We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +46 850282424 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (often abbreviated to MHOR) is a set of guidelines enacted in the United Kingdom to promote safety during tasks in the workplace. These regulations help reduce the risk of injury from activities such as lifting, carrying, pushing, and pulling objects. Employers are required to conduct risk assessments and, where possible, make reasonable adjustments to minimise hazards. This may include providing mechanical assistance like trolleys or hoists or offering training to employees to ensure they understand proper techniques. The ultimate goal is to protect workers and create a safer working environment. Read this blog to learn about the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992, its scope, employers’ and employees’ responsibilities, and its benefits.
Table of Contents
1) What is Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992?
2) Scope and application of Manual Handling Operations 1992
a) Industries covered
b) Job roles inclusive
c) Manual Handling activities defined
d) Physical and cognitive consideration
e) Temporary and permanent tasks
f) Self- employed individuals
3) Responsibilities of employers under MHOR 1992
4) Responsibilities of employees under MHOR 1992
5) Benefits of MHOR 1992
6) Conclusion
What is Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992?
The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 is a set of legal guidelines designed to reduce the risk of injuries caused by activities in the workplace. These regulations apply to various industries and job roles, emphasising the significance of protecting employees from harm while carrying out tasks.

Scope and application of Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
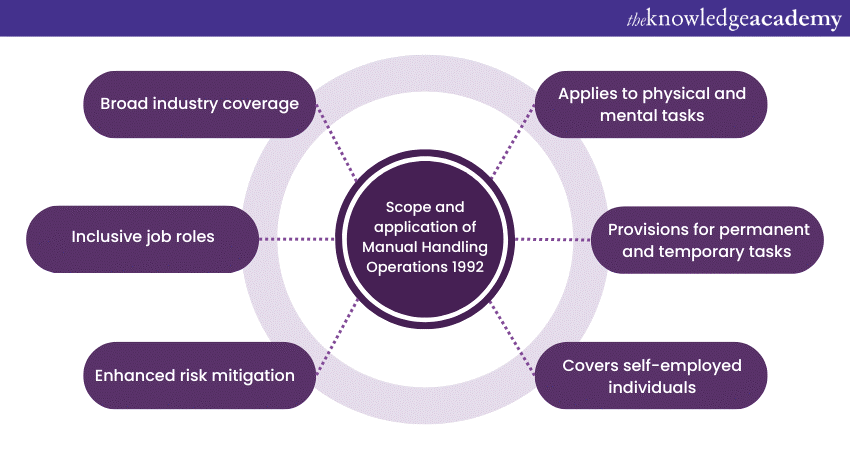
The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 is a comprehensive framework that helps govern activities in workplaces across the United Kingdom. These regulations have been meticulously designed to encompass several industries, job roles, and tasks, acknowledging the varied nature of work and ensuring the safety of workers engaged in such activities.
Broad industry coverage
The scope of the MHOR 1992 is intentionally broad, aiming to safeguard employees in various sectors. These regulations apply universally, from manufacturing to healthcare, hospitality to construction, and everything in between. Industries requiring repetitive lifting, lowering, carrying, pushing, or pulling of objects are specifically targeted due to the inherent risks of such activities. Whether it's a factory floor, a healthcare facility, or an office space, the MHOR 1992 applies across the board.
Inclusive job roles
Every role that involves Manual Handling activities, directly or indirectly, falls under the umbrella of the MHOR 1992. The regulations extend their protective reach from warehouse operatives to nurses, construction workers and retail staff. This inclusivity ensures that regardless of the position held within an organisation if a task involves Manual Handling, the individual is covered by the MHOR 1992's provisions.
Learn about essential Manual Handling Equipment for safer operations. Check out our blog for guidance!
Enhanced risk mitigation
The regulations classify Manual Handling activities as any action involving moving objects by hand or bodily force. This encompasses lifting, lowering, pushing, pulling, carrying, and even holding an object. The weight, shape, and object's size can influence the risks associated with the activity, and the MHOR 1992 aims to mitigate those risks.
Applies to physical and mental tasks
It's important to recognise that Manual Handling doesn't solely pertain to the physical lifting of objects. The regulations also encompass tasks that require cognitive effort, such as decision-making while moving objects or activities that involve maintaining a particular posture for extended periods. These cognitive aspects are equally crucial, as they can influence the overall risk profile of the task.
Provisions for permanent and temporary tasks
The MHOR 1992 extends its reach to both temporary and permanent Manual Handling tasks. This means that whether a task is a part of an employee's routine or a one-off requirement, the regulations' safety provisions are applicable. This approach ensures that no matter the frequency or duration of Manual Handling activities, adequate precautions are taken to safeguard employees from potential harm.
Covers self-employed individuals
The MHOR 1992 even addresses the responsibilities of self-employed individuals who engage in Manual Handling activities. This ensures that even those who work for themselves are accountable for adhering to safety measures and mitigating the associated risks. It highlights the inclusive nature of the regulations, encompassing a diverse workforce.
Learn how to administer First Aid and the contents of its kit with our First Aid At Work course. Join now!
Responsibilities of employers under Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 emphasises the responsibility of employers to create a safe working environment for their employees engaged in Manual Handling activities. These regulations outline specific duties and obligations that employers must fulfil, with the ultimate goal of preventing workplace injuries and ensuring the well-being of their workforce. The following are some of the key responsibilities of employers under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992.
a) Risk assessment: Employers are required to conduct thorough and systematic Manual Handling Risk Assessments for all tasks within their organisation. This involves identifying potential Manual Handling Hazards, evaluating the level of risk, and implementing measures to control or eliminate those risks. Risk assessments are the foundation upon which safe handling procedures are built.
b) Avoiding Manual Handling when possible: Wherever reasonably practicable, organisations should encourage employees to avoid Manual Handling activities altogether. This might involve redesigning tasks, introducing mechanised equipment, or altering work processes to reduce the need for employees to engage in manual lifting, lowering, or carrying.
c) Provision of training: Employers must ensure their employees receive adequate training in safe Manual Handling Techniques. This training should cover proper lifting and carrying methods and information about the risks associated with incorrect practices. Regular refresher training sessions should also be provided to keep employees informed about the latest safety protocols.
d) Equipment and tools: Employers should provide suitable equipment and tools to facilitate safe Manual Handling. This might include trolleys, hoists, or ergonomic lifting aids, depending on the specific tasks and requirements. The equipment should be well-maintained, easily accessible, and properly suited to the tasks at hand.
e) Monitoring and review: Regular monitoring and reviewing the Manual Handling practices are essential. Employers should establish mechanisms to gather employee feedback, assess the effectiveness of safety measures, and identify any emerging risks. Based on these reviews, adjustments and improvements can be made to maintain high safety standards.
f) Collaboration and communication: Effective communication between employers and employees is vital. Employers should encourage open dialogue regarding safety concerns and suggestions for improvement. Involving employees in decision-making enhances their sense of ownership and fosters compliance with safety measures.
Learn how to act in an emergency situation and how to analyse and evaluate risks with our Health And Safety In The Workplace Training. Register now!
Responsibilities of employees under Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
While the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 places significant responsibilities on employers to ensure their workforce's safety, employees are also critical in maintaining a safe working environment. The MHOR highlights the importance of collaboration between employers and employees to minimise the risks associated with Manual Handling activities.
a) Training and education: Employees are responsible for actively engaging in the training and education provided by their employer. It equips them with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform Manual Handling tasks safely. By attentively participating in these sessions, employees contribute to their safety and their colleagues' safety.
b) Follow safe practices: Employees should adhere to the safe Manual Handling practices outlined in the training. This includes using proper lifting techniques, avoiding excessive force, and using available equipment and tools appropriately. By following these guidelines, employees reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
c) Reporting hazards and concerns: Employees must be vigilant and proactive in identifying Manual Handling Hazards or concerns. If they encounter unsafe conditions, faulty equipment, or practices that could lead to injuries, they should promptly report these issues to their supervisors or relevant authorities. Timely reporting enables swift corrective action to be taken.
d) Open communication: Maintaining open lines of communication with supervisors and colleagues is essential. Employees who feel uncomfortable or uncertain about a particular Manual Handling task should voice their concerns without hesitation. Effective communication fosters a supportive environment where employees can work together to find safer alternatives.
e) Proper use of equipment: When provided with equipment designed to facilitate safe Manual Handling, employees are responsible for using it correctly. This includes understanding how the equipment functions, following operating procedures, and reporting any malfunctions or defects immediately.
f) Active participation in health surveillance: If an employer implements health surveillance, employees should actively participate in it and other such initiatives. Regular health assessments can help identify any signs of discomfort or injury related to Manual Handling activities, allowing for timely intervention and preventive measures.
Join our Health And Safety Training For Managers And Supervisors course to learn how to use accident prevention techniques effectively and efficiently.
Benefits of Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992

Implementing and adhering to the MHOR provides several benefits for employers and employees. These regulations are not just a legal obligation but a crucial framework that promotes safety, health, and productivity in workplaces across the United Kingdom. The following are some of the key benefits of implementing Manual Handling Operations Regulations:
a) Injury prevention: Perhaps the most significant benefit of the MHOR 1992 is the prevention of workplace injuries. By enforcing proper Manual Handling Techniques, providing training, and ensuring the use of appropriate equipment, the risk of injuries such as strains, sprains, and musculoskeletal disorders is reduced significantly. This results in a healthier and more efficient workforce.
b) Increased productivity: A workforce free from injuries is a more productive workforce. When employees are confident in their ability to perform Manual Handling tasks safely, they can work efficiently without fearing accidents. Reduced injuries also mean fewer workdays lost due to absence, contributing to consistent productivity.
c) Improved employee morale: Employees who feel their employer prioritises their safety and well-being tend to have higher job satisfaction and morale. Knowing that the company adheres to regulations designed to protect employees fosters a sense of trust and loyalty, leading to a positive work atmosphere.
d) Legal compliance: Complying with the MHOR 1992 ensures employers meet their legal obligations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal consequences, fines, and potential lawsuits. By following the guidelines, employers safeguard themselves from legal complications and maintain a strong reputation.
e) Reduced financial costs: Workplace injuries incur significant financial costs for employers, including medical expenses, compensation claims, and the costs of hiring and training replacements. Adhering to the MHOR 1992 reduces the likelihood of such costs, contributing to long-term financial stability.
f) Enhanced reputation: Companies that prioritise employee safety and adhere to regulations develop a positive reputation. Such organisations attract top talent and are more likely to retain skilled employees, as prospective and current workers appreciate the commitment to their well-being.
Join our Healthy Working Environment Training to learn and become familiar with different international policies about Workplace health.
Conclusion
The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 is crucial in developing and maintaining a safe and healthy work environment. Adhering to these regulations, employers can ensure the well-being of their workforce, reduce the risk of injuries, and foster a positive workplace culture. Employees, in turn, benefit from increased safety, improved job satisfaction, and a sense of security in their workplace. As companies prioritise safety, the MHOR 1992 remains a cornerstone of responsible and ethical business practices across the UK industries.
Learn more about Health & Safety in the Workplace Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Manual Handling at Work
Manual Handling at Work
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


