We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +0800 780004 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the Internet of Things (IoT)and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) often come up in discussions. Both concepts are related to connectivity and data exchange but have distinct differences. Learning the Difference Between IoT and M2M can allow you to use them more efficiently in your everyday lives.
This blog post aims to comprehensively compare the Internet of Things and Machine-to-Machine technologies, highlighting their unique features, applications, and benefits. Learn about the Difference Between IoT and M2M and how these cutting-edge concepts differ in functionality, scope, and application domains.
Table of Contents
1) What is IoT?
2) What is M2M?
3) What is the Difference Between IoT and M2M?
4) Conclusion
What is IoT?
IoT is a large network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities. These devices can collect a data pool, exchanging it as necessary, which creates a dynamic ecosystem of connected systems. IoT devices communicate with each other and with users over the internet, enabling seamless integration and automation in various domains.
Applications of IoT
The technology behind IoT allows for the efficient monitoring, control, and analysis of data, leading to enhanced efficiency, productivity, and convenience in sectors such as health industries, transportation, smart homes set ups, and industrial automation. IoT has revolutionised how we interact with technology and has tremendous potential for shaping the future of our connected world.
1) Smart homes: IoT enables integration of various household devices, such as lighting systems, security cameras, displays, air conditioners and thermostats, allowing for centralised control and automation.
2) Industrial automation: In industries, IoT plays a crucial role in optimising processes, monitoring equipment, and enhancing productivity through connected sensors and machines.
3) Healthcare: IoT applications in healthcare include remote patient monitoring, wearable devices for health tracking, and smart medical equipment for improved diagnosis and treatment.
4) Transportation: IoT is revolutionising transportation with connected vehicles, traffic management systems, and logistics optimisation, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Try our Internet of Things (IoT) Training Course and unleash new possibilities!
Advantages of IoT
IoT enables automation, optimisation, and streamlined processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced human effort, and improved productivity across industries. IoT devices provide convenience, personalisation, and seamless integration, enhancing the user experience in smart homes, wearable devices, and connected appliances.
Learn about cutting-edge innovations with our Advanced Technologies Courses!
What is M2M?
M2M is the phenomenon of two devices or machines communicating without human intervention. In M2M technology, devices are equipped with sensors and communication modules to exchange data and perform actions based on the received information. This direct communication allows real-time monitoring, control, and automation of various processes and systems.
Applications of M2M
M2M is commonly used in industries such as fleet management, vending machines, and remote monitoring, where machines must communicate and coordinate seamlessly. By enabling machines to interact and share information efficiently, M2M technology enhances operational efficiency, improves decision-making, and streamlines processes in numerous applications.
1) Fleet management: M2M technology enables real-time tracking and management of vehicle fleets, improving logistics, route optimisation, and maintenance scheduling.
2) Vending machines: M2M connectivity allows vending machines to report inventory levels, process payments, and transmit data for efficient restocking and maintenance.
3) Remote monitoring: M2M devices are used to remotely monitor equipment, such as industrial machinery, pipelines, or environmental sensors, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Advantages of M2M
M2M technology enables remote monitoring and control of machines and processes, ensuring prompt response, reducing downtime, and increasing operational efficiency. M2M facilitates efficient use of resources, such as energy, materials, and time, leading to cost savings and sustainability through optimised resource utilisation.
Try our 5G Wireless Training and gain in depth knowledge of wireless communication!
What is the Difference Between IoT and M2M?
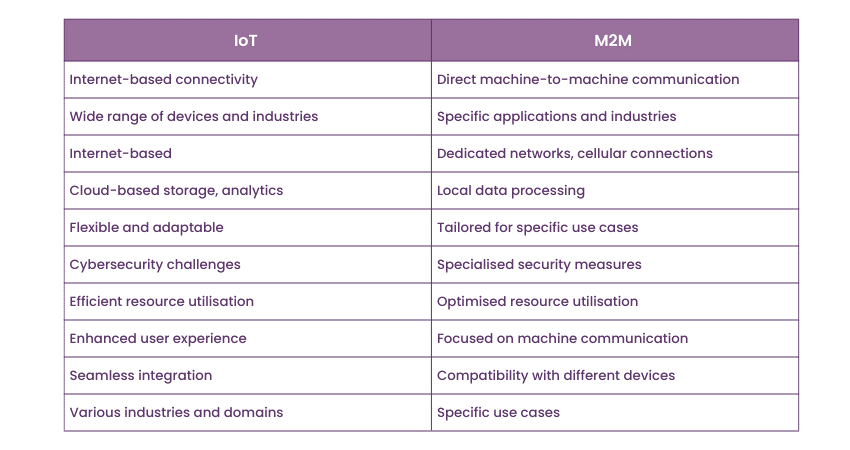
When comparing IoT and M2M, several key factors come into play. Connectivity differs between the two, with IoT relying on internet connectivity and cloud-based services, while M2M often utilises dedicated networks or cellular connections for direct machine-to-machine communication. Some such differences between IoT and M2M are as follows:
Connectivity
IoT emphasises internet-based connectivity and leverages cloud services for data storage, processing, and analytics. It enables seamless integration of devices and systems, providing centralised control and access to data from anywhere. M2M, on the other hand, prioritises direct connectivity between machines. It establishes dedicated networks or cellular connections for direct communication without relying on the internet.
Scope and scale
IoT has a wider scope and encompasses a broad range of devices, industries, and applications. It connects not only machines but also everyday objects, appliances, and systems to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data. M2M, on the other hand, focuses specifically on machine-to-machine communication and is often tailored for specific use cases.
Data processing
IoT relies on cloud-based storage and advanced analytics to process large volumes of data generated by connected devices. It leverages data analytics and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms to extract valuable insights for informed decision-making. M2M, in contrast, focuses on local data processing for immediate responses. It often involves real-time monitoring and control of machines and processes.
Try our Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training Course today!
Flexibility and adaptability
IoT is designed to be flexible and adaptable to new devices and technologies. It can integrate with various types of devices, systems, and platforms, enabling scalability and interoperability. M2M, on the other hand, is often tailored for specific use cases and requires customisation for different applications and industries.
Human interaction
IoT aims to enhance the user experience by providing convenience, personalisation, and seamless integration. Smart homes, wearable devices, and connected appliances offer a user-centric approach, allowing individuals to interact with their surroundings in intuitive ways. M2M, on the other hand, is more focused on machine-to-machine communication and may have less emphasis on direct user interaction.
Security
IoT faces cybersecurity challenges due to the large number of interconnected devices and the vast range and quantity of data exchanged. A robust security measure becomes mandatory to protect against data breaches and unauthorised access. M2M, especially in critical infrastructure sectors, prioritises specialised defensive measures to ensure the security and confidentiality of data exchanged between machines.

Conclusion
As this blog concludes, we hope it was able to convey how IoT and M2M are two distinct yet interconnected technologies that enable efficient data exchange and automation. Understanding the Difference Between IoT and M2M and their applications is crucial for organisations and individuals looking to leverage the benefits of these technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 5G Wireless Training
5G Wireless Training
Thu 5th Dec 2024
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


