We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In today's world, organisations have a lot of data. To make the most of it, they use Business Intelligence (BI) and Business Analytics (BA). While these terms often get mixed up, they actually serve different purposes.
Understanding the difference between BI and BA is important for making smart decisions and improving data strategies. The global market for these tools is expected to reach an £14.48 billion by 2026, showing just how crucial they are.
This blog will break down the main differences between Business Intelligence vs Business Analytics and show how combining them can lead to incredible, data-driven success.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Intelligence?
2) What is Business Analytics?
3) Business Intelligence vs Business Analytics: Key Differences
a) Definition and Focus
b) Data Usage and Analysis Techniques
c) Output and Deliverables
d) Business Objectives and Applications
4) Can Business Intelligence and Business Analytics be Integrated?
5) Conclusion
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) focuses on gathering, integrating, analysing, and presenting data to help organisations make informed decisions. Here are the key components of BI:
a) Data Collection and Integration:
a) Collecting data from various sources.
b) Combining it into a central system for a unified view.
b) Data Warehousing:
a) Storing large amounts of data.
b) Structuring the data for easy retrieval and analysis.
c) Data Visualisations and Reporting:
a) Turning complex data into easy-to-understand visual formats.
b) Using charts and dashboards to aid interpretation and decision-making.
What is Business Analytics?
Business Analytics (BA) goes beyond the traditional reporting and analysis offered by Business Intelligence (BI). It dives deeper into data, using advanced techniques to extract valuable insights. Here are the key components of BA:
a) Data Exploration and Preparation:
a) Identifying relevant data sources.
b) Cleaning and transforming the data.
c) Uncovering patterns and relationships.
b) Statistical Analysis and Predictive Modelling:
a) Using advanced statistical methods to extract insights.
b) Predicting trends and forecasting outcomes based on historical data.
c) Data-Driven Decision-Making:
a) Using analytics-derived insights to inform strategic decisions.
b) Guiding operational decisions within the organisation.
Unlock new career opportunities in business analysis with our IIBA Certification of Competency In Business Analysis (CCBA) Course. Sign up now!
Business Intelligence vs Business Analytics: Key differences
Business Intelligence and Business Analytics are two distinct approaches used by organisations to derive insights from data. While both involve the use of data analysis techniques, there are key differences between the two methodologies. Understanding the difference between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics is crucial for organisations to effectively utilise data and make informed decisions.
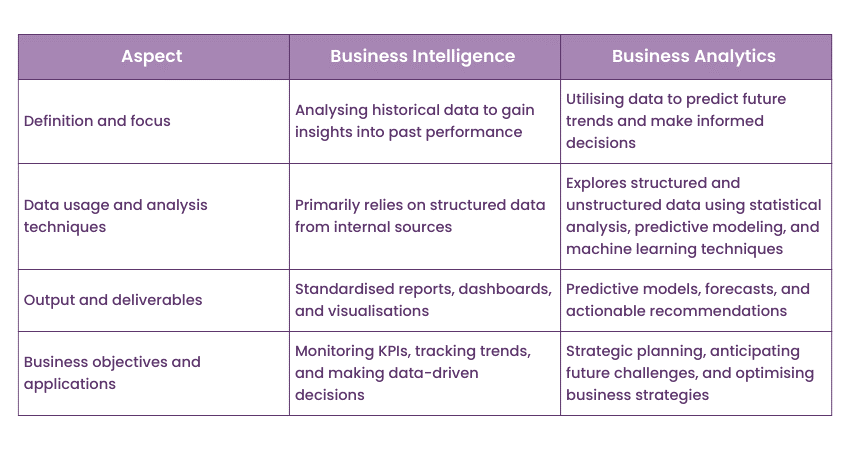
Definition and Focus
Business Intelligence (BI):
a) Focus: Collecting, integrating, interpreting, and presenting historical data.
b) Analytics Type: Descriptive analytics to answer questions about past events.
c) Purpose: Provides a comprehensive view of an organisation’s performance.
d) Benefits:
a) Helps stakeholders monitor key metrics.
b) Evaluates performance indicators effectively.
Business Analytics (BA):
a) Focus: Forward-looking approach.
b) Techniques:
a) Statistical analysis.
b) Predictive modeling.
c) Data-driven decision-making.
c) Purpose: Uncovers insights by delving deeper into data.
d) Benefits:
a) Identifies trends and patterns.
b) Forecasts future outcomes.
c) Guides strategic decision-making with diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics.
Data Usage and Analysis Techniques
Business Intelligence (BI):
a) Data Sources: Primarily uses structured data from internal systems like transactional databases, CRM platforms, and ERP systems.
b) Data Processing:
a) Cleaning and transforming data.
b) Storing data in data warehouses or marts.
c) Tools: BI tools collect, summarise, and create reports and dashboards, providing a clear and combined view of the organisation's data.
Business Analytics (BA):
a) Data Sources: Utilises a wider variety of data sources, including both structured and unstructured data from inside and outside the organisation.
b) Analysis Techniques:
a) Advanced statistical analysis.
b) Machine learning.
c) Data mining.
d) Text analytics.
c) Focus: While BI is about reporting, BA predicts future trends and outcomes using historical data patterns.
Output and Deliverables
Business Intelligence (BI):
a) Deliverables:
a) Dashboards.
b) Standard reports.
c) Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
b) Purpose: Provides a quick look at past data to see how the business has performed and identify areas for improvement. Uses clear visuals like charts and graphs for easy understanding.
Business Analytics (BA):
a) Deliverables:
a) Predictive models.
b) Forecasts.
c) Actionable suggestions.
b) Purpose: Offers advanced and dynamic insights to aid in strategic decision-making. Uses statistical methods like regression analysis and time series forecasting to predict future trends. Provides recommendations to enhance business strategies, spot new opportunities, and make informed decisions to tackle complex challenges.
Business Objectives and Applications
Business Intelligence (BI):
a) Focus: Operational efficiency, performance monitoring, and historical analysis.
b) Applications: Financial reporting, sales analysis, and supply chain management. Helps track key metrics, identify trends, and evaluate operational effectiveness using historical data.
Business Analytics (BA):
a) Focus: Predictive and prescriptive analytics for strategic decision-making and gaining a competitive advantage.
b) Applications: Customer segmentation, targeting, demand forecasting, risk assessment, fraud detection, and optimising marketing campaigns. Enables organisations to make informed decisions, uncover growth opportunities, and proactively manage potential risks through advanced analytics.
Can Business Intelligence and Business Analytics be Integrated?
While there are distinctions between Business Intelligence (BI) and Business Analytics (BA), there is also a growing realisation of their synergy. Organisations are increasingly recognising the value of integrating both approaches to maximise the benefits of data analysis. By combining BI's focus on historical reporting and BA's predictive and prescriptive capabilities, organisations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their data landscape and make informed decisions based on both historical and future insights.
Synergy of BI and BA
a) Comprehensive Data Analysis:
a) Historical Reporting (BI):
i) Provides insights into past performance.
ii) Helps in tracking key metrics and performance indicators.
b) Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics (BA):
i) Identifies trends and patterns.
ii) Forecasts future outcomes.
iii) Offers actionable recommendations.
b) Enhanced Decision-Making:
a) Informed Decisions:
i) Combines historical data with future predictions.
ii) Supports strategic and operational decision-making.
b) Proactive Strategies:
i) Enables organisations to anticipate changes and challenges.
ii) Helps in developing proactive strategies to address potential issues.
c) Optimised Business Processes:
a) Efficiency Improvements:
i) Uses BI to identify areas for operational improvement.
ii) Applies BA to optimise processes and enhance efficiency.
b) Resource Allocation:
i) Utilises data insights to allocate resources effectively.
ii) Ensures optimal use of assets and personnel.
d) Competitive Advantage:
a) Market Insights:
i) Leverages BI to understand market trends and customer behaviour.
ii) Uses BA to predict market shifts and customer needs.
b) Innovation and Growth:
i) Drives innovation by identifying new opportunities.
ii) Supports growth initiatives with data-driven insights.
Take your business analysis skills to the next level with our IIBA Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) Course. Sign up now!
Conclusion
Business Intelligence (BI) and Business Analytics (BA) are both critical when making data-based decisions. BI involves looking at past data and reports to understand how things went. BA, on the other hand, takes it a step further by using stats and predictive analysis to help anticipate what might happen. Understanding these distinctions is essential for companies that want to up their data game and stay ahead in today’s digital world.
Enhance your business analysis expertise with our comprehensive IIBA Business Analysis Training Courses. Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

BI professionals typically focus on data reporting, dashboard creation, and historical trend analysis. BA professionals, however, specialise in predictive modelling, statistical analysis, and forecasting, often aligning closely with strategic planning and decision-making roles.

BI aids in evaluating past performance to improve operational efficiency, while BA provides predictive insights for future strategies. Together, they enable businesses to make informed, data-driven decisions that align with current and future goals.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various IIBA® Business Analysis Training, including IIBA® Entry Certificate in Business Analysis (ECBA™) Course, IIBA® Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®) Course and IIBA® Certification of Competency in Business Analysis (CCBA®) Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Mind Map.
Our Business Analysis Blogs cover a range of topics related to Business Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 IIBA® Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®)
IIBA® Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®)
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 27th Mar 2025
Thu 15th May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 13th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


