We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 800969236 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Whether you’re an IT pro safeguarding your company’s digital fortress or a curious business owner, understanding the Types of Attacks in Cyber Security is crucial. These attacks come in all shapes and sizes, from the familiar to the obscure.
Imagine them as a rogue’s gallery of digital mischief-makers, each with its own modus operandi and motivations. In this blog, we’ll unravel the mysteries behind 15 common Types of Cyber Attacks, revealing their tactics and potential impact. So, grab your virtual magnifying glass, and let’s explore!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Cyber Attack?
2) 15 Different Types of Cyber Attacks
a) Malware
b) Phishing
c) Denial-of-service Attack
d) SQL Injection
e) Man-in-the-middle Attack
f) DNS Spoofing
g) Whale-phishing Attack
h) Crypto Jacking
i) Business Email Compromise
j) Drive-by Attacks
3) How to Protect Against Cyber Attacks?
4) Conclusion
What is a Cyber Attack?
A Cyber Attack is an attempt by cybercriminals, hackers, or other digital adversaries to infiltrate a computer network or system. The aim is typically to modify, steal, destroy, or expose information.
Cyber Attacks can target a wide range of victims, from individuals to businesses and governments. When targeting businesses or organisations, hackers often seek access to sensitive resources such as intellectual property, customer data, or payment information.
15 Different Types of Cyber Attacks
When attempting to hack into a network, a hacker never tries reinventing the wheel. Instead, attackers employ tried-and-tested approaches that they know are highly effective. Here is the list of different types of attacks in Cyber Security.
1) Malware
Malware, or "malicious software," is a virus designed to disrupt, damage, or steal data from computers, networks, or servers. Hackers trick users into installing malware, which then runs secretly in the background, bypassing security measures and giving hackers access to sensitive data and control over the system.
Malware is a common type of Cyber Attack, with several variants to be aware of:
a) Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts files on a victim's computer and demands a ransom, typically in cryptocurrency, for the decryption key. If the ransom isn’t paid, the decryption key is often destroyed, making data recovery impossible. Even paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee data retrieval, as the provided key may be useless due to data corruption during the attack. Ransomware can target both individuals and companies, sometimes attacking multiple computers or central servers critical to business operations.
b) Spyware
Spyware secretly monitors a victim’s online activities, tracks login credentials, and collects sensitive data without consent. Cybercriminals use spyware to steal credit card numbers, banking information, and passwords, which are then exploited by the attacker. Recent victims include Google Play customers in South and Southeast Asia, and even government agencies have used spyware like Pegasus to surveil activists, legislators, diplomats, bloggers, and researchers.
c) Trojan
A Trojan horse is malicious software disguised as legitimate. It often arrives as an innocent-looking email attachment or free download. Once the user clicks or installs the software, the hidden malware is activated, executing tasks programmed by the attacker. This could be an immediate attack or the creation of a backdoor for future use.
d) Rootkit
A rootkit consists of tools that open a backdoor on a victim’s system, allowing the attacker to install additional malware, like ransomware and keyloggers, or gain control over other network devices. Rootkits often disable security software to avoid detection. Once in control, they can send spam, join botnets, or collect and send sensitive data back to the attacker.
Build a foundation for a secure digital future – Sign up now for our course on Introduction to System and Network Security Course.
2) Phishing
Phishing is a Cyber Attack where the attacker pretends to be from a trusted entity including a bank, tax department or a friend/relative, via an email or other method.
The aim is to ultimately lure the victim into clicking links that lead to the malware or disclosing personal information, passwords, financial information, or trade secrets. Phishing attacks can be launched quickly and can frequently yield high returns. Such attacks can also be made through a phone call (voice phishing or voice over IP phishing) or Short Message Service (SMS phishing).
3) Denial-of-service Attack
A Denial-of-service (DoS) attack is where a device and its operating system are flooded with traffic that it cannot handle thus forcing it to stop functioning. Unlike many other attacks, this type of attack is not performed specifically to acquire information.
It aims to disrupt the target's operations, costing them time and money to restore their systems. Cybercriminals often deploy DoS attacks against trade organisations or government entities to create significant disruption.
4) SQL Injection
SQL Injection attacks are some of the worst types of assault on a system since they allow hackers to input statements into applications that are data driven and consequently gain entry to databases. By means of SQL Injection attacks, attackers can edit, steal or even delete some or all data.
The main distinction between SQL Injection and XSS attacks lies in their targets. SQL Injection is a server-side vulnerability aimed at compromising the application's database, while XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) is a client-side vulnerability targeting other users of the application.
5) Man-in-the-middle Attack
A Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack occurs when attackers secretly intercept and relay communications between two parties. Here the two parties still believe that they are directly communicating with each other.
The attackers infiltrate the online communication, allowing them to read, copy, or modify messages in real-time before passing them to the unsuspecting recipient. A successful MitM attack can enable hackers to steal or alter sensitive information, such as login credentials, transaction data, and credit card numbers.
6) DNS Spoofing
In a Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing attack, a hacker diverts traffic to a fake or "spoofed" website. Once victims land on the fraudulent site, they may unknowingly submit sensitive information, which the hacker can then use or sell. Alternatively, the hacker might create a low-quality site with defamatory or provocative content to tarnish a competitor’s reputation.
DNS spoofing exploits the victim’s trust, making them believe they are visiting a legitimate site. This deception allows the attacker to commit crimes under the guise of a reputable firm, at least from the perspective of the unsuspecting visitor.
7) Whale-phishing Attack
A whale-phishing attack specifically targets high-ranking individuals within an organisation, such as C-suite executives or other authority figures, often referred to as the "big fish" or "whales." These individuals are likely to possess valuable information, including proprietary knowledge about the company and its operations.
If a targeted "whale" falls victim to ransomware, they may be more inclined to pay the ransom to prevent the attack from becoming public and damaging the organisation's reputation. Whale-phishing attacks can be prevented by adopting the same precautions as standard phishing attacks: carefully reviewing emails, attachments, and URLs and being vigilant for unusual destinations or parameters.
8) Crypto Jacking
Crypto jacking involves unauthorised use of someone else’s computer to mine cryptocurrency. Attackers gain access by infecting websites or tricking victims into clicking malicious links.
They also embed JavaScript code in online ads for this purpose. The mining code runs silently in the background, with the only noticeable sign being a slowdown in the computer's performance.
9) Business Email Compromise (BEC)
A Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack targets specific individuals, typically employees authorised to approve financial transactions, tricking them into transferring funds to an account controlled by the attacker.
Effective BEC attacks require careful strategy and research. Attackers gather information about the target organisation's executives, employees, customers, and business partners to convincingly deceive the employee into transferring the funds. BEC attacks are among the costliest Types of Cyber Attacks.
10) Drive-by attacks
A Drive-by attack occurs when a hacker inserts malicious code into an unsecured website. When a user visits the site, the script automatically executes, infecting their system. The term "drive-by" implies that simply visiting the site is enough to get infected; there is no need to click anything or enter any information.
To prevent drive-by attacks, users should ensure their computers are running the latest software, including applications like Adobe Acrobat and Flash that are often used while browsing. Additionally, employing web-filtering software can help identify risky sites before users access them.
11) Birthday attack
A birthday attack exploits the hash algorithms used to verify the authenticity of communications. Hash algorithms create a digital signature that the recipient checks to confirm the message's legitimacy. If a hacker can generate a hash identical to the one the sender used, they can replace the original message with their own. The receiving device will accept the altered message because it has the correct hash.
The term "birthday attack" comes from the birthday paradox, which suggests a higher than 50% probability that two people in a room of 23 share the same birthday. Similarly, while hashes are intended to be unique, they do not always make such attacks possible.
12) Session Hijacking
Session hijacking is a type of man-in-the-middle attack where the attacker takes control of a client-server session. The attacker replaces the client's IP address with their own, allowing them to connect to the server without needing authentication.
Once a session is hijacked, hackers can perform any actions the client's account is authorised to do. For instance, if you're accessing your company's internal database while on a business trip, a hacker who hijacks your session would gain access to all your company's files.
13 Watering Hole Attack
A watering hole attack targets specific groups within an organisation or region by compromising websites frequently visited by the targeted group. Attackers either monitor the group's online behaviour or make educated guesses to identify these websites.
Once identified, they infect these sites with malware designed to steal personal information or allow remote access to the victim's system.
14) Password Attack
Passwords are the primary tool for verifying access, making them a prime target for hackers. Attackers can obtain passwords through various methods:
a) Physical Theft: Hackers may find passwords on sticky notes or pieces of paper around a target's desk, or they might pay someone on the inside to retrieve them.
b) Network Interception: Attackers can intercept unencrypted network transmissions to capture passwords.
c) Social Engineering: Hackers trick targets into entering their passwords by posing as a legitimate problem that needs solving.
d) Guessing: Default or simple passwords, like "1234567," are easy for attackers to guess.
e) Brute-Force Attacks: Using personal information (e.g., name, birthdate) or social media details, hackers attempt various combinations to guess the password.
f) Dictionary Attacks: Hackers use common words and phrases from a dictionary to guess the password.
15) Insider Threat
IT teams that focus solely on external threats miss half the picture. Insider threats may come from current or former employees who have direct access to the company network, sensitive data, and knowledge of business processes. These internal actors can pose significant dangers due to their access and insider knowledge.
Insider threats are often malicious, driven by motives like financial gain from selling confidential information on the dark web or emotional coercion through social engineering. However, some insider threats stem from negligence rather than malicious intent. To address this, organisations should implement comprehensive Cyber Security training programs to educate stakeholders about potential attacks, including those from insiders.
Learn the fundamentals of Cyber Security Awareness. Sign up for our Cyber Security Awareness course now!
How to Protect Against Cyber Attacks?
Preventing Cyber Attacks starts with awareness. It helps make sure you and your employees recognise potential threats and are aware of how to mitigate them. Here are a few tips on how to prevent Cyber Attacks:
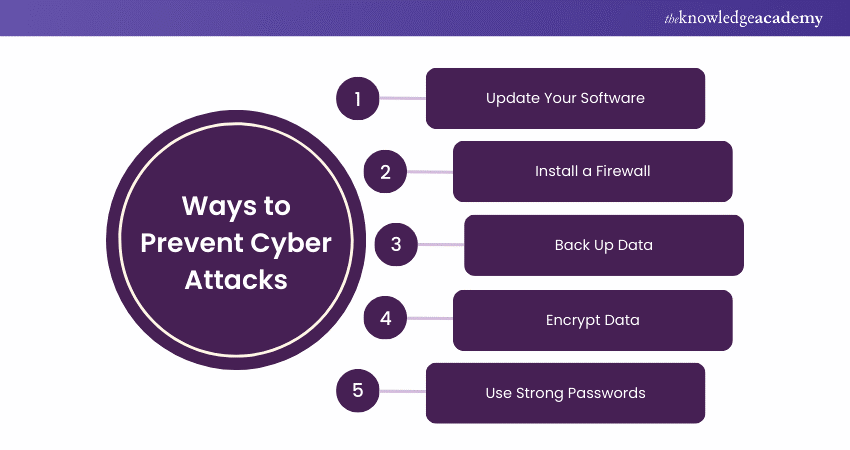
Update Your Software
Keeping software up to date ensures resilience against attacks. Updates fix flaws and vulnerabilities. Investing in a patch management system can help maintain current software versions.
Install a Firewall
Firewalls control network traffic, preventing attacks like backdoors and denial of service. They block suspicious activity deemed harmful to your computer.
Back Up Data
Regularly back up data to a secure location, such as cloud storage or a physical device. This ensures you can recover lost data in case of an attack.
Encrypt Data
Encrypting data ensures it's only accessible with a decryption key. This makes it difficult for attackers to access information, as they would need to guess the correct key through brute force.
Use Strong Passwords
Use unique, strong passwords for different accounts and systems. Combine special characters, upper and lowercase letters, and numbers. Regularly update passwords to enhance security and avoid reuse.
Conclusion
Armed with knowledge, you’re now a digital Sherlock Holmes, ready to foil the nefarious plots of cyber villains. Remember, Cyber Attacks are like puzzle pieces—each one fits a different scenario. We’ve explored over 15 common Types of Cyber Attacks, from phishing to ransomware, and even the elusive zero-day exploits. But fear not! You’re not alone in this virtual maze. Implement robust defences, stay vigilant, and keep your firewalls fortified. And just like that, you’ll be the hero your network deserves!
Secure your digital assets with a comprehensive Cyber Security Risk Management Course. Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

During a Cyber Attack, attackers infiltrate a computer system or network to steal, alter, or destroy data, disrupt operations, or gain unauthorised access. This can involve malware, phishing, or exploiting system vulnerabilities.

Cyber Attacks are caused by motives such as financial gain, espionage, political agendas, or personal grievances. They exploit system vulnerabilities, user negligence, or social engineering tactics to gain unauthorised access to data and systems.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Trainings, including the Certified Cyber Security Professional Training, Cyber Security Awareness Course and Cyber Security Risk Management Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into IT Security.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cyber Security, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


