We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the modern work environment where digital workflows grow ever more complex, the idea of one physical machine performing the job of many is nothing short of a miracle. This is precisely what Hypervisors help accomplish. Seen as a Virtual Machine whisperer, the Hypervisor is the fuel behind Virtualisation technology, allowing multiple Virtual Machines to coexist on a single server. If you are intrigued by this piece of innovation, then join in as this blog takes you on a journey towards understanding What is Hypervisor. So read on and learn how it can reshape the digital aspects of your business!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Hypervisor?
2) How do Hypervisors Function?
3) What are the Types of Hypervisors?
4) What is a Cloud Hypervisor?
5) Key Use Cases of Hypervisors
6) Benefits of a Hypervisor
7) Difference Between Containers and Hypervisors
8) Conclusion
What is a Hypervisor?
A Hypervisor (also called a Virtual Machine monitor or VMM) is a type of firmware, software, or hardware that enables the creation and management of Virtual Machines (VMs). It enables multiple Operating Systems (OS) to run concurrently on a single physical machine. This is achieved by abstracting and allocating the underlying hardware resources such as memory, CPU, and storage to each VM.
Why is a Hypervisor Important?
Hypervisors are the underlying technology behind Virtualisation or the decoupling of hardware from software. IT Administrators can develop multiple Virtual Machines on a single host machine. You can install software applications on a VM, much like you do on a physical computer.
The fundamentals of Virtual Machines and other such technologies have allowed Cloud computing services to transform enterprise applications. They enable you to scale computing services efficiently with limited hardware infrastructure. For instance, multiple business departments can run different workloads separately using multiple Virtual Machines on a single server.
How do Hypervisors Function?
Hypervisors support creating and managing Virtual Machines (VMs) by abstracting a computer’s software from its hardware. Here are the important points to consider:
1) Hypervisors make Virtualisation possible through the translation of requests between the physical and virtual resources.
2) Bare-metal Hypervisors are often embedded into the firmware at the same level as the motherboard's basic input/output system (BIOS). This enables the OS on a computer to access and use Virtualisation software.

What are the Types of Hypervisors?
There are two main Hypervisor types: Type 1 (or bare metal) and Type 2 (or hosted Hypervisor). While bare-metal Hypervisors directly run on the computing hardware, the latter runs on top of the host machine's Operating System. Let's explore both in detail:
Type 1 Hypervisor
Type 1 Hypervisors are also called bare metal Hypervisors for the reason that they are installed directly on the physical server. Here are some key points of this Hypervisor to remember:
a) Direct access to the physical server's resources makes it highly efficient.
b) This design makes Type 1 Hypervisors more secure by limiting the attack surface and the potential for compromise.
c) This type of Hypervisor is the most common choice within enterprise IT contexts due to its strong scalability, stability, security, and performance.
d) Examples of widely used Hypervisors include Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware ESXi, and Citrix Hypervisor.

Type 2 Hypervisor
Type 2 Hypervisors differ from Type 1 because they function as applications on a physical server’s preexisting OS. Since they run on the host OS (which sits between the physical server and Hypervisor), they are also called “hosted” Hypervisors. The key points to note are the following:
a) These Hypervisors are not ideal for server-based environments because they possess higher latency and risk exposure than Type 1.
b) They are relatively easy to install.
c) They can work well in specific use cases, including individual PC users who need to run multiple OS, where security and performance are not principal concerns.
Stay ahead in your professional journey by gaining deeper insight into the latest Advanced Technology and their application in our Advanced Technologies Training - Sign up now!
What is a Cloud Hypervisor?
Now that organisations commonly use Cloud Computing, it’s important to recognise how critical Hypervisors are to the Cloud. A Cloud Hypervisor monitors and controls the VMs running on physical servers across data centres owned by Cloud providers.
1) These Hypervisors smoothen the process of managing distributed workloads across cloud architecture, which is typically multi-tenant.
2) In the Cloud, scalability is almost infinite, and organisations can pay only for the resources they consume.
3) Hypervisors allow these organisations to utilise the Cloud's agility and speed.
4) While users can access applications and data in virtual environments, IT continues to retain control of the organisation’s apps and data.
5) Hypervisors make moving workloads and applications to the Cloud very easy, which increases an organisation’s efficiency.
Key Use Cases of Hypervisors
Virtualisation software powered by Hypervisors has several use cases, including failure recovery, desktop Virtualisation, resource optimisation and legacy system support.
Failure Recovery and System Resilience
The Hypervisor captures snapshots of the VM's previous state in a Virtual Machine image. It's a file containing the installation configurations, instructions, and other details. System Administrators can use the image file for restoring the VM in case of failure. Additionally, it can generate backup copies or move the Virtual Machine to a different host.
Desktop Virtualisation Solutions
Employees use desktop Virtualisation software to replicate their workstation computing environment on a server. This enables remote access to their work applications and files.
Supporting Legacy Systems
Some organisations invest significantly in software that has outlasted the underlying server. Hypervisors deliver an option to continue running the software by virtualising the required hardware environment. This enables organisations to support their Cloud transformation efforts with minimum disruption.
Master the concepts of Virtualisation and Hypervisors with our comprehensive Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Course - Sign up now!
Optimising Resource Utilisation
Companies employ Hypervisors to consolidate multiple computers performing different functions into a single server. For instance, if marketing, customer support and production teams drive their workloads on individual physical servers, it may lead to idle resources. With a Hypervisor, you can host the VMs for respective business units on a single server, even if they require other OS and software components.
Benefits of a Hypervisor
As explained above, organisations employ Virtualisation software such as Hypervisors because it helps them use resources efficiently and significantly reduce hardware investment. Virtualisation brings various other benefits, including:
Scalability
Hypervisors help organisations maximise resource usage on physical computers. Instead of using different machines for different workloads, Hypervisors create multiple virtual computers to run numerous workloads on a single machine. This translates to quicker scalability and reduced hardware expenditure for organisations.
Portability
IT teams can allocate networking, memory, processing, and storage resources across multiple servers as required. They can shift workloads between platforms or machines rapidly. When an application requires additional processing power, the Hypervisor provides seamless access to more physical resources.
Hardware Independence
A Hypervisor abstracts the host's hardware from the OS environment. IT Administrators can deploy, configure and manage software applications without being limited to a specific hardware setup. For instance, macOS can be run on a VM instead of iMac computers.
Efficiency
Hypervisors make setting up a server OS more efficient. Manually installing the OS and related software components is a time-consuming endeavour. Instead, you can configure the Hypervisor to create your virtual environment immediately.
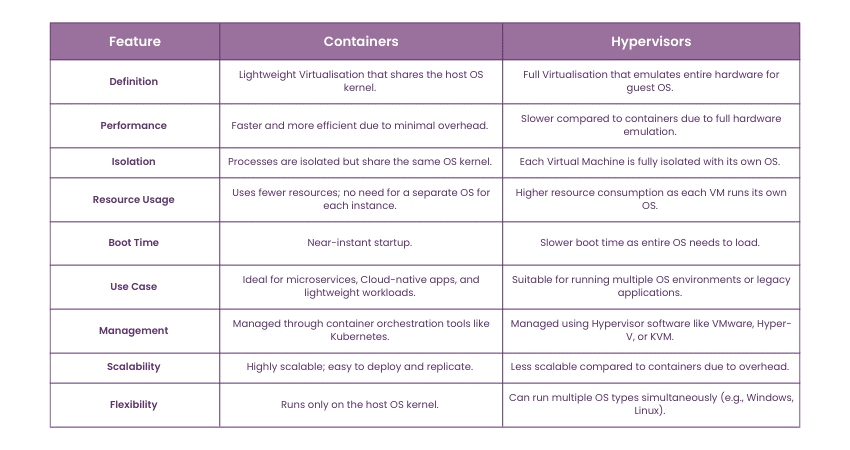
Difference Between Containers and Hypervisors
The following table summarises the key differences between Containers and Hypervisors:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hypervisors are the backbone of Virtualisation, as they enable multiple Virtual Machines to run efficiently on a single physical system. They help boost flexibility, optimise resource utilisation, and reduce costs. Whether you’re exploring Virtualisation for personal projects or enterprise solutions, understanding What is Hypervisor is essential as they are indispensable in modern IT environments.
Master Cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google in our up-to-date Cloud Computing Training - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

No, you can't run a VM without a Hypervisor because it creates and manages VMs by allocating resources from the physical hardware to the virtual environment.

A Hypervisor can support different types of Virtualisation, including full Virtualisation and paraVirtualisation.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies Courses, including the 5G Wireless Training and the Quantum Computing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Digital Twin.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Virtualisation, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Virtual Machine skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


