We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Music, the universal language that transcends boundaries, carries the power to evoke emotions, tell stories, and create connections. At the heart of understanding its complexities lies the practice of Music Analysis. It helps unveil the secrets of composition, allowing us to unravel the fascinating DNA of Music.
According to Glassdoor, the average pay of a Music Composer in the UK is about £55,607 annually. If you are interested in becoming a Music Composer, then possessing the right analytical skills is crucial, and that is what you will learn here. In this blog, you will learn what Music Analysis is, its key elements, methods, benefits as well as how to perform it.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Music Analysis
2) The Elements of Music Analysis
3) Methods of Music Analysis
4) Benefits of Music Analysis
5) How to perform Music Analysis?
6) Conclusion
Understanding Music Analysis
Music Analysis is a discipline that involves examining and interpreting various aspects of musical compositions to gain deeper insights into their structure, meaning, and emotional impact. By dissecting the elements of a piece of music, analysts can uncover hidden patterns, relationships, and artistic choices made by composers. This process enhances our appreciation and comprehension of Music Theory, allowing us to connect with it on a more profound level.
Interpretation in Music Analysis
Interpretation in Music Analysis refers to the process of understanding and explaining the meanings, emotions, and intentions behind a musical composition. Analysts interpret how the composer's choices in melody, harmony, rhythm, and other elements contribute to the overall message or expression of the Music. This can involve exploring the cultural, historical, and personal significance in which the piece was created. Interpretation bridges the gap between the technical analysis of musical elements and the emotional impact on listeners.
Written aspects of Music Analysis
The "written" aspect of Music Analysis likely refers to the documentation of analytical findings. Analysts often write reports, essays, or scholarly articles to communicate their insights, interpretations, and observations. These written documents provide a structured way to share the results of their analysis with others and contribute to the field of the music scholarship.
In essence, Music Analysis combines technical examination and interpretation to reveal the intricate layers of meaning and emotion within a musical composition, enriching our understanding and connection with the art form.
The Elements of Music Analysis
Music Analysis involves dissecting and examining various elements within a musical composition to gain deeper insights into its structure, meaning, and emotional impact. By delving into these elements, analysts can uncover the intricate craftsmanship and intentions of the composer. Understanding these aspects can also boost music production skills. Here are the key elements for analysing music:
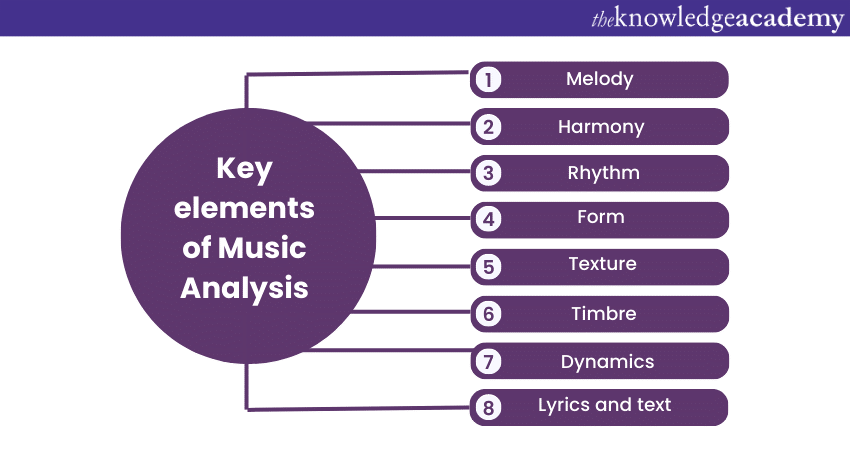
1) Melody: The melody is the central theme or tune of a composition. Music Analysis focuses on the pitch, intervals, and contour of the melodic line, revealing how it conveys emotions and narrative.
2) Harmony: Harmony refers to the simultaneous combination of musical notes to create chords. Analysis of harmony involves identifying chord progressions, their functions, and the emotional qualities they bring to the music.
3) Rhythm: Rhythm encompasses the time-based patterns of music, including beats, tempo, and rhythmic structures. Analysis of rhythm uncovers the rhythmic complexity and dynamic energy of the composition.
4) Form: Form relates to the structure and organisation of a composition. Analysts identify sections, transitions, repetitions, and variations within the piece, uncovering how musical ideas develop and interact.
5) Texture: Texture pertains to the layers of sound in a composition, including how instruments or voices interact. Music Analysis examines the thickness or thinness of the texture and how it changes throughout the piece.
6) Timbre: Timbre is the unique quality of different instruments or voices. Analysis of timbre explores how the choice of instruments contributes to the overall character and mood of the music.
7) Dynamics: Dynamics refer to variations in volume and intensity. Analysis of dynamics delves into how changes in loudness and softness shape the emotional arc of the music.
8) Lyrics and text: In vocal music, lyrics or text add a layer of meaning. Analysis of text considers how words interact with the Music to convey messages and emotions.
Methods of Music Analysis
Analysing music involves a variety of methods and approaches that allow analysts to explore the intricate elements of a musical composition. These methods provide insights into the structure, meaning, and artistic choices within the music. Here are some of the Types of Music Analysis methods:
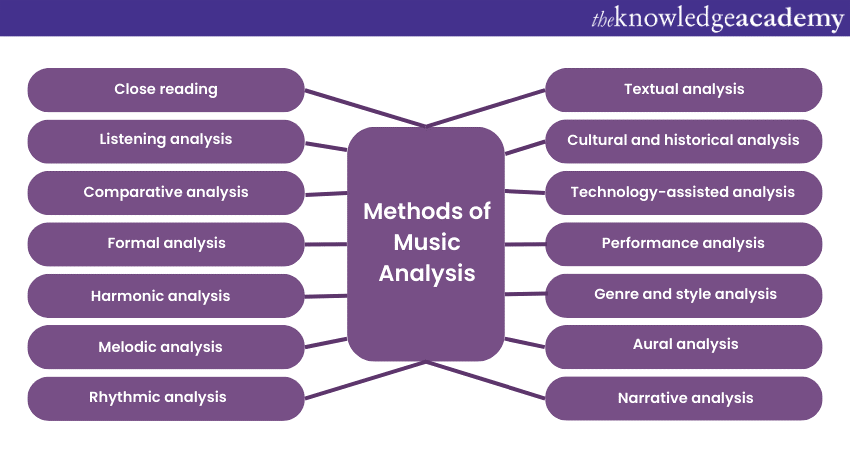
1) Close reading: This method involves a detailed examination of the musical score. Analysts closely study the notation, identifying themes, motifs, harmonic progressions, and rhythmic patterns. Close reading helps uncover compositional techniques and structural elements.
2) Listening analysis: Active listening is a fundamental method. Analysts attentively listen to a composition multiple times. It helps in focusing on specific elements such as melody, harmony, rhythm, and dynamics. This method helps analysts connect with the emotional and expressive qualities of the music.
3) Comparative analysis: Comparative analysis involves comparing different compositions, versions of the same piece, or works by different composers. This method highlights similarities, differences, influences, and evolving styles across various musical pieces.
4) Formal analysis: Formal analysis centres on the structure and organisation of a composition. Analysts identify sections, transitions, repetitions, and variations within the piece. This method highlights how musical ideas are developed and transformed.
5) Harmonic analysis: Harmonic analysis examines the chord progressions and relationships within a composition. Analysts identify the underlying harmonic framework and study how chords contribute to the emotional impact of music.
6) Melodic analysis: Melodic analysis focuses on the main themes or melodies within a composition. Analysts analyse pitch, interval patterns, and contour to understand how melodies convey emotion and narrative.
7) Rhythmic analysis: Rhythmic analysis explores the rhythmic patterns, meters, and tempo changes in composition. This method uncovers the rhythmic energy and pulse of the music.
8) Textual analysis: In vocal music, textual analysis considers the interaction between lyrics and Music. Analysts explore how the words' meanings and emotions align with the music's expressive qualities.
9) Cultural and historical analysis: This method places a composition within its cultural and historical context. Analysts examine how societal influences, artistic trends, and historical events shape the music's style and message.
10) Technology-assisted analysis: Digital tools and software aid in analysing complex Musical structures. Spectrograms, waveform visualisations, and software algorithms can reveal patterns, frequencies, and textures that are challenging to discern through traditional methods.
11) Performance analysis: Performance analysis focuses on interpreting how a composition is performed. Analysts study the tempo choices, dynamics, articulations, and phrasing made by performers to understand their interpretive decisions.
12) Genre and style analysis: This method involves studying the characteristics that define a particular musical genre or style. Analysts explore how specific elements contribute to the genre's identity and conventions.
13) Aural analysis: Aural analysis trains analysts' ears to recognise musical elements such as intervals, chords, and rhythmic patterns through active listening. It enhances their ability to identify these elements in real-time performances.
14) Narrative analysis: Narrative analysis examines how a composition conveys a story, imagery, or emotions. This method focuses on how the music aligns with intended narratives or themes.
By utilising these methods, Music analysts gain comprehensive insights into the technical, emotional, and contextual dimensions of a composition, enriching their understanding of the Music and its significance. These skills are also valuable for a career in music production.
Elevate your music prowess with our Music Production Masterclass. Sign up now!
Benefits of Music Analysis
Music Analysis is a valuable practice that offers numerous benefits to musicians, scholars, educators, and music enthusiasts. By dissecting and interpreting the intricate elements of a musical composition, individuals can gain deeper insights into the structure, meaning, and emotional impact of the music. Here are some of its key benefits:
1) Enhanced appreciation: Music Analysis allows listeners to engage more deeply with music. By understanding the compositional techniques and structural elements, individuals can appreciate the craftsmanship and artistic choices that contribute to the music's beauty.
2) Deeper understanding: Music Analysis provides a window into the intentions of composers. It helps individuals understand how musical elements like Melody, Harmony, and Rhythm work together to convey emotions, themes, and messages.
3) Critical thinking: Analysing music cultivates critical thinking skills. Analysts must identify patterns, relationships, and contrasts within a composition, promoting an analytical mindset that can be applied to various aspects of life.
4) Aural skills: Active listening is a crucial aspect of Music Analysis. By honing their aural skills, individuals become more adept at recognising intervals, chords, and rhythmic patterns, which can improve their overall musicianship.
5) Artistic expression: For musicians and composers, analysis offers inspiration and tools for creative expression. Studying the techniques of renowned composers can inspire new compositions and innovative approaches to music-making.
6) Educational tool: Music educators use analysis to teach students about music theory, structure, and historical context. It enhances students' understanding of the music they perform and helps them become more informed musicians.
7) Genre appreciation: Music Analysis introduces individuals to different genres and styles. Understanding the unique characteristics of various genres promotes a broader appreciation for diverse musical expressions.
Music Analysis provides a multifaceted approach to experiencing and understanding music. Its benefits extend beyond the technical aspects, enriching our connection with music and broadening our perspectives on its cultural, emotional, and artistic dimensions.
Unravel the artistry of mixing and sculpt your sonic visions with our Art Of Mixing Masterclass Training. Sign up today!
How to perform Music Analysis?
Music Analysis involves a systematic process of dissecting and interpreting various elements within a composition. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to perform it effectively:
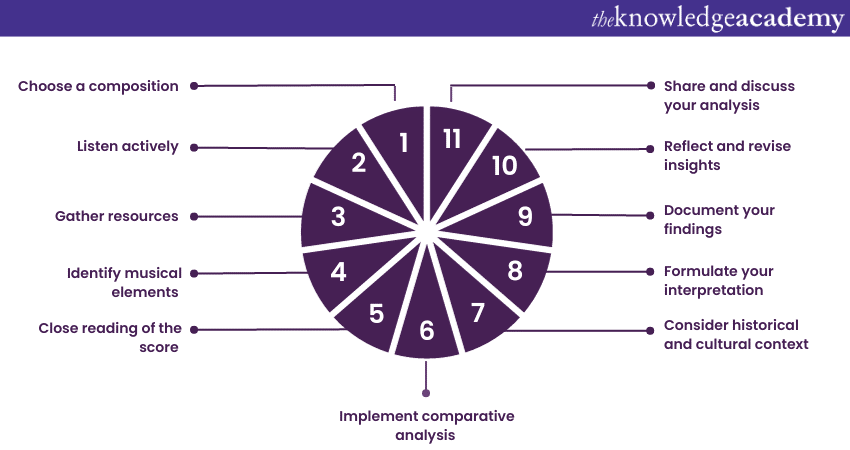
1) Choose a composition: Select a musical piece that you want to analyse. It could be a song, a symphony, a jazz improvisation, or any other type of music that interests you.
2) Listen actively: Listen to the composition multiple times with focused attention. Pay close attention to the melody, harmony, rhythm, dynamics, and other elements that contribute to the overall sound.
3) Gather resources: Obtain the sheet music or score of the composition if available. This will help as a visual reference for your analysis.
4) Identify musical elements: Identify the main theme or themes within the composition. Note the pitch, intervals, and contour of the melody. Analyse the chord progressions and harmonic relationships. Determine the key signature and the chords used throughout the piece. Determine the layers of sound, including which instruments or voices are prominent at different points.
5) A close reading of the score: Examine the sheet music closely. Identify recurring motifs, thematic developments, and variations. Mark significant musical events, such as key changes, modulations, and climactic moments.
6) Comparative analysis: If relevant, compare the analysed composition with other pieces in the same genre, by the same composer, or from a similar time period. Identify commonalities and differences.
7) Consider the historical and cultural context: Research the composer's background, the era in which the piece was composed, and any cultural influences that might have shaped the music. Understand how historical events, societal norms, and artistic trends may have impacted the composition.
8) Interpretation: Formulate your interpretation of the composition's overall meaning, emotion, and message. Consider how the interplay of musical elements contributes to the composition's intended effect on the listener.
9) Document findings: Write a comprehensive analysis that covers each musical element, your observations, and interpretations. Include examples from the score to support your analysis.
10) Reflect and revise: Review your analysis and ensure that it effectively encapsulates the essence of the composition. Reflect on how your insights contribute to your understanding and appreciation of the music.
11) Share and discuss: Share your analysis with peers, teachers, or fellow music enthusiasts for feedback and discussions. Engaging in conversations can offer new perspectives and enhance your analytical skills.
Performing Music Analysis is a rewarding journey that deepens your connection to music and expands your understanding of its intricacies. Remember that practice and experience will refine your analytical abilities over time.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about Music Analysis. It allows us to decode Music's DNA and appreciate its intricate architecture. It also helps unveil the emotions, stories, and human expressions woven into melodies, harmonies, rhythms, and lyrics. It helps us gain a greater understanding of the language that unites us all, Music.
Ignite your curiosity and explore a world of hobbies with our Hobbies & Interests Training. Sign up today!
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Music Production Course
Music Production Course
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


