We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +46 850282424 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Are you ready to dive into the exciting universe of Software Testing? Buckle up, because this journey promises both adventure and rewards. As we explore the dynamic career roles in Software Testing, you’ll discover how they play a vital role in ensuring top-notch quality and flawless functionality in digital products. Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned pro, understanding Software Testing Job Roles is your secret weapon for success. So, let’s embark on this exhilarating ride together!
Table of Content
1) What is the Role of a Software Tester?
2) Software Testing Job Roles
3) Software Testing Skills
4) Career Path for Software Testers
5) Major Challenges of Software Testing
6) Conclusion
What is the Role of a Software Tester?
Software Testers play an important role in the development cycle, ensuring that programs are bug-free before release. Their main responsibilities include creating the test environment and plan, conducting tests, documenting bugs, and ensuring the software meets required standards. Testers collaborate with developers, product managers, and other stakeholders to deliver a high-quality product.
Software Testing Job Roles
Software Testing job roles are essential in the development cycle, focusing on ensuring the quality and reliability of software products. These roles encompass a variety of responsibilities aimed at identifying and eliminating bugs before the software is released to consumers. Here are some key Software Testing job roles:
QA Engineer / Test Engineer
QA Engineers, also known as Test Engineers, work on developing strategies that will enable the produced software to meet the quality requirements. They are responsible for designing the kinds of automated and manual tests performed, interpreting test results, and even solving problems with the developers of the application.
Their responsibilities include:
a) Developing strategies to meet quality requirements.
b) Designing and implementing automated and manual tests.
c) Interpreting and analysing test results.
d) Collaborating with developers to resolve issues.
e) Identifying bugs early in the development cycle.
Impress hiring managers with your knowledge of Software developer interview questions. Show your expertise and land the job you’ve always wanted!
Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET) / Automation Tester
SDET or Automation Testers are considered subcategory testers who have their coded background. They work on the creation and sustenance of automated testing scripts, build those into the pipeline, and ensure they run. SDETs overcome the middle-distance race between development and testing and improve the quality of testing.
Their key responsibilities are:
a) Creating and maintaining automated testing scripts.
b) Integrating automated tests into the development pipeline.
c) Ensuring automated tests run smoothly and efficiently.
d) Enhancing the quality of testing through automation. Maintaining detailed software testing documentation ensures that automated scripts are tracked and optimized over time, improving efficiency.
QA Manager / Director of Quality Assurance
QA Managers oversee the entire testing process within an organisation. They develop testing strategies, manage QA teams, and ensure that testing activities align with business goals. Directors of Quality Assurance take on a higher strategic role, focusing on long-term quality goals and continuous improvement initiatives across multiple projects.
Their responsibilities include:
a) Developing and implementing testing strategies.
b) Managing and coordinating QA teams.
c) Ensuring testing activities align with business objectives.
Directors of Quality Assurance take on a more strategic role:
a) Setting long-term quality goals.
b) Leading continuous improvement initiatives across multiple projects.
Test Consultant
Test Consultants are experts hired to provide specialised testing services. They assess current testing practices, recommend improvements, and often lead the implementation of new testing methodologies. Their goal is to enhance the Quality Assurance process, ensuring it is robust and efficient.
Their responsibilities include:
a) Assessing current testing practices.
b) Recommending improvements and new methodologies.
c) Leading the implementation of improved testing processes.
d) Ensuring the overall QA process is robust and efficient.
Explore Software Tester Salary: Maximize Your Earnings. Discover More Now!
Software Testing Skills
To excel in the various Software Testing Job Roles, professionals need a specific set of skills. These skills ensure that testers can effectively identify and resolve issues, contributing to the delivery of high-quality software products. Here are some essential Software Testing skills:
Communication Skills
Effective communication is vital for Software Testers. They need to clearly document and report bugs, provide constructive feedback, and collaborate with team members. Strong verbal and written communication skills ensure that issues are understood and addressed promptly.
Analytical and Logical Mindset
Software Testers must possess a keen analytical mind to identify potential issues and logical thinking to devise effective test cases. This skill helps in understanding complex systems and predicting where problems might arise.
Project Management Skills
Project management skills are essential for testers to plan, execute, and monitor testing activities efficiently. They must manage their time, resources, and tasks to meet deadlines without compromising on quality.
Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are crucial for working effectively within a team. Testers need to build strong relationships with developers, product managers, and other stakeholders to ensure a smooth testing process and effective issue resolution. Including this collaborative skill in your Software Tester Resume can showcase your ability to work seamlessly with cross-functional teams, enhancing your appeal to potential employers.
Excellent Time Management
In the fast-paced world of Software Development, time management is crucial. Testers must prioritise tasks, manage their time efficiently, and ensure that testing is completed within project timelines.
Adaptability
The technology landscape is constantly evolving, and testers must adapt to new tools, methodologies, and environments. Being flexible and open to change is essential for staying relevant in the field.
Automation Testing
Knowledge of automation tools and techniques is increasingly important. Automation testing helps in executing repetitive tests quickly and accurately, allowing testers to focus on more complex issues.
Advance your career with the ISTQB Advanced Level Test Manager Course. Join now to excel in Software Testing management!
Career Path for Software Testers
Becoming a Software Tester involves a combination of education, experience, and specialised training. Here's a detailed guide to help you navigate this career path effectively.
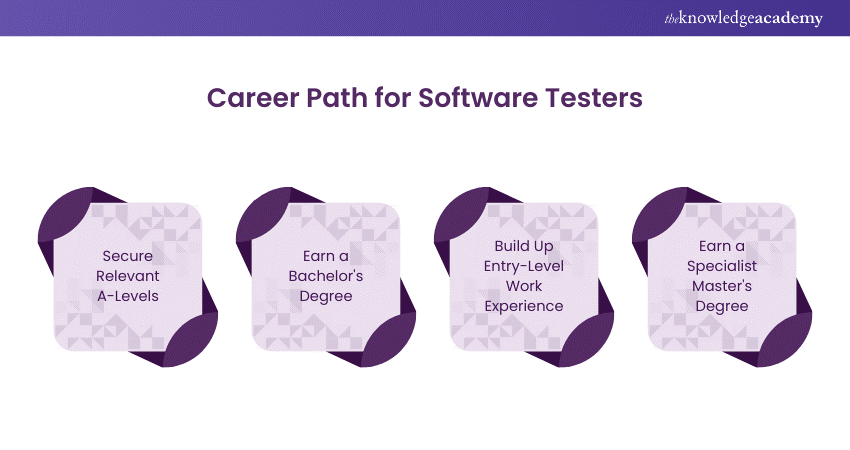
1) Secure Relevant A-Levels
a) Start by earning relevant A-Levels. Consider IT, Computer Science, or Mathematics A-Levels to gain programming and technical writing skills.
b) Physics, chemistry, or electrical engineering A-Levels can also be beneficial.
c) Review entry requirements for your preferred universities to understand their expectations.
d) Obtain these qualifications either at a local college or remotely.
2. Earn a Bachelor's Degree
a) After securing A-Levels, join a bachelor’s degree program.
b) Specialise in computer science or a related field to develop quality assurance skills.
c) Alternatively, explore project management by pursuing a bachelor’s in project management.
d) Learn about managing data sets, building websites, and planning software functions.
3. Build Up Entry-Level Work Experience
a) After university, apply for entry-level Software Development or quality assurance jobs.
b) Software roles include Junior Software Developer, Junior Software Engineer, and Website Developer.
c) Quality assurance positions include Junior Project Manager and Quality Assurance Assistant.
d) Gain experience in writing clean code, designing software functions, and developing organisational and communication skills.
4) Earn a Specialist Master's Degree
a) Consider pursuing a Master’s degree to enhance your expertise.
b) Depending on your Bachelor’s degree, specialise further in computer science or computing skills.
c) Explore options like a Master’s in System Test Engineering or Software Engineering (conversion).
d) These programs cover reliable Software Testing processes, system requirements, and Software Development planning.
Advance your Automation Testing skills with JUnit 5 by registering in Automation Testing With JUnit 5 Course
Major Challenges of Software Testing
Software Testing presents its own unique set of challenges. Testers must navigate tight deadlines, rapidly changing requirements, and complex systems. Additionally, ensuring comprehensive test coverage and staying current with the latest testing tools and methodologies are ongoing hurdles. Overcoming these challenges requires a proper strategic approach, continuous learning, and effective communication.
Master your skills with Certified Software Testing Manager (CSTM) Training. Sign up now to become a certified testing manager!
Conclusion
Navigating the Software Testing job roles can be a thrilling adventure filled with opportunities to ensure software excellence. As you explore this dynamic field, whether you're a fresher or a seasoned professional, understanding the diverse roles within testing is crucial. Embracing Agile Methodology in Software Testing can further enhance your skills, helping you tackle challenges effectively. By acquiring the necessary expertise and embracing these challenges, you'll chart a course toward ensuring software excellence.
Master the art of seamless software quality with our Software Testing Automation Course – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a Software Tester contribute to the development process?

Software Testers contribute by ensuring that software is free of bugs and meets quality standards. They collaborate with developers and other team members to identify issues early, provide feedback, and help deliver a reliable and user-friendly product.
How can I Advance my Career in Software Testing?

Advancing your career in Software Testing involves gaining experience, pursuing higher education like a specialist master's degree, obtaining certifications, and continuously learning new testing tools and methodologies. Building strong communication and project management skills also contributes to career growth.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and How Does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Software Testing Courses, including ISTQB Advanced Level Test Manager, ISTQB Advanced Level Test Analyst, Certified Software Testing Professional (CSTP) and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Programming Fundamentals.
Our Programming & DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to Software Testing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Software Testing Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level Test Management Course
ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level Test Management Course
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


