We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800969236 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Music Production Equipment stands as the bridge between raw inspiration and polished artistry. These tools, ranging from intricate software to tactile hardware, have revolutionised how Artists manifest their Musical visions.
According to Statista, digital Music purchases worldwide surpassed 1.7 billion GBP as of 2022. As technology advances, so does the potential of what can be achieved in a studio setting. The journey of setting up a studio is pivotal in the role played by the right equipment that helps shape sonic masterpieces. Read this blog to learn more about the various types of Music Production Equipment and how they help you produce Music to fulfil your dreams.
Table of Contents
1) What is the importance of Music Production Equipment?
2) Different types of Music Production Equipment
a) A user-friendly Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
b) A MIDI controller
c) Studio headphones
d) Audio interface
e) Studio recording microphone
f) Subscription to sample services
3) The four key stages of building your studio
a) Stage 1 – The bedroom studio
b) Stage 2 – The home studio
c) Stage 3 – The semi pro studio
d) Stage 4 – The pro studio
4) Conclusion
What is the importance of Music Production Equipment?
Music Production Equipment is the backbone for any producer, aspiring or professional. Quality gear does more than just reproduce sound; it captures the nuances, emotions, and intentions underlying every Musical note.
For producers, the sonic clarity that high-grade equipment provides can be the difference between a hit track and a mediocre one. Superior microphones, for instance, can capture the subtle tonal variations in a vocalist's performance, while top-tier audio interfaces ensure that these details aren't lost in translation during recording. Furthermore, good studio monitors honestly represent the mix, ensuring that the Music sounds impeccable across all listening devices, from high-end speakers to everyday earbuds.
Beyond technicalities, the right equipment also acts as an enabler for creativity. Producers can focus on the artistry with reliable gear, knowing that their vision will be accurately translated into the final production. Now that Music has become increasingly digitised; the right equipment ensures that the essence of the sound isn't lost amidst the bytes and bits. Therefore, investing in quality Music Production Equipment is not just about achieving a professional sound but about honouring the Music's and its creators' integrity.
Different types of Music Production Equipment
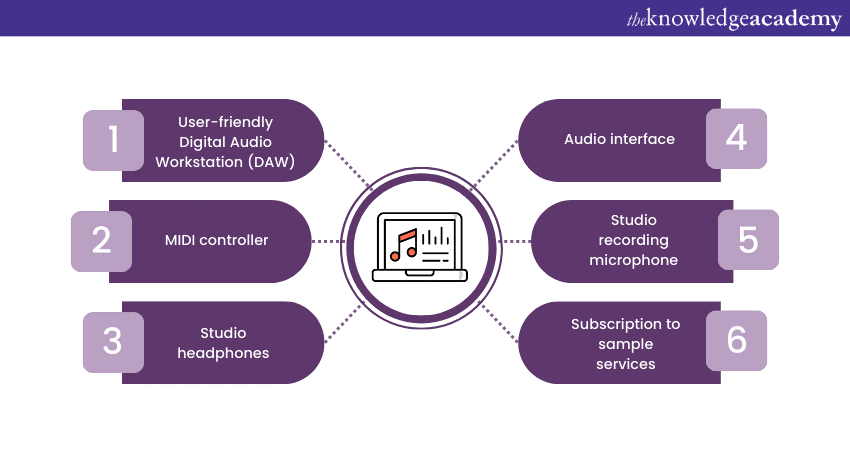
Here is a curated list of some of the key Music Production Equipment that every producer should have in their studio:
A user-friendly Digital Audio Workstation (DAW)
Choosing your first user-friendly Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) is vital in your Music Production journey. As a beginner, you'll want a DAW that balances power with ease of use. Look for features like a visually intuitive interface, drag-and-drop functionality, and a broad range of built-in virtual instruments and effects.
DAWs like Ableton Live, FL Studio, and GarageBand are popular choices for newcomers. Ableton Live offers a session view for live performance and an arrangement view for traditional composition, making it versatile for different workflows. FL Studio's step-based sequencing and pattern blocks cater to electronic Music enthusiasts. GarageBand, a software ideal for Mac users, presents a user-friendly interface with pre-recorded loops and simple MIDI arrangements.
Consider your Music style, whether electronic, hip-hop, or acoustic, when choosing your DAW. Check if it supports the Virtual Studio Technology (VST) plugin format for expanding your sound library. Most importantly, explore trial versions of DAWs to determine your comfort level with their workflows.
A MIDI controller
Selecting the right MIDI controller is a pivotal decision for any Music Producer, as it's a direct extension of your creative expression. The choice largely depends on your production style and preferences.
A MIDI keyboard controller with various keys and responsive action is essential for keyboard enthusiasts. Look for models that offer velocity sensitivity and aftertouch for nuanced playing. If you're into electronic Music Production, a controller with pads and knobs is invaluable for tactile control over virtual instruments and effects.
Drum pad MIDI controllers are perfect for beatmakers and electronic Music Producers. These controllers offer an array of touch-sensitive pads, often backlit, that let you trigger drum sounds and samples with dynamic precision.
When evaluating this Music Equipment, consider compatibility with your chosen Digital Audio Workstation (DAW). Most controllers come bundled with software and presets tailored to specific DAWs. Additionally, ensure your MIDI controller provides customisation options to map controls to various functions within your DAW, enhancing your workflow efficiency.
Learn basic Piano skills to compose Music with a MIDI keyboard, by signing up for the Piano Masterclass now!
Studio headphones
Selecting the perfect studio headphones is a critical decision for every Music Producer, as they serve as your sonic window into the intricacies of Music. When choosing studio headphones, prioritise accuracy and comfort.
Additionally, look for headphones that offer a flat frequency response, meaning they reproduce sound faithfully without exaggerated bass or treble. This accuracy ensures that your mixes translate well across different playback systems.
Closed-back headphones are ideal for recording and tracking sessions, as they isolate the sound and prevent bleed into microphones. Open-back headphones, on the other hand, provide a more natural and spacious sound for critical listening and mixing.
Comfort is paramount, especially during extended sessions. Opt for headphones with adjustable headbands, cushioned ear pads, and breathable materials to prevent fatigue. Consider your weight comfort for the headphones, as heavy ones might become uncomfortable over time.
Additionally, pay attention to the impedance and sensitivity ratings. Higher-impedance headphones may require a headphone amplifier for optimal performance, especially with audio interfaces with weaker headphone outputs.
Audio interface
Selecting the right audio interface ensures high-quality sound and seamless connectivity in your Music Production setup. Here's a concise point-format guide to help you make an informed decision:
a) Input/output configuration: Consider the number of inputs and outputs you need for your projects (microphones, instruments, monitors, etc.). Look for a balance of XLR, TRS, and MIDI connections to accommodate various gear.
b) Sound quality: Research the audio interface's preamp quality and signal-to-noise ratio for clean recordings. Higher bit depth and sample rates contribute to better audio fidelity.
c) Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with your chosen Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) and operating system (Windows, macOS). Check for driver support and software updates.
d) Latency performance: Low-latency monitoring is crucial for real-time recording without audio delay. Look for dedicated DSP (digital signal processing) interfaces for latency-free monitoring.
e) Build and durability: Quality construction and sturdy components contribute to long-term reliability. Consider a portable or rack-mounted design based on your studio setup.
f) Phantom power and gain control: If you will be using microphones that require phantom power, ensure the interface provides it. Individual gain controls for each input help tailor levels for different sources.
g) Included software and plugins: Some interfaces come with bundled software and plugins, enhancing your production capabilities.
h) Budget and expandability: Set a budget and compare options within your price range. Consider future expansion needs, such as additional inputs or outputs.
i) Reviews and recommendations: Research user reviews, professional opinions, and forums to gauge real-world performance.
j) Warranty and support: Check the manufacturer's warranty and customer support quality for peace of mind.
Acquire Guitar skills to compose Music digitally, by signing up for the Guitar Masterclass now!
Studio recording microphone
Choosing the right studio recording microphone is essential for capturing pristine vocals and instruments. Here's a concise point-format guide to help you navigate this crucial decision:
a) Microphone type: Choose between dynamic, condenser, and ribbon microphones based on your recording needs. Condensers excel in capturing detail and sensitivity, while dynamics handle high sound pressure levels.
b) Polar pattern: Different polar patterns (cardioid, omnidirectional, figure-8) determine the microphone's sensitivity to sound directionality. Select a pattern that suits your recording environment and desired sound isolation.
c) Frequency response: Consider the microphone's frequency response range. A flat response captures sound accurately, while a coloured response may add character.
d) Application: Match the microphone to its intended use (vocals, instruments, podcasting, etc.). Some microphones are versatile for various sources, while others are specialised.
e) Budget: Set a budget range and research microphones within that range. Understand that investing in a quality microphone is a long-term investment in sound quality.
f) Build and durability: Sturdy build quality ensures longevity. Look for shock mounts or isolation features to minimise handling noise.
g) Sensitivity and SPL handling: Sensitivity indicates how efficiently a microphone converts sound into an electrical signal. High Sound Pressure Level (SPL) handling is crucial for loud sources without distortion.
h) Reviews and recommendations: Research professional reviews, user testimonials, and forums to gather insights.
i) Accessories: Consider additional accessories like pop filters, windscreens, and shock mounts for optimal results.
j) Trial and experience: Whenever possible, try out microphones before making a decision. Remember that personal preference plays a role; choose the microphone that suits your sonic vision.
Subscription to sample services
Subscribing to sample services offers producers many high-quality sounds and loops to elevate their Music Productions. Here's a concise point-format guide to help you navigate the world of sample subscriptions:
a) Variety of Sounds: Sample services provide access to a diverse range of sounds, from drums and percussion to synths, vocals, and FX. Choose a service that aligns with your Music genre and style.
b) Frequency of updates: Subscriptions often offer regular updates, expanding your sound library with fresh content. Look for services that provide consistent additions to keep your Music Production current.
c) Royalty-free licensing: Ensure that samples are royalty-free for commercial use to avoid legal issues. Most subscription services provide clear licensing terms.
d) Customisation and editing: High-quality samples can be edited, sliced, and manipulated to suit your creative needs. Look for services that offer customisable samples to match your production ideas.
e) Search and filtering tools: User-friendly interfaces with search and tagging systems simplify finding the right samples quickly. Services like Splice offer advanced search filters for efficient browsing.
f) Collaboration features: Some services allow for collaboration by sharing projects and samples with other producers. Consider this if you work with others or want to showcase your work-in-progress.
g) Mobile accessibility: Check if the subscription service offers mobile apps for on-the-go inspiration and browsing.
h) Trial periods: Many services offer free trials or limited-access plans, allowing you to explore their offerings before committing.
i) Community and tutorials: Access to a supportive community and tutorials can enhance your learning and creativity. Some services offer educational resources and user forums.
Partake in more activities for your relaxation, by signing up for the Hobbies & Interests course now!
The four key stages of building your studio

Building a studio as a Music Producer involves several stages like: selecting a suitable space, soundproofing and acoustically treating the room, and choosing the right equipment, such as a DAW, audio interface, monitors, and microphones.
They can further efficiently organise their workspace and continuously update their gear and software to stay current with industry standards. Here are the four key stages described in detail:
Stage 1 – The bedroom studio
Building the initial stage of your studio, often termed the "bedroom studio," is an exciting endeavour for budding Music Producers. Here's a concise point-format guide to help you set up the fundamentals of your first Music-making space:
a) Selecting the right space: Identify a quiet and comfortable room, often a bedroom or spare room. Ensure adequate space for your desk, equipment, and movement.
b) Room acoustics: Begin with basic soundproofing to minimise external noise. Invest in essential acoustic treatments like bass traps, diffusers, and foam panels to optimise sound quality. Focus on corners and wall-to-ceiling junctions for the best results.
c) Primary equipment setup: Choose a beginner-friendly Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) to initiate your Music Production journey. Additionally, an audio interface is essential for connecting instruments and microphones to your computer. Lastly, obtain a pair of decent-quality studio speakers for accurate sound reproduction.
d) Headphones: Invest in a good set of closed-back headphones for detailed listening and tracking.
e) Microphone and accessories: Purchase an affordable but reliable condenser microphone. Don't forget essential accessories like a microphone stand, pop filter, and XLR cable.
f) MIDI controller: Opt for a versatile MIDI keyboard with both keys and pads to initiate your electronic Music experiments.
g) Ergonomic desk and chair: Prioritise comfort with an ergonomic desk setup and a comfortable chair to prevent fatigue during long sessions.
h) Cable management: Organise cables neatly using ties or clips to maintain a clutter-free environment.
i) External storage: Invest in external hard drives or cloud storage solutions to back up projects and samples.
j)Ambience and inspiration: Personalise your space with inspiring artwork, LED lights, or plants. Maintain a tidy environment to foster creativity and productivity.
Learn to mix multi-track recordings in your studio, by signing up for the Art of Mixing Masterclass Training now!
Stage 2 – The home studio
Transitioning from a bedroom setup to a full-fledged home studio represents a commitment to taking your Music Production to a more professional level. Here's a point-format guide to help you navigate this advanced phase:
a) Dedicated room selection: Move beyond the bedroom to a dedicated room, ensuring better space and isolation. Moreover, basement or attic spaces can be optimal choices.
b) Advanced acoustic treatment: Dive deeper into room acoustics with broadband absorption, bass traps, and advanced diffusers. Consider hiring a professional for an acoustic assessment and advice.
c) Equipment upgrades: Upgrade to higher-end studio monitors and consider adding a subwoofer for accurate bass reproduction. With regards to microphones, expand your collection to include dynamic, ribbon, and specialty microphones for various applications.
d) External outboard gear: Introduce outboard gear like preamps, EQs, and compressors to refine your sound further.
e) Isolation booth: Consider building or investing in an isolation booth for pristine vocal and instrument recordings.
f) Expanded connectivity: Upgrade to a larger audio interface or add a patchbay to handle more equipment connections.
g) Advanced MIDI setup: Integrate drum pads, control surfaces, and advanced MIDI controllers for extended functionality.
h) Monitoring solutions: Implement studio monitor isolation, calibration tools, and possibly a second set of reference monitors.
i) Furniture and ergonomics: Invest in studio racks for outboard gear, specialised studio desks, and comfortable seating solutions for longer sessions.
j) Ambient enhancements: Introduce mood lighting, calming colour palettes, and even acoustic-friendly decor to inspire creativity. Prioritise a vibe that feels inviting and conducive to long hours of work.
k) Safety and security: Ensure electrical safety with reliable power strips and surge protectors. Consider security measures, like surveillance or alarm systems, given the value of your equipment.
Stage 3 – The semi pro studio
The third stage represents an environment geared towards both high-level personal projects and client work. This setup aims for professional standards without the massive overheads of commercial studios. Here's a guide to achieving this stage:
a) Optimised acoustic design: Ensure comprehensive room treatment with premium acoustic panels, bass traps, and ceiling clouds. Factor in room modes and resonant frequencies for optimal sound.
b) Professional monitoring system: Integrate high-end monitor speakers, possibly with a tri-amped or quad-amped setup. Introduce a monitor management system for multiple source inputs, speaker switching, and room correction.
c) Variety of microphones: Acquire a diverse range of top-tier microphones for different applications, including tube condensers for warm vocal recordings.
d) High-quality outboard gear: Implement professional-grade preamps, EQs, compressors, and analogue summing mixers for a richer sonic palette.
e) Advanced digital converters: Upgrade to top-tier AD/DA converters to ensure the highest fidelity in your recordings and mixes.
f) Isolated recording spaces: Expand beyond a single booth to multiple isolated spaces for bands or ensemble recordings.
g) Advanced MIDI and synthesis: Incorporate modular synthesisers, advanced MIDI controllers, and a variety of sound modules.
h) Instrument collection: Keep a selection of instruments (e.g., drums, guitars, keyboards) and amplifiers for diverse recording needs.
i) Networking and collaboration: Incorporate audio over IP or other networking solutions to collaborate with other studios and producers seamlessly.
j) Client comfort: Factor in a lounge or waiting area for clients. Ensure amenities like Wi-Fi, refreshments, and entertainment are available for longer sessions.
k) Professional software suite: Invest in a full suite of industry-standard software, plugins, and sound libraries.
l) Backup and redundancy: Implement rigorous backup solutions, both on-site and off-site, and consider uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for critical equipment.
Stage 4 – The pro studio
The fourth stage epitomises the pinnacle of Music Production environments, equipped for top-tier projects and high-end client work. Here's a detailed guide to understand this elite level:
a) State-of-the-art acoustics: Engage experts for custom studio design, ensuring ideal room dimensions and sound isolation. Utilise advanced room treatments like quadratic diffusers and Helmholtz resonators.
b) Main control room: House a large-format mixing console, top-tier monitor systems, and a vast array of outboard gear.
c) Multiple recording rooms: Design diverse rooms tailored for drums, ensemble recordings, and intimate vocal booths.
d) Premium monitoring: Invest in flagship studio monitors and subwoofers, complete with advanced room calibration systems.
e) Extensive microphone locker: Store a vast collection of vintage and modern microphones for any conceivable recording scenario.
f) Top-of-the-line outboard gear: Acquire iconic preamps, compressors, EQs, and effects units for unparalleled sonic quality.
g) Digital and analogue integration: Seamlessly integrate cutting-edge digital technology with revered analogue equipment for diverse sound scaping.
h) Dedicated spaces: Offer lounges, green rooms, and perhaps even residential amenities for longer-term clients or projects.
i) Networking and infrastructure: Incorporate high-speed networking for real-time collaboration globally, and state-of-the-art patching systems.
j) Security and confidentiality: Prioritise advanced security systems and protocols, ensuring client privacy and equipment safety.
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog on Music Production Equipment and understood their various types and the role they play for a Music Producer. As one progresses, these equipment not only amplifies technical capabilities but also serves as an extension of a producer's artistic expression, elevating Music to unparalleled heights.
Gain professional growth and expand your sound engineering skills, by signing up for the Music Production Masterclass Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Music Production Course
Music Production Course
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


