Project Manager Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 13 Project Management Trends.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Career Development Course
Career Development Course
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


