We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine creating a digital copy of anything in the real world and using it to test, analyse, and improve its functionality. You could predict failures, prevent downtime, enhance quality, and save resources. This is the concept of Digital Twin, a technology transforming how we design, operate, and maintain physical assets. In this blog, we will explore What is Digital Twin basics of Digital Twin, its applications, and its implications for the future. Read further for a better understanding.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Digital Twin
2) How does Digital Twin work?
3) Various types of Digital Twins
4) Benefits of Digital Twins
5) Challenges with Digital Twins
6) The future of Digital Twin technology
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Digital Twin
A Digital Twin is a virtual model of a physical entity that mirrors its behaviour, state, and properties. It is created by collecting data from sensors, cameras, and other sources and using it to build a digital replica that can be updated in real-time. A Digital Twin can simulate various scenarios, monitor performance, and optimise the outcomes of the physical counterpart.
For example, a Digital Twin of a car can be used to test its aerodynamics, fuel efficiency, and safety features without building a physical prototype. A factory's Digital Twin can monitor the production process, detect anomalies, and improve quality and productivity.
How does Digital Twin work?
A Digital Twin has three main components: the physical entity, the digital model, and the data connection. The physical entity is the real-world object, system, or process that is being replicated. The digital model is the software representation that mimics the characteristics and behaviour of the physical entity. The data connection enables the exchange of information between the physical and digital domains.
The data connection can be bidirectional, meaning that the Digital Twin can receive data from the physical entity and send commands or feedback to influence its actions. For example, a Digital Twin of a wind turbine can receive wind speed, temperature, and vibration data and send commands to adjust the blade angle or rotation speed to optimise the power generation.
Transform your industry expertise with our Digital Twin Course. Sign up today!
Various types of Digital Twins
There are different types of Digital Twins, depending on the level of complexity, scope, and purpose. Some of the common types are:
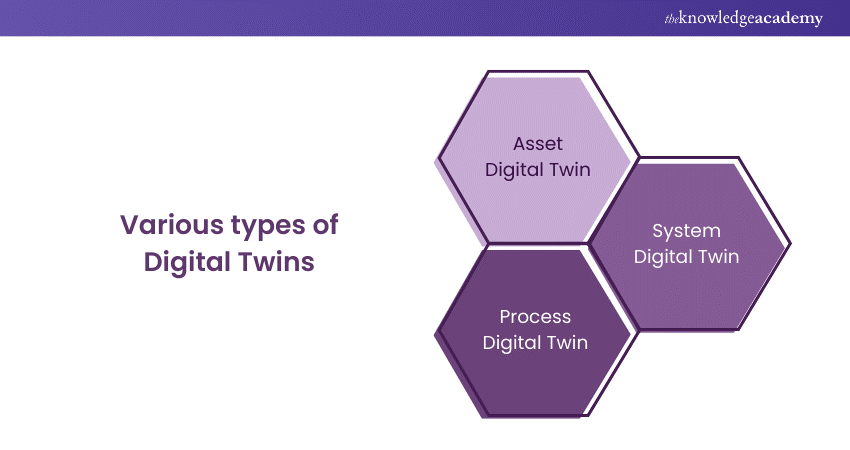
a) Asset Digital Twin: This is the simplest type of Digital Twin, which focuses on a single physical asset, such as a machine, a device, or a component. It is used to monitor the condition, performance, and health of the asset, and to predict and prevent failures, maintenance needs, and defects.
b) System Digital Twin: This is a more complex type of Digital Twin, which encompasses multiple assets that form a system, such as a network, a plant, or a fleet. It is used to analyse the interactions, dependencies, and dynamics of the system, and to optimise its efficiency, reliability, and resilience.
c) Process Digital Twin: This is the most advanced type of Digital Twin, which covers the entire process or value chain, from design to operation to disposal. It is used to simulate the impact of different factors, such as market demand, customer behaviour, environmental conditions, and regulatory changes, on the process, and to identify opportunities for improvement, innovation, and transformation.
Benefits of Digital Twins
Digital Twin technology offers a number of benefits for various stakeholders, such as manufacturers, operators, customers, and regulators. Some of the benefits are:
a) Reduced costs: Digital Twin technology can help reduce the costs of development, testing, production, operation, and maintenance, by enabling faster and cheaper prototyping, optimisation, and troubleshooting. It can also help reduce the costs of waste, rework, and downtime, by enabling proactive and preventive actions.
b) Improved quality: Digital Twin technology can help improve the quality of products, services, and processes, by enabling data-driven decision making, continuous monitoring, and real-time feedback. It can also help improve the quality of customer experience, by enabling personalisation, customisation, and satisfaction.
c) Increased efficiency: Digital Twin technology can help increase the efficiency of resources, energy, and time, by enabling optimal utilisation, allocation, and consumption. It can also help increase the efficiency of operations, by enabling automation, synchronisation, and coordination.
d) Enhanced innovation: Digital Twin technology can help enhance the innovation of products, services, and processes, by enabling experimentation, exploration, and discovery. It can also help enhance the innovation of business models, strategies, and markets, by enabling differentiation, diversification, and disruption.
Challenges with Digital Twins
Despite the benefits, Digital Twin technology also faces some challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the challenges are:
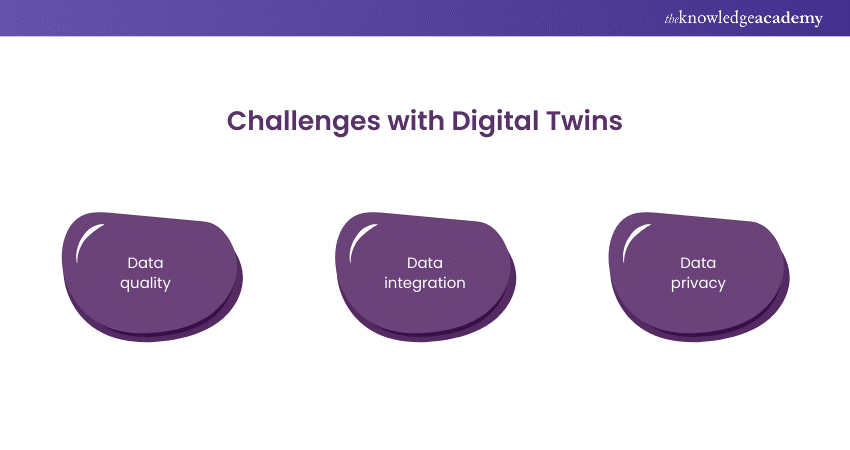
a) Data quality: The accuracy and reliability of Digital Twins depend on the quality of the collected, processed, and analysed data. Poor data quality can lead to erroneous or misleading results, compromising the effectiveness and efficiency of Digital Twins. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the data is complete, consistent, and correct and that the data sources are trustworthy, secure, and compliant.
b) Data integration: Integrating data from different sources, formats, and standards can be challenging for Digital Twins, especially for complex and large-scale systems and processes. Data integration can pose technical, organisational, and legal issues like interoperability, compatibility, and ownership.
c) Data privacy: The collection, storage, and sharing of data for Digital Twins can raise privacy concerns, especially for sensitive and personal data, such as health, financial, and behavioural data. Data privacy can pose ethical, social, and regulatory issues like consent, access, and protection
Explore the future of technology with our Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Course. Join now for advanced skills and hands-on expertise!
The future of Digital Twin technology
Digital Twin technology is expected to grow and evolve in the future, as more data, devices, and domains become connected and integrated. Several emerging trends and advancements are poised to influence the trajectory of Digital Twin technology in the future:
a) Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can enhance the capabilities and functionalities of Digital Twins, by enabling advanced data analysis, prediction, and optimisation. AI can also enable Digital Twins to learn, adapt, and improve over time, and to generate new insights and solutions.
b) Internet of Things: Internet of Things (IoT) can expand the scope and scale of Digital Twins, by enabling the connection and communication of more physical entities, such as sensors, actuators, and smart devices. IoT can also enable Digital Twins to interact and collaborate with other Digital Twins, and to form a digital ecosystem.
c) Augmented Reality: Augmented reality (AR) can improve the visualisation and interaction of Digital Twins, by enabling the overlay and integration of digital information on the physical environment. AR can also enable Digital Twins to provide immersive and engaging experiences, and to support decision making and problem solving.
Digital Twin adoption across markets and industries
Digital Twin technology has applications and implications across various markets and industries, such as manufacturing, energy, transportation, healthcare, and education. Some of the examples of Digital Twin adoption are:
a) Manufacturing: Digital Twin technology can help manufacturers design, produce, and deliver better products, faster and cheaper, by enabling virtual prototyping, testing, and optimisation, and by enabling real-time monitoring, control, and maintenance of the production process and equipment.
b) Energy: Digital Twin technology can help energy providers and consumers manage and optimise their energy consumption and generation, by enabling smart grid, smart metering, and smart home solutions, and by enabling real-time simulation, forecasting, and balancing of the energy demand and supply.
c) Transportation: Digital Twin technology can help transportation operators and users improve their mobility and safety, by enabling smart traffic, smart parking, and smart vehicle solutions, and by enabling real-time tracking, routing, and navigation of the transportation network and vehicles.
d) Healthcare: Digital Twin technology can help healthcare providers and patients enhance their health and wellness, by enabling personalised medicine, telemedicine, and remote monitoring solutions, and by enabling real-time diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases and conditions.
e) Education: Digital Twin technology can help educators and learners enrich their learning and teaching, by enabling interactive and immersive learning environments, and by enabling real-time assessment, feedback, and guidance of the learning and teaching process and outcomes.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed What is Digital Twin, how it works, its types, benefits, challenges, and future prospects. Digital Twin is a technology that creates a virtual model of a physical entity that can be used to optimise its performance. It offers various benefits across various domains and industries, but also faces some challenges. It is expected to evolve in the future, as more data, devices, and domains are integrated.
Explore cutting-edge technologies with our Advanced Technologies Courses for a future-ready skill set. Elevate your expertise today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Digital Twin technology creates virtual duplicates of physical objects or systems, integrating real-time data to accurately mimic their behaviour, status, and performance. These digital replicas enable analysis, prediction, and optimisation, enhancing decision-making and problem-solving. Widely applied in manufacturing, healthcare, automotive, and smart cities, Digital Twins streamline operations, improve efficiency, and facilitate innovation across diverse sectors.




Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


