We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +0800 780004 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
What is Graphic Design, you ask? It's a harmonious blend of art and functionality, playing a pivotal role in today's business environment. It is a powerful force that shapes our perceptions, guides our choices, and enriches our daily experiences.
Every day, you are surrounded by the fruits of Graphic Design, from the logos on your morning coffee cups to the layouts of your favourite apps. This underscores its pivotal role in our daily lives.
If you wish to learn more about Graphic Design it, you have come to the right blog. Keep reading this blog as we explain What is Graphic Design, a creative process that combines visual pieces of art with information to communicate a specific message or idea visually.
Table of Contents
1) The Roots of Graphic Design
2) Understanding What is Graphic Design
3) Key Elements of Graphic Design
4) Graphic Design Principles
5) Types of Graphic Design
6) The Process of Graphic Design
7) Definition of AI Graphic Design
8) Graphic Design Trends
9) Different Types of Graphic Design Software
10) Conclusion
The Roots of Graphic Design
To truly grasp what Graphic Design is, it’s essential to delve into its history. Although the term was coined in the 20th century, its origins stretch back to the dawn of civilisation. Ancient societies, such as the Egyptians with their iconic hieroglyphics and the Greeks with their pottery and architectural details, understood the significance of visual representation.
These early forms of Graphic Design were crucial for communication, religious expression, and documenting historical events. The Renaissance period further enhanced the appreciation for the arts and gave rise to modern typography.
However, the true game-changer in the world of design was the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. This innovation not only revolutionised the distribution of books but also laid the foundation for advertising, as mass production of visual content became feasible.
With the Industrial Revolution, the 19th and 20th centuries witnessed a surge in advertising as businesses sought to stand out in increasingly crowded markets. Graphic Design evolved rapidly, adapting to the needs of print, billboards, and later, digital media.
Today, as we navigate the digital age, designs are omnipresent. From the apps on our phones to the billboards on our streets, Graphic Design’s rich and varied history is evident everywhere.
Understanding What is Graphic Design
At its core, Graphic Design is the intricate art and practice of projecting experiences and ideas through visual and textual mediums. It isn't just about making something look good but rather a strategic endeavour that aims to deliver a particular message to a target audience.
The primary purpose of Graphic Design revolves around communication. It acts as a bridge, connecting an idea from one entity to the audience, ensuring that the message isn't just received but is also understood and felt. Moreover, it addresses specific challenges and problems, providing solutions that enhance User Experience.
The Graphic Design tools have evolved considerably over the years. It was primarily a hands-on process, with designers relying on pens, paper, and a variety of physical tools to bring their visions to life. But the digital revolution ushered in an era of transformation. Today, software like Adobe Illustrator and are indispensable in the Graphic Design world, allowing for precision, versatility, and the ability to make changes on the fly.
Key Elements of Graphic Design
Now, that you have understood What is Graphic Design and its history, let’s learn about its key elements. It is a vast realm, but at its heart lies a set of foundational elements that give structure and meaning to a design. Let’s delve into these building blocks:
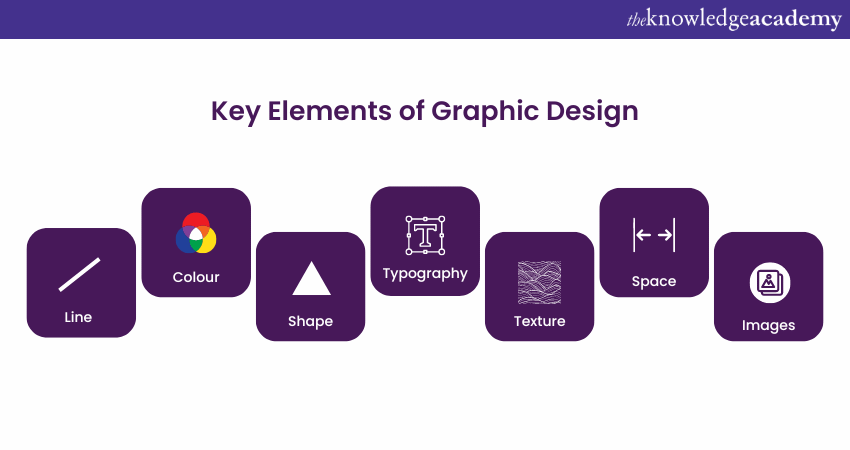
a) Line: Often regarded as the most fundamental design element, lines direct the viewer's gaze throughout the artwork. Whether bold and straight or soft and flowing, lines define spaces, create emphasis, and form patterns, guiding the eye from one point to another in a visual journey.
b) Colour: Colours are more than just shades; they evoke emotions, set moods, and convey ideas. Warm tones can ignite feelings of passion or energy, while cool tones often suggest calmness or professionalism. Mastery of colour theory is essential for designers to elicit the desired emotional response.
c) Shape: Shapes, whether geometric like circles and squares or organic forms, are crucial in defining objects and spaces within a design. They symbolise concepts, highlight areas, and create patterns, contributing significantly to the overall message of the design.
d) Typography: Words are not merely message carriers but can also be artistic elements. Typography involves the careful arrangement of type, considering font style, size, spacing, and layout to ensure the text is not only legible but also visually engaging.
e) Texture: Texture adds a tactile dimension to design, providing depth and a sensory experience. Whether real, as in embossed print, or implied, through photographic representation, texture enriches the viewer’s interaction with the design.
f) Space: Space encompasses both what is present and what is absent. Positive and negative space influence focus, balance, and clarity within a design. Proper use of space ensures that the design remains uncluttered and harmonious.
g) Images: Visual elements like photos, illustrations, and icons quickly communicate complex ideas. They captivate attention, inform the viewer, and often serve as the focal point, anchoring the overall design.
Graphic Design Principles
Graphic Design Principles are the foundation for creating visually compelling and communicative designs:
1) Balance: Achieving equilibrium in the arrangement of visual elements is crucial. Whether symmetrical or asymmetrical, balance ensures that no single component dominates, contributing to a harmonious composition.
2) Contrast: Contrast involves highlighting differences in colour, size, shape, or other attributes to create visual interest and draw attention. It adds dynamism to a design, making key elements stand out.
3) Unity: Unity ensures that all elements work cohesively to convey a singular message or theme. Consistent use of colour schemes, fonts, and imagery fosters a sense of completeness and professionalism.
4) Alignment: Precise alignment organises elements to create a clear and visually appealing structure. It aids readability and guides the viewer's eye through the design with logical flow.
5) Repetition: Consistent repetition of visual elements fosters a sense of cohesiveness and reinforces the overall design theme. It helps establish patterns and associations within the viewer's mind.
Mastery of these principles empowers Graphic Designers to create impactful visuals that effectively convey messages, evoke emotions, and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Types of Graphic Design
The field of Graphic Design is expansive, branching out into various specialisations, each with its unique focus and expertise. Here are some of the prominent types:
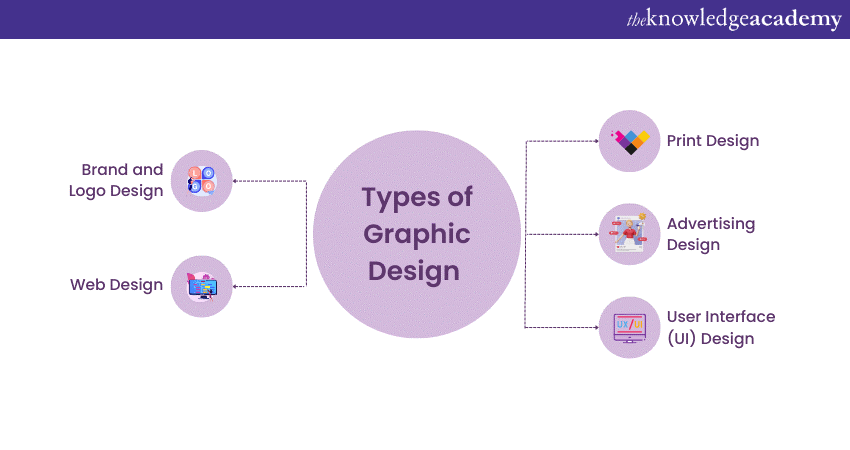
a) Brand and Logo Design: At the core of a company's public image, this design discipline focuses on creating a distinctive identity that resonates with audiences and stands out in the market. It involves crafting logos, defining colour schemes, and shaping the overall brand aesthetics, all of which contribute to the visual representation of a company's reputation.
b) Web Design: In today’s digital world, Web Designers concentrate on developing visually appealing and user-friendly website layouts. This includes selecting appropriate colour schemes, typography, and imagery while ensuring a seamless User Experience across various devices.
c) Print Design: Despite the rise of digital media, print design remains relevant. This specialty focuses on creating visuals for physical materials like magazines, brochures, business cards, and posters. The challenge is to deliver designs that are consistent and impactful in their tangible form.
d) Advertising Design: More than just promotion, advertising design seeks to captivate and persuade. Whether it’s a billboard, magazine ad, or digital banner, designers in this field blend creativity with strategy to effectively market products or services.
e) User Interface (UI) Design: As technology becomes integral to daily life, the design of software applications, particularly their interfaces, is crucial. UI Designers ensure that the visual and interactive elements of an app or website are intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing.
Bring your ideas to life and design with flair through our dynamic Animation and Design Training – join now!
The Process of Graphic Design
The Graphic Design journey, from initial idea to final output, is a structured, collaborative process. It ensures that the resulting design isn’t just visually compelling but also meets the intended purpose. Here’s a succinct breakdown of the steps involved:
1) Briefing: The design journey begins with a comprehensive brief. Here, designers engage with clients to understand their needs, goals, and target audience. This step sets the foundation, offering clarity and direction for the subsequent stages.
2) Research: With the brief in hand, designers delve into research. They gather data about the industry, audience preferences, competitors, and the latest design trends. This phase ensures the design is informed, relevant, and has a competitive edge.
3) Brainstorming: Here, creativity takes centre stage. Designers converge, bringing diverse perspectives to the table and generating a plethora of ideas. The best concepts are shortlisted for further exploration.
4) Sketching and Conceptualisation: Before diving into using digital tools, rough sketches are often made. These rudimentary drawings act as blueprints, allowing designers to visualise and refine their ideas.
5) Feedback and Revisions: Collaboration continues as the initial design is presented to the client. Feedback is solicited, leading to iterative revisions until the design aligns perfectly with the client's vision.
6) Finalisation and Delivery: Once approved, the design undergoes final touches, ensuring it meets quality standards. It's then packaged and delivered to the client, ready for its intended use.
Definition of AI Graphic Design
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionised Graphic Design by introducing advanced tools that enhance creativity, efficiency, and the design process. AI-driven Graphic Design leverages Machine Learning algorithms to automate tasks, generate designs, and provide intelligent insights, transforming how designers approach their work.
These AI tools streamline repetitive tasks, offer creative suggestions, and broaden the scope of visual expression. While they significantly boost efficiency, they also prompt discussions about the evolving role of designers in an AI-driven world.
As this field continues to advance, the collaboration between human creativity and AI innovation is set to redefine Graphic Design, opening new opportunities for exploration and artistic expression.
Graphic Design Trends
Staying aware of evolving trends in Graphic Design is essential for creating visually captivating and contemporary designs. Let's delve into some key Graphic Design trends:
1) Minimalism:
Minimalism continues to dominate, emphasising simplicity, clean lines, and ample white space. This trend focuses on essential elements, conveying a message with clarity and elegance. Minimalistic designs often feature bold typography and limited colour palettes.
2) Maximalism and Vibrant Colours:
As opposed to minimalism, maximalism has gained traction, embracing vibrant colours, intricate patterns, and rich textures. This trend encourages designers to break free from restraint, creating visually immersive experiences that captivate attention.
3) 3D and Depth:
Integrating three-dimensional elements adds depth to designs, creating a more immersive visual experience. This trend is particularly prominent in Web Design and branding, where 3D graphics elevate the overall aesthetic.
4) Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Design:
Eco-friendly design is rising, reflecting the growing emphasis on environmental consciousness. Graphic Designers are incorporating sustainable elements, earthy tones, and eco-friendly messaging to align with the global push for sustainability.
5) Abstract and Geometric Patterns:
Abstract and geometric patterns continue to captivate audiences. From intricate geometric shapes to playful abstract forms, these patterns add uniqueness and creativity to various design elements, from logos to packaging.
6) Bold Typography:
Typography takes centre stage with bold, expressive fonts. Designers experiment with typography, using oversized letters, unconventional placements, and creative combinations to make a powerful statement.
7) Neon and Futuristic Elements:
Futuristic design elements and neon colours evoke a sense of innovation and modernity. This trend, reminiscent of the '80s aesthetic, injects energy into designs, especially in digital media and branding.
8) Nostalgia and Vintage Revival:
A nod to the past, nostalgia and vintage design elements are returning. Designers are incorporating retro colour schemes, typography, and imagery, creating a sense of familiarity and warmth.
These trends provide a roadmap for creative exploration in the Graphic Design landscape. Designers often blend multiple trends to craft unique and impactful visual narratives, ensuring their work remains fresh, relevant, and visually striking.
Interested in Graphic Designing? Try our Virtual Graphic Designer Training today!
Different Types of Graphic Design Software
Graphic Design software cater to various design needs, from creating digital illustrations to editing photos and designing layouts. Here are some prominent types of Graphic Design Software:
1) Adobe Creative Cloud:
Adobe's suite includes industry-standard software like Photoshop for photo editing, Illustrator for vector graphics, and InDesign for page layout. Its comprehensive tools make it a go-to choice for many designers.
2) CorelDRAW:
Known for vector illustration and page layout, CorelDRAW is popular for its versatility. It helps both beginners and experienced designers, offering features for creating logos, brochures, and more.
3) Affinity Designer:
This software provides a cost-effective alternative with professional level capabilities. Affinity Designer is known for its vector Graphic Design and offers robust tools for precision and creative freedom.
4) Sketch:
Particularly popular among UI/UX Designers, Sketch focuses on digital design. It streamlines the creation of user interfaces and interactive prototypes, emphasising simplicity and efficiency.
5) Canva:
Canva is user-friendly and accessible for those with limited design experience. It provides numerous templates for social media graphics, presentations, and posters, making design accessible to a broader audience.
6) Gravit Designer:
Gravit Designer is a cloud-based vector Graphic Design tool. It's free and compatible with various platforms, enabling collaboration and flexibility in design creation.
7) GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP):
An open-source alternative to Photoshop, GIMP offers powerful photo editing tools. It's suitable for users seeking robust functionality without the subscription model.
8) Procreate:
Exclusive to iPad, Procreate is a favoured choice for digital illustrators. Its intuitive interface and substantial brush library make it ideal for creating intricate illustrations.
Benefits of Graphic Design
Investing in Graphic Design offers numerous advantages for a company, including:
Consistent, Recognisable Branding
A Graphic Designer can craft or select the right logos, images, graphics, and layouts for your creative materials, ensuring visual consistency across all channels used to engage with clients. Consider any successful company and how integral Graphic Design is to its branding and public-facing design choices.
Visual Communication
Beyond defining your brand, Graphic Design is essential for conveying your message to your target audience. A photograph or text alone cannot achieve the depth of communication that effective graphics can. It’s the role of a Graphic Designer to create visually compelling materials that resonate emotionally with your audience.
Increased Sales and Competitive Edge
Strong Graphic Design enhances a company's visibility in the marketplace, leading to increased revenue. With its impact on usability and User Experience, good Graphic Design has a proven influence on customer behaviour, contributing to a stronger competitive position.
Conclusion
Graphic Design is everywhere, subtly shaping our world. When we ask, "What is Graphic Design?" we acknowledge its profound influence on communication, business, and daily life. As we move through this visually rich era, let's appreciate the art and strategy behind each design, recognise its significance and encourage deeper exploration or reflection.
Inspired to bring your design and art to life? Try our Animation Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

A career in Graphic Design typically requires a bachelor’s degree in Graphic Design, Visual Arts, or a related field. Many designers also enhance their skills with certifications in specific design software and ongoing creative development.

Graphic Design offers various career paths, including branding and logo design, web design, print design, User Interface (UI) design, advertising design, and motion graphics. Designers can work in-house at agencies, or as freelancers.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and Interview Questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Virtual Online Job Courses including Virtual Assistant Masterclass, Travel Agent Training etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Graphic Design Interview Questions.
Our Business Skills blogs cover a range of topics related to Graphic Designing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Graphic Designing expertise, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Virtual Assistant Course
Virtual Assistant Course
Fri 20th Dec 2024
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


