We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +65 6929 8747 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Whether you are preparing to shine in a Penetration Testing interview or seeking insights to hire the best, our curated list covers essential aspects of Penetration Testing interview questions and answers expertise.
According to Gartner, the average salary for a Penetration Tester is £56,624 per year in London, United Kingdom. If you are looking for a career in Penetration Testing, you need to ace the interview. This blog will prepare you for Penetration Testing interview questions with a list of frequently asked questions. Explore a list of interview questions and crafted answers.
Table of Contents
1) Fundamental Penetration Testing Interview Questions
2) Penetration Testing Interview Questions on techniques and tools
3) Penetration Testing Interview Questions on vulnerabilities and exploitation
4) Penetration Testing Interview Questions on network and system security
5) Miscellaneous topic on Penetration Testing Interview Questions
6) Conclusion
Fundamental Penetration Testing Interview Questions
In this section, we will explore core concepts of Penetration Testing, which are essential for building a robust foundation. These fundamental questions serve as stepping stones, ensuring you grasp the basics before venturing into more intricate aspects of the field.
Q1) What is Penetration Testing, and why is it important?
Penetration Testing, ethical hacking, involves simulating cyberattacks on systems, networks, or applications to uncover vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. It is essential to proactively identify digital infrastructure weaknesses, helping organisations enhance their security posture and safeguard sensitive data from potential breaches.
Q2) Differentiate between vulnerability assessment and Penetration Testing.
Vulnerability assessment aims to identify and categorise vulnerabilities within a system or network. Penetration Testing, on the other hand, involves exploiting these vulnerabilities in a controlled manner to understand the potential impact of a real-world attack. While vulnerability assessment provides a snapshot of weaknesses, Penetration Testing provides insights into possible consequences.
Q3) Explain the main types of Penetration Testing.
Penetration Testing encompasses various approaches:
a) Black-Box Testing: Testers do not know the target system and simulate attacks as an outsider would.
b) White-Box Testing: Testers have complete knowledge of the target system, enabling a more thorough assessment.
c) Grey-Box Testing: Combines black-box and white-box testing elements, striking a balance between realism and insight.
Q4) What are the key steps in planning a Penetration Testing engagement?
Planning a penetration test involves several critical steps:
a) Define Objectives: Identify what needs to be tested and the desired outcomes.
b) Scope Definition: Determine the systems, networks, or applications to be tested and any limitations.
c) Rules of Engagement: Set rules for testers to ensure adherence to ethical and legal guidelines.
d) Resource Allocation: Allocate necessary tools, personnel, and resources for the assessment.
Q5) How do you define the scope of a Penetration Testing project?
Defining the scope requires a clear understanding of the target environment, including assets, systems, and networks to assess. Consider the business impact, potential vulnerabilities, and goals of the test. The scope should be well-defined to avoid unnecessary complications during the assessment.
Elevate Your Security: Embrace the Future with Automation & Penetration Testing for Comprehensive Cyber Protection.
Penetration Testing Interview Questions on techniques and tools
Aspiring penetration testers must grasp these concepts to effectively identify vulnerabilities and strengthen cybersecurity defences.
Q6) What legal and ethical considerations should be taken into account before starting a penetration test?
Performing penetration tests requires a strong ethical foundation and adherence to legal guidelines. Ensuring proper authorisation from the system owner, obtaining explicit consent, and safeguarding sensitive data are vital steps to ensure responsible and lawful testing practices.
Q7) Describe the process of foot printing in Penetration Testing.
Foot printing involves collecting data regarding a target system, network, or organisation methodically. This information includes details about IP addresses, domain names, network architecture, and potential entry points. By analysing this footprint, penetration testers can identify potential areas of exploitation and develop a more comprehensive testing strategy.
Q8) How can WHOIS records be useful during information gathering?
WHOIS records provide essential information about domain names, such as registration details, contact information, and registration dates. These records are valuable for surveillance, helping testers understand the entities associated with the target, potential third-party vendors, and other critical information that aids in the testing process.
Q9) What is port scanning, and how is it used in Penetration Testing?
Port scanning involves actively probing a target system to discover open ports and services. It's a critical step in identifying potential attack surfaces and understanding the network's architecture. By determining which ports are available and what services are running, penetration testers gain insights into vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
Q10) What is Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) gathering?
Open Source Intelligence, or OSINT, involves collecting information from publicly available sources, such as social media, websites, and public records. This initial reconnaissance phase helps gather insights into the target's digital footprint, identifying potential vulnerabilities and areas of focus for Penetration Testing.
Penetration Testing Interview Questions on vulnerabilities and exploitation
This section explores Penetration Testing by examining vulnerabilities and the techniques used to exploit them. These questions probe your knowledge of identifying weaknesses and understanding the potential consequences of controlling them.
Q11) Explain the concept of banner grabbing.
Banner grabbing involves gathering information about a target system, such as its operating system, software versions, and services running. This information helps attackers tailor their exploits. Ethical hackers leverage banner grabbing to assess whether a system is running outdated or vulnerable software.
Q12) How does enumeration help in identifying potential vulnerabilities?
Enumeration involves systematically gathering information about a target to identify valid user accounts, network resources, and more. This process aids penetration testers in pinpointing weak points that could be exploited, allowing for a more targeted and practical assessment.
Q13) Differentiate between active and passive vulnerability assessment.
Active assessment involves actively scanning and probing the target system for vulnerabilities. Passive assessment does not interact directly with the target; instead, it relies on collecting information from network traffic or logs. Each approach has its merits, with active assessment providing real-time data and passive review minimising the risk of detection.
Q14) How do you prioritise vulnerabilities based on their severity?
Prioritising vulnerabilities is crucial due to resource constraints. Typical methods involve considering the impact, exploitability, and ease of patching. To mitigate the most significant risks, vulnerabilities with a high impact, high exploitability, and easy patching are usually addressed first.
Q15) What is the Metasploit Framework, and how is it used in Penetration Testing?
The Metasploit Framework is powerful tool penetration testers use to develop, test, and execute exploit code against a remote target. It provides a structured environment for creating and deploying exploits, making it an essential asset in the penetration tester's toolkit.
Q16) Explain the concept of privilege escalation.
Privilege escalation involves gaining higher levels of access on a system than originally intended. Attackers often seek to elevate privileges to gain control over critical resources or manipulate the target system. Penetration testers simulate this to evaluate the system's defences against unauthorised privilege escalation.
Q17) How can you maintain persistence in a compromised system?
Persistence refers to an attacker's ability to control a compromised system after the initial breach. Penetration testers use techniques, such as creating hidden backdoors or rootkits, to determine if a system can detect and prevent unauthorised persistence mechanisms.
Q18) Describe the steps you would take to test for SQL injection in a web application.
Testing for SQL injection involves sending malicious SQL queries to a web application's input fields to exploit vulnerabilities in its database handling. Steps include identifying input points, crafting antagonistic questions, and observing the application's response. Successful exploitation indicates inadequate input validation.
Q19) How can Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks be prevented?
Cross-Site Scripting involves injecting malicious scripts into a web application, affecting compromised content users. Prevention methods include input validation, output encoding, and implementing security controls such as Content Security Policy (CSP) to mitigate the risk of XSS attacks.
Enhance your cybersecurity skills with our comprehensive guide on Tools and Techniques for Penetration Testing – Equip yourself to defend and outsmart digital threats!
Penetration Testing Interview Questions on network and system security
This section will explore questions that centre around safeguarding digital assets and understanding the crucial aspects of defending against cyber threats.
Q20) What are the key differences between WEP and WPA/WPA2 wireless security protocols?
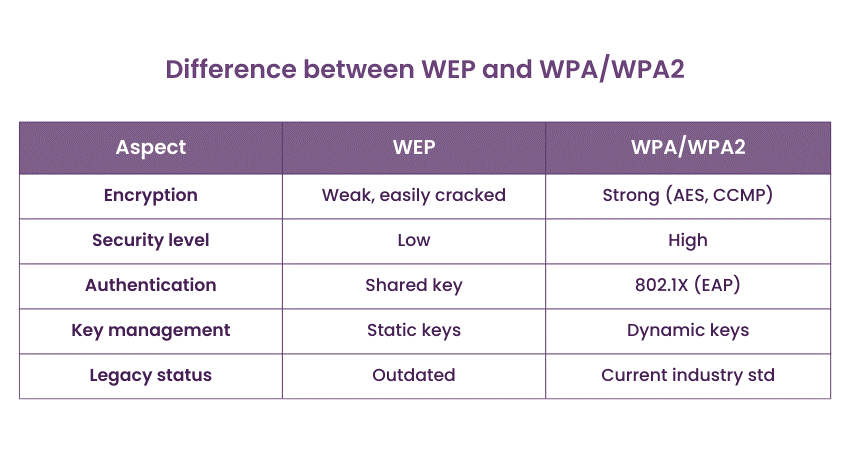
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) are wireless security protocols. WEP is outdated and vulnerable, while WPA/WPA2 offer more robust encryption and security features. WPA2, the current standard, uses advanced encryption methods, making it significantly more secure than WEP.
Q21) How would you perform a wireless network assessment?
Conducting a wireless network assessment involves several steps. Begin by identifying all visible networks in the vicinity. Evaluate signal strengths and map coverage areas. Detecting unauthorised access points is crucial, as rogue devices can provide entry points for attackers.
Q22) Define social engineering in the context of Penetration Testing.
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information, passwords or perform actions that compromise security. In Penetration Testing, social engineering techniques are used to assess an organisation's susceptibility to human-based attacks.
Q23) What is a physical security assessment, and what methods are commonly used?
A physical security assessment evaluates the physical safeguards to protect an organisation's assets. Techniques include assessing access controls, camera coverage, security policies, and even simulating break-ins to identify weak points.
Q24) What components should be included in a Penetration Testing report?
A comprehensive Penetration Testing report should cover critical elements:
1) Executive summary: Concise overview for management.
2) Methodology: Explanation of the testing process.
3) Vulnerabilities identified: Detailed description of security weaknesses.
4) Exploitation results: How vulnerabilities were exploited, if applicable.
5) Risk assessment: Ranking vulnerabilities based on potential impact.
6) Recommendations: Actionable steps to improve security.
Q25) How do you effectively communicate technical findings to non-technical stakeholders?
Effective communication is critical. Convert technical jargon into understandable language, emphasise potential business impacts, and provide clear visuals to help non-technical stakeholders grasp the significance of identified vulnerabilities and their implications.
Q26) What is a VPN, and how does it enhance network security?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts and routes internet traffic through a secure tunnel, ensuring privacy and security. It enhances network security by protecting data transmitted over potentially insecure networks and allowing users to access resources remotely without compromising security.
Q27) Describe the concept of IDS and IPS in network defence
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) monitors network traffic for suspicious activities, generating alerts when potential threats are detected. An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) goes further by actively blocking or mitigating threats in real time to prevent unauthorised access or attacks.
Unlock the power of cybersecurity with Kali Linux Fundamentals – equip yourself with essential tools and skills to navigate the world of ethical hacking and Penetration Testing confidently.
Miscellaneous topic on Penetration Testing Interview Questions
Here are some important miscellaneous questions asked in Penetration Testing
Q28) What is the purpose of encryption in cybersecurity?
Encryption plays a pivotal role by utilising cryptographic algorithms to convert data into an unintelligible form. This ensures that unauthorised parties, even if granted access, cannot comprehend the data's content, delivering a robust shield for safeguarding sensitive information.
Q29) Explain the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric encryption employs a single secret key for both encryption and decryption. Asymmetric encryption, however, uses two keys: one for encryption and another for decryption. While symmetric encryption is faster, asymmetric encryption offers better security due to the separation of keys.
Q30) How does a digital signature work, and why is it important?
A digital signature employs cryptographic methods to link a digital identity with a message or document, ensuring the sender's content's genuineness, unaltered state, and irrefutability. It enhances trust and responsibility in digital interactions.
Q31) Define malware and explain the different types of malware.
Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a range of harmful software designed to infiltrate, damage, or gain unauthorised access to systems.
Various forms of malware encompass viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware, each harbouring specific malevolent purpose.
Q32) Describe the steps involved in analysing a malicious file.
Here are the steps involved in analysis a malicious file:
1) Isolate the file
2) Identify file type and hash
3) Analyse headers and behaviour
4) Execute in a sandbox
5) Analyse code
6) Identify malware family
7) Create a detailed report
8) Share findings for collaboration
Q33) What is an incident response plan, and why is it important?
An incident response plan outlines predefined steps taken during cybersecurity incident. It ensures a structured approach to managing and mitigating incidents, minimising damage, reducing downtime, and maintaining business continuity.
Q34) Walk through the steps of handling a security breach incident.
Responding to a security breach involves several crucial steps:
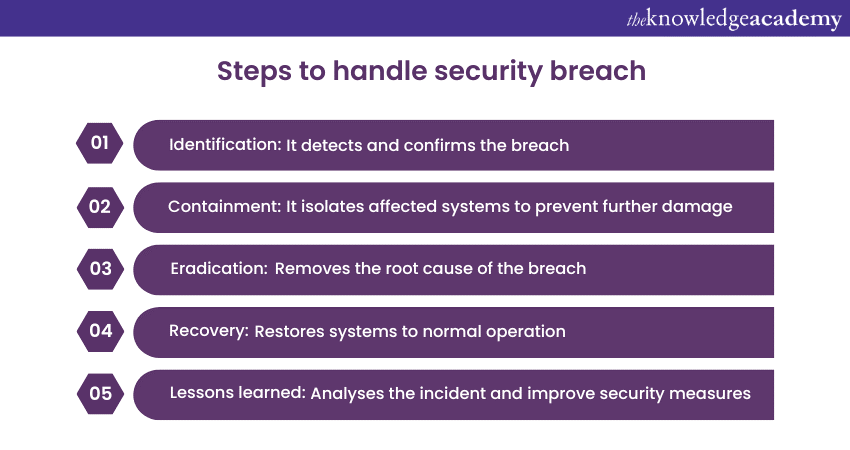
1) Identification: It detects and confirms the breach.
2) Containment: It isolates affected systems to prevent further damage.
3) Eradication: Removes the root cause of the breach.
4) Recovery: Restores systems to normal operation.
5) Lessons learned: Analyses the incident and improve security measures.
Q35) Why is secure coding important in software development?
Secure coding practices prevent vulnerabilities and security flaws from being introduced during software development. Developers create robust applications resistant to common attacks and vulnerabilities by adhering to secure coding principles.
Q36) Explain the principle of input validation and its significance.
Input validation guarantees that user-provided data adheres to anticipated parameters before processing. It safeguards against attacks like SQL injection, effectively thwarting efforts to embed harmful code within an application.
Q37) What are the main security concerns when using cloud services?
Cloud security concerns include data breaches, data loss, misconfigured settings, lack of control over infrastructure, and compliance challenges. Properly addressing these concerns requires a combination of provider security measures and vigilant user practices.
Q38) Describe the shared responsibility model in cloud security.
The shared responsibility model outlines the division of security responsibilities between cloud service providers and customers. Providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for ensuring cloud data, applications, and configurations.
Q39) How can you protect a wireless network from unauthorised access?
Securing a wireless network involves steps such as:
1) Implementing strong encryption, preferably WPA3.
2) Using strong, unique passwords for network access.
3) Disabling remote administration.
4) Hiding the network's SSID (name) to prevent casual discovery.
Q40) Explain the concept of a rogue access point and its risks.
A rogue access point refers to an unapproved wireless entry point linked to a network. Malicious actors establish these unauthorised APs to intercept network communication, seize data, and execute attacks. This presents a notable threat by sidestepping security protocols and rendering the network vulnerable to potential breaches.
Q41) What are the security challenges associated with IoT devices?
IoT devices present security challenges due to their limited processing power, lack of standardised security measures, and potential attack exposure. Their proliferation increases the attack surface, making them vulnerable to various exploits.
Q42) How can you secure an IoT network from potential attacks?
Securing an IoT network requires measures such as:
1) Implementing strong device authentication.
2) Regularly updating firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
3) Segregating IoT devices from critical networks.
4) Monitoring network traffic for anomalies.
Q43) What is a buffer overflow, and how does it pose a security risk?
A buffer overflow arises when a program deposits excessive data into a buffer, surpassing its capacity. It can result in overwriting nearby memory, possibly inducing crashes or empowering attackers to execute malevolent code and assume system control.
Q44) Describe methods to prevent and mitigate buffer overflow vulnerabilities.
Preventing buffer overflows involves programming languages with built-in safeguards (like Java), input validation, and functions that automatically manage memory boundaries—tools like static analysis and code reviews aid in identifying vulnerabilities.
Q45) What is reverse engineering, and why is it used in cybersecurity?
Reverse engineering involves dissecting and analysing software or hardware to understand its components, functionality, and potential vulnerabilities. In cybersecurity, it helps identify weaknesses, uncover hidden functionality, and assess the security of third-party code.
Q46) Explain the steps involved in reverse engineering a binary.
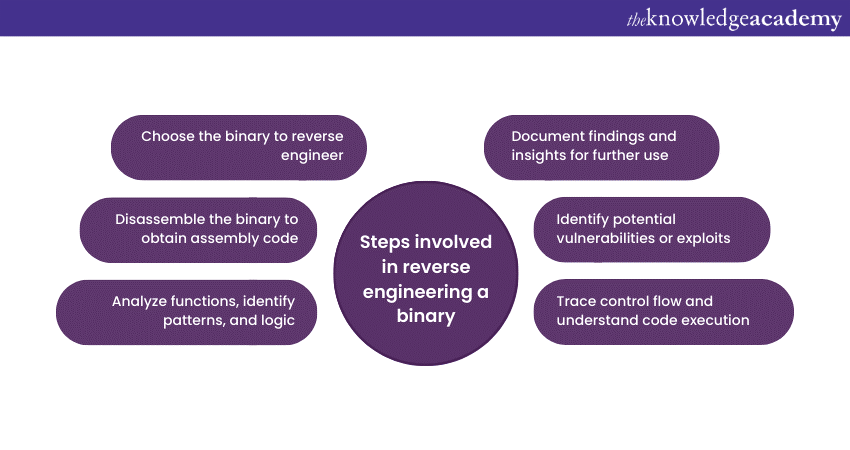
Reverse engineering binaries includes steps like disassembling the code into assembly language, analysing its functions and data structures, understanding its logic, and identifying potential vulnerabilities or security flaws.
Q47) What is the purpose of SSL/TLS protocols in securing communication?
SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) protocols encrypt communication between clients and servers, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity during transmission. They are essential for secure online transactions, sensitive data exchange, and user privacy.
Q48) How does ARP spoofing work, and how can it be prevented?
ARP spoofing involves sending fake Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages to link an attacker's MAC address with a legitimate IP address, enabling data interception. Prevention methods include using static ARP entries, implementing network segmentation, and deploying tools that detect ARP anomalies.
Q49) Describe SQL injection and how it can be prevented.
SQL injection involves inserting malicious SQL code into an application's input fields to manipulate its database. Prevention methods include using parameterised queries, input validation, and escaping user input to prevent unauthorised database access.
Q50) Explain the concept of least privilege in database security.
The principle of least privilege restricts users and applications from accessing only the minimum resources necessary for their tasks. In database security, it ensures that users have limited access rights, reducing the potential impact of a breach.
Q51) What is red teaming, and how does it differ from Penetration Testing?
Red teaming involves simulating real-world attacks to assess an organisation's security posture. Unlike Penetration Testing, which focuses on specific vulnerabilities, red teaming evaluates an organisation's ability to detect, respond to, and mitigate complex and persistent attacks.
Q52) How can red teaming help organisations improve their security posture?
Red teaming exposes vulnerabilities that traditional security measures may miss. It provides insights into weaknesses in processes, procedures, and human responses, allowing organisations to fine-tune their security strategies and enhance their overall readiness against cyber threats.
Q53) Mention some popular ethical hacking tools and their use cases.
Ethical hackers use tools like Nmap for network scanning, Wireshark for packet analysis, Metasploit for exploit development, and Burp Suite for web application testing. These tools aid in identifying vulnerabilities and testing the effectiveness of security measures.
Q54) How can you ensure responsible use of hacking tools during testing?
Responsible use of hacking tools involves obtaining proper authorisation, using the tools exclusively for legal and ethical purposes, and ensuring that the testing environment is isolated from production systems to prevent unintentional harm.
Q55) What is threat intelligence, and how can it be used in cybersecurity?
Threat intelligence involves collecting and analysing data about potential threats, including attack tactics, techniques, and procedures. It aids organisations in understanding evolving threats, improving incident response, and enhancing proactive defence strategies.
Q56) Describe the role of threat intelligence in proactive defence.
Threat intelligence aids organisations in anticipating and preparing for potential attacks. Organisations can implement preventive measures, fine-tune security policies, and swiftly respond to new challenges by staying informed about emerging threats and attackers' tactics.
Q57) Explain the concept of a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) in network security.
It is a network segment that separates an organisation's internal network from external networks, such as the Internet. It hosts publicly accessible services while protecting internal resources from direct exposure to potential threats.
Q58) How can you secure a web server against common attacks?
Securing a web server involves:
1) Regularly updating server software and plugins
2) Implementing a web application firewall (WAF)
3) Applying security headers to HTTP responses
4) Conducting thorough code reviews and vulnerability assessments
Q59) What is endpoint security, and why is it important?
Endpoint security involves protecting individual devices, such as computers and smartphones, from various cyber threats. It is essential as endpoints are often entry points for attacks and can spread malware throughout the network.
Q60) Describe methods to protect endpoints from malware attacks.
Protecting endpoints from malware involves using antivirus software, implementing strong access controls, keeping systems updated, using behaviour-based analysis tools, and educating users about safe online practices.
Q61) What are the risks of oversharing on social media from a cybersecurity perspective?
Oversharing on social media can expose personal information, such as birthdates, addresses, and relationships. Attackers can use this information to identify theft, social engineering, and craft targeted phishing attacks.
Q62) How can users protect their personal information on social media platforms?
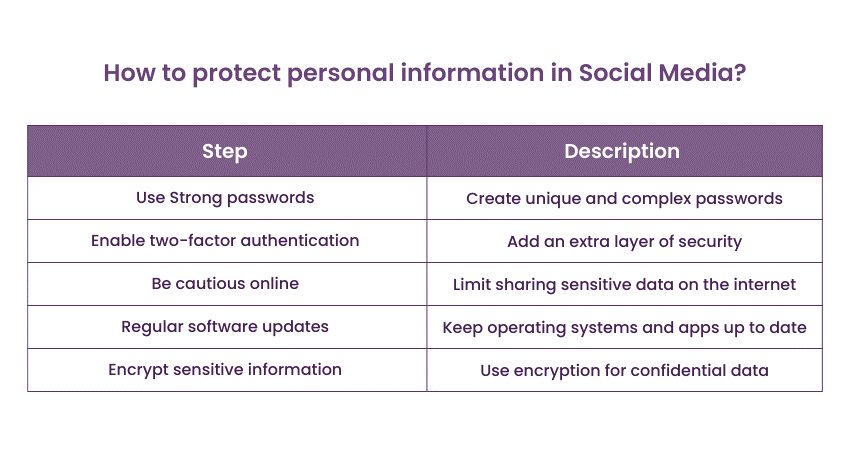
Users can protect their personal information by:
1) Adjusting privacy settings to limit who can view their posts.
2) Avoiding sharing sensitive details like phone numbers and addresses.
3) Being cautious about accepting friend requests from unknown individuals.
Q63) Provide a list of essential cybersecurity best practices for individuals and organisations.
1) Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
2) Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
3) Keep software and systems up to date.
4) Regularly back up important data.
5) Educate employees/users about phishing and social engineering.
6) Establish incident response plans for quick action in case of breaches
Q64) What are zero-day vulnerabilities, and how can they impact cybersecurity?
Zero-day vulnerabilities are undisclosed software flaws that hackers exploit before developers create fixes. They can cause severe damage by enabling unauthorised access, data breaches, and widespread attacks, undermining cybersecurity defences.
Q65) Explain the concept of a firewall and its role in network security.
A firewall is a security tool that regulates network traffic using predetermined security protocols. It shields between a reliable internal network and potentially insecure external networks, permitting solely authorised data to traverse the barrier.
Conclusion
Mastering the essentials, vulnerabilities, network security, and diverse concepts is essential. By becoming proficient in these areas, you will be well-prepared to address these Penetration Testing Interview Questions. You are now positioned to excel in evaluating, mitigating threats, and enriching the ever-evolving cybersecurity domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Manual Testing Training
Manual Testing Training
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


