We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +46 850282424 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Are you curious about how researchers find answers to important questions? Research Methodology is the process that guides researchers in collecting, analysing, and interpreting data systematically. It ensures accuracy, reliability, and clarity in research findings.
By using the right methodology, researchers can solve problems, test theories, and make informed decisions. It is a crucial step for anyone aiming to produce credible and meaningful research.
Ready to learn more? Read this blog to explore how Research Methodology helps create meaningful results and supports the discovery of new knowledge!
Table of Contents
1) What is Research Methodology?
2) Why is Research Methodology Important?
3) Different Types of Research Methodology
4) Types of Sampling Designs in Research Methodology
5) Data Collection Methods
6) Steps to Writing a Research Methodology
7) Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Research Methodology
8) Conclusion
What is Research Methodology?
Research Methodology outlines how a researcher plans to conduct their study. It is a structured and logical approach to solving a research problem. The methodology explains the researcher's strategy to obtain reliable and valid results that meet their goals and objectives. It includes details on what data will be collected, where it will be sourced, and how it will be gathered and analysed.
Why is Research Methodology Important?
The purpose of a Research Methodology is to justify your approach to conducting research, including your data collection methods, analysis techniques, and other essential aspects of your study. Think of it as creating a plan or outline for your intended actions. During research, it’s easy to stray or deviate from your set methodology.
Different Types of Research Methodology
When designing a Research Methodology, a researcher faces several important decisions. One crucial choice is whether to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-method approach. Regardless of the research type, data will be in the form of numbers or descriptions, and researchers can choose to focus on words, numbers, or both. Let’s explore the different Types of Research Methodology in detail.
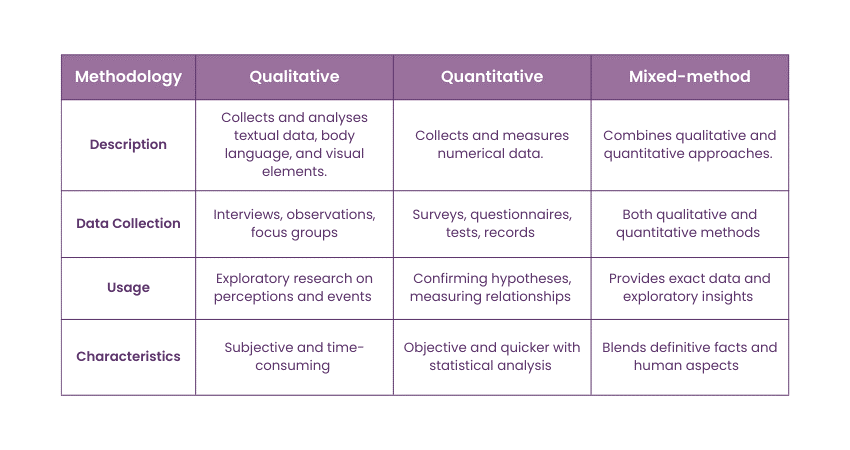
Qualitative
a) Description: Involves collecting and analysing written or spoken words and textual data. May include body language and visual elements to create detailed descriptions.
b) Data Collection: Interviews, observations, and focus groups with a few carefully selected participants.
c) Usage: Often used for exploratory research, such as understanding human perceptions of events, people, or products.
d) Characteristics: Subjective and time-consuming.
Quantitative
a) Description: Focuses on collecting, testing, and measuring numerical data from a large sample.
b) Data Collection: Surveys, questionnaires, tests, databases, and organisational records.
c) Usage: Used to confirm hypotheses or measure relationships between variables.
d) Characteristics: Objective and quicker, often using statistical software for analysis
Mixed-method
a) Description: Combines quantitative and qualitative approaches for additional perspectives and richer results.
b) Usage: Provides both exact data and exploratory insights.
c) Characteristics: Offers a blend of definitive facts and human aspects.
Types of Sampling Designs in Research Methodology
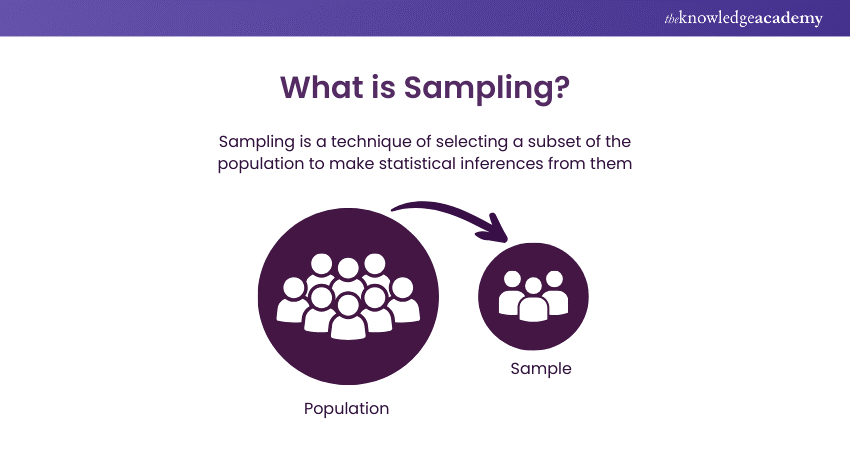
When creating a sample design, researchers decide from whom or what they will collect data and the techniques and procedures for selecting items or individuals. Sample designs fall into two main categories:
a) Probability Sampling
This method involves randomly selecting a sample from the population of interest. Every person or item has an equal chance of being chosen. This approach ensures a representative sample, allowing researchers to generalise the results to the entire population.
b) Nonprobability Sampling
In this method, the researcher deliberately selects people or items for the sample. Also known as deliberate, judgment, or purposive sampling, it does not give everyone in the population an equal chance of being selected, and results are typically not generalisable to the entire population.
Learn how Emotional Intelligence can be applied in organisations with our Emotional Intelligence Training – Join today!
Data Collection Methods
Once researchers have their population sample, they need to decide how to collect data. Here are some common methods:
a) Interviews: Can be formal or informal, based on the structure of the questions.
b) Surveys: Can be online or in-person, with free-answer or multiple-choice questions, or a mix.
c) Focus Groups: Small groups discuss specific topics, guided by a moderator.
d) Observations: Collect data from published reports, official documents, and internal records.
These methods help gather the necessary data for research studies.
Steps to Writing a Research Methodology
Your methodology plan should include:

a) Research Method: Specify if you'll use quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method research, based on your goals.
b) Reasoning: Explain why you chose this method and how it solves your research problem.
c) Instruments: List your data collection methods (e.g., interviews, surveys) and why you chose them.
d) Data Analysis: Describe how you'll analyse the data.
e) Reader Guidance: Provide background on your methods, especially if non-standard.
f) Sampling Process: Explain how you'll select your sample and why.
g) Practical Limitations: Discuss any potential limitations in your research.
This plan will help guide your research and ensure clarity and effectiveness.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Research Methodology
When choosing a Research Methodology, consider these factors:
a) Research Objective: Determine what information you need to meet your project's goals, which helps select the right methodology and methods.
b) Significance of Statistics: Decide if you need precise, data-driven results and statistical answers or if you need to understand reasons, perceptions, opinions, and motivations.
c) Nature of Research: If your goals are exploratory, use qualitative methods. If you aim to measure or test something, use quantitative methods.
d) Sample Size: Consider how large the sample needs to be to answer your questions and meet your objectives. This can influence whether to use in-person interviews for smaller samples or online surveys for larger ones.
e) Time Available: If time is limited, use techniques like random or convenience sampling and methods that allow quick data collection. With more time, consider in-person interviews and observations.
Master effective communication with our Active Listening Training – Join today!
Conclusion
Research Methodology is the backbone of any study, ensuring a structured and reliable approach to collecting and analysing data. It helps researchers draw accurate conclusions and make meaningful contributions. By following a clear methodology, studies become credible, reproducible, and impactful in advancing knowledge across various fields.
Learn to articulate ideas clearly with our Effective Communication Skills Course – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three factors are the research objective, the nature of the study, and available resources. Objectives define the purpose, the study’s nature (qualitative or quantitative) guides the approach, and resources like time, budget, and tools determine the feasibility of the chosen methods.

The four Ps are Purpose, Process, Participants, and Publishing. Purpose defines the goal of the research, Process outlines the methods used, Participants refer to the subjects involved, and Publishing ensures the findings are shared with the intended audience for validation or further exploration.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses, including the Career Development Course, Active Listening Training, and Emotional Intelligence Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Customer Experience Automation.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Research Methodology, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Active Listening Training
Active Listening Training
Fri 31st Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 30th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


