We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +65 6929 8747 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today's dynamic educational landscape, it is crucial for teachers to adapt their approaches to meet their student's unique needs and learning styles. Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) provides a framework for them to understand and work with the cognitive and emotional processes that influence student behaviour and performance.
NLP offers a robust set of techniques and strategies that can greatly benefit teachers in their classrooms. Effective utilisation of NLP principles enables them to enhance their teaching practices, improve student engagement, and maintain a positive learning environment.
NLP techniques help teachers personalise learning, provide targeted feedback, and create engaging content. Discover how NLP techniques can be applied effectively.
Table of Contents
1) Why is NLP important for teachers?
2) Techniques of NLP for Teachers
a) Anchoring
b) Reframing
c) Sensory acuity
d) The meta-model
e) Outcome setting
3) Conclusion
Why is NLP important for teachers?
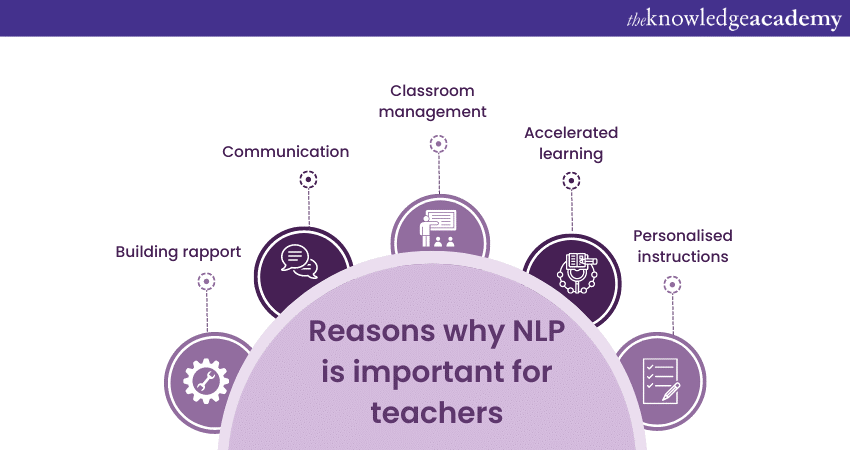
NLP training for teachers provide them with practical tools to create a positive and empowering learning environment. Here are three vital reasons why NLP is essential for teachers:
1) Building rapport: Students learn faster and more efficiently when they feel heard by their teachers and have a positive connection with them. Teachers can establish strong connections with their students via various NLP techniques like reading non-verbal cues, mirroring and matching, and active listening skills. This also helps students understand their mentors better and in creating a trusting environment.
2) Effective communication: Clear communication is the basis of quality teaching. NLP provides teachers with valuable techniques and strategies to enhance their communication skills. Specific language patterns like embedded commands and active listening help them convey information effectively to students.
3) Improved classroom management: Classroom management is a critical aspect of effective teaching, and NLP, aligned with the Principles of Teaching, equips teachers with techniques to optimise student behaviour and engagement. Theys can create positive associations with learning activities through anchoring techniques, improving student focus, concentration, and motivation.
4) Accelerated learning: NLP provides teachers with tools to facilitate accelerated learning and cater to diverse learning styles. They can use modelling techniques to showcase exemplary behaviours and skills, inspiring students to adopt those behaviours and excel academically.
5) Personalised instructions: NLP strategies can identify and understand individual students' preferred learning modalities, enabling teachers to tailor their instructions accordingly and create personalised learning experiences that maximise student engagement.
Techniques of NLP for Teachers
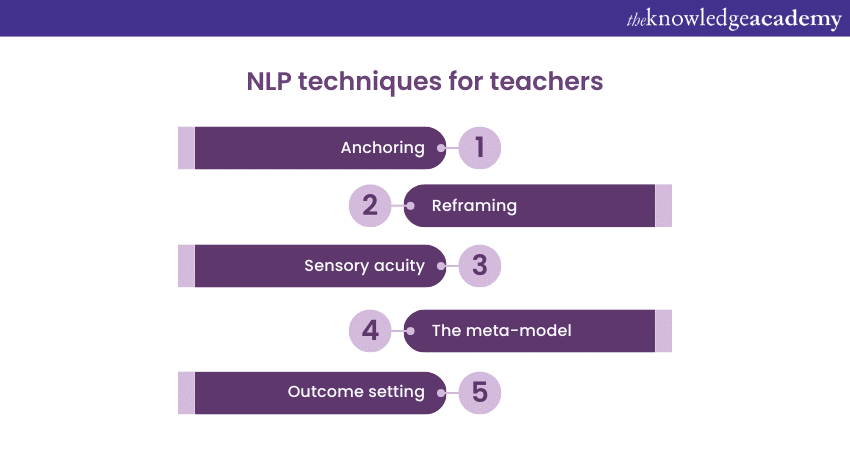
NLP provides a wide range of tools and techniques which help teachers improve their teaching methods and conduct effective classes for their students. Here are five effective techniques of NLP for Teachers:
1) Anchoring
Anchoring is a powerful technique in NLP that involves associating a specific state of mind or emotion with a particular trigger or stimulus. The purpose of anchoring is to create a reliable response in oneself or others by establishing a connection between an internal state and an external cue.
In teaching, anchoring can be used to enhance student learning, motivation, and performance. Anchoring in NLP can be used in classrooms with the following steps:
1) Identify the desired state: Teachers must fixate on the state they wish to anchor in their students, such as a state of confidence, creativity, focus, etc.
2) Creating the anchor: Once you have identified the desired state, you need to establish a sensory cue or anchor that will trigger that state. Anchors can be visual, auditory, or kinesthetic.
3) Eliciting the state: To create the anchor, you must elicit and intensify the desired state in the students. This can be done by engaging them in activities or discussions that evoke the specific state you want to anchor.
4) Applying the anchor: Once the desired state is elicited and peaked, introduce the anchor using the chosen cue. For instance, you might touch a specific spot on the student's arm while they are in a state of confidence.
5) Testing and reinforcing the anchor: To solidify the anchor, you test its effectiveness by using the cue in different contexts and observing the desired state being quickly accessed. Students can learn to activate the desired state at will when the anchor is applied by consistently reinforcing the anchor through repetition and practice.
2) Reframing
Reframing is a fundamental technique provided by NLP that involves shifting perspectives and interpreting situations in a new and empowering way. It enables teachers to reframe students’ challenges and limiting beliefs into opportunities for growth and positive change. Here are the steps to effectively implement reframing in classrooms:
1) Recognising negative perspectives: The first step in reframing is identifying unhelpful perspectives or limiting beliefs hindering learning or student progress.
2) Challenging the assumption: The next step involves teachers helping students to challenge the assumptions underlying their beliefs and explore alternative interpretations of the situation.
3) Shifting focus: Teachers can guide students to look for positive aspects, strengths, or lessons learned from challenging situations, which helps them view the situation from different angles.
4) Language: Teachers can use positive and empowering language to reframe situations and encourage students to do the same.
5) Modelling reframing: Teachers can model reframing by sharing personal stories of how they have reframed challenges or setbacks in their own lives.
Explore the power of NLP with our NLP Training courses now!
3) Sensory acuity
Sensory acuity is a fundamental aspect of NLP that focuses on developing heightened awareness and sensitivity to sensory information. Sensory acuity helps teachers gather valuable information about their students' emotional states, learning preferences, and engagement levels, allowing for more effective communication and personalised instruction. They can apply the NLP technique to the classroom in ways like:
1) Observing non-verbal cues: Sensory acuity involves keen observation of non-verbal cues such as facial expressions, body posture, eye contact, gestures, and breathing patterns.
2) Listening to tone and voice quality: Listening to the tone of voice, pitch, pace, and overall quality of students' speech reveals indications of confidence, excitement, hesitation, or stress.
3) Noticing micro-expressions: Developing sensory acuity in Micro Teaching allows teachers to detect subtle emotional shifts or hidden reactions that students may not explicitly communicate.
4) Adapting to learning preferences: Sensory acuity helps teachers recognise students' preferred learning modalities. Some students may prefer visual aids and diagrams, while others may be required auditory or kinesthetic.
4) Building rapport: By being present and fully engaged in interactions, teachers demonstrate their attentiveness, respect, and genuine interest in students' well-being.
5) Responding with sensitivity: Sensory acuity enables teachers to adapt their teaching strategies and interventions based on the sensory information they receive.
4) The meta-model
The meta-model is a linguistic tool and technique in NLP that helps mentors identify and challenge the language patterns that limit understanding and communication. It provides a framework for expanding upon vague or general statements by asking specific questions to uncover missing information, assumptions, and underlying beliefs. Teachers can apply this technique in their classrooms via:
1) Identifying language patterns: The Meta-Model helps teachers recognise common language patterns like generalisations, deletions, and distortions that may limit or distort communication.
2) Asking specific questions: The meta-model prompts teachers to ask specific questions to uncover missing information, clarify assumptions, and challenge generalizations, deepening understanding and promoting critical thinking.
3) Expanding on deletions: When a student makes a statement that omits essential information, the teacher can ask questions to fill in the gaps. For example, if a student says, "I didn't understand the lesson," the teacher can use the Meta-Model to ask, "What specifically did you find challenging? Can you give me an example?"
4) Challenging generalisations: The meta-model encourages teachers to challenge broad generalisations by seeking specific instances and examples.
5) Questioning distortions: Distortions involve inaccurately representing or exaggerating information. The meta-model prompts teachers to ask questions that challenge distortions and seek clarification.
6) Encouraging precision and quality: Teachers encourage students to be more precise and specific in their language. This fosters more transparent communication and promotes critical thinking skills.
Level up your teaching skills with our NLP Foundation And Practitioner Training course now!
5) Outcome setting
Outcome setting is a key technique in NLP that involves guiding individuals to define clear and specific goals or outcomes. By setting outcomes, teachers can provide students with a clear focus, motivation, and a roadmap for achieving their academic objectives. The technique can be applied in the classroom with the following steps:
1) Clarifying goals: Outcome setting begins with defining goals or desired outcomes. Teachers can guide students to identify what they want to achieve academically, whether mastering a specific skill or improving their grades.
2) Visualising success: They can facilitate outcome setting by encouraging students to visualise and imagine themselves successfully achieving their goals.
3) Defining action steps: Outcome setting involves breaking down the desired outcomes into actionable steps. Teachers can guide students to identify the specific actions they need to take to progress towards their goals.
4) Tracking progress: They can help students track their progress towards their outcomes via Regular check-ins and feedback sessions.
5) Encouraging reflection and adaptation: Teachers can facilitate reflection and adaptation by encouraging students to reflect on their experiences and make necessary adjustments to their goals.
6) Celebrating achievements: Celebrating achievements reinforces a sense of accomplishment, boosts confidence, and motivates students to continue pursuing their goals.
Conclusion
NLP training for teachers offers multiple powerful techniques that can greatly benefit them in their classrooms. The multiple techniques by NLP for Teachers can enhance their communication and effectiveness in guiding students’ learning journeys by incorporating them. We hope this blog has helped you understand in detail about techniques like anchoring, reframing, etc., which help teachers create a more engaging and inclusive learning environment.
Enhance your teaching abilities and become proficient in NLP with our Master Diploma In NLP course now!
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Neuro Linguistic Programming
Neuro Linguistic Programming
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


