We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
If you’re just starting in problem-solving or improving processes, you’ve probably heard the term Root Cause Analysis thrown around. You might wonder – What is RCA and how is it used?
Root Cause Analysis is widely used across various industries like manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and aviation. It helps businesses identify systemic weaknesses, process inefficiencies, and human errors.
Do you wish to learn more about this topic to excel in quality improvement? Read this blog to learn about What is Root Cause Analysis. Also, explore its key principles, steps involved in conducting an RCA, and benefits.
Table of Contents
1) What is Root Cause Analysis?
2) What are the various methods to conduct RCA?
3) Process of conducting Root Cause Analysis
4) Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
5) Tips for performing effective Root Cause Analysis
6) Conclusion
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis is the most used technique for determining why the problem occurred in the first place. This technique involves a step-by-step process for identifying the origin of the problem. You can also use some tools along with implementing RCA to help you identify the issues.
With RCA, you can understand what happened, why the problem occurred, and what you can do to reduce the instances of the issue occurring again. With RCA, you can know that both systems and events are interrelated to each other.
For instance, when one thing happens, it causes another, which then causes more things to happen. By following these steps back, you can find where the problem started and how it grew into the issue you’re dealing with.
When should you perform a Root Cause Analysis
There are three types of causes that you may encounter:
a) Physical causes: These physical causes are tangible. For example, Your car’s brakes may stop working.
b) Human causes: These types of causes are generally a result of human errors. For example, your car may stop working because you might have forgotten to fill it with brake fluid.
c) Organisational causes: These causes happen when people don’t stick to rules or systems. For example, if a car wasn’t serviced right, the brakes might not work as they should.
RCA considers all these causes and helps you figure out why the problem occurred in the first place.
Key principles of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis has some simple rules that make it good at finding and solving the true cause of a problem. If organisations follow these RCA principles, they can carry out strong investigations and come up with clear solutions. Here are the fundamental principles of Root Cause Analysis
a) Find out the full story: To understand a problem, you need to gather all the details about what happened, when it happened, and what caused it.
b) Look deeper than the obvious: Instead of just fixing what seems wrong at first glance, try to find the real reason behind the problem.
c) Stop it from happening again: Learn from mistakes to prevent them in the future. Find out why something went wrong and fix that root issue.d) Take your time to do it well: When you’re trying to solve a problem, don’t rush. Make sure you have enough people and money to do a thorough job.
What are the various methods to conduct RCA?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) employs various methods and tools to systematically investigate and uncover the underlying causes of a problem. Here are some commonly used Tools for conducting RCA:
a) The five whys:
The Five Whys Technique is like being a detective. You keep asking “why” over and over to get to the bottom of a problem. It’s like peeling an onion – you remove one layer at a time to find the core issue.
Using the Five Whys means you don’t just guess what’s wrong. You act like a curious kid, asking questions until you find the real reason something happened. This helps everyone think more deeply and find the true cause of a problem.
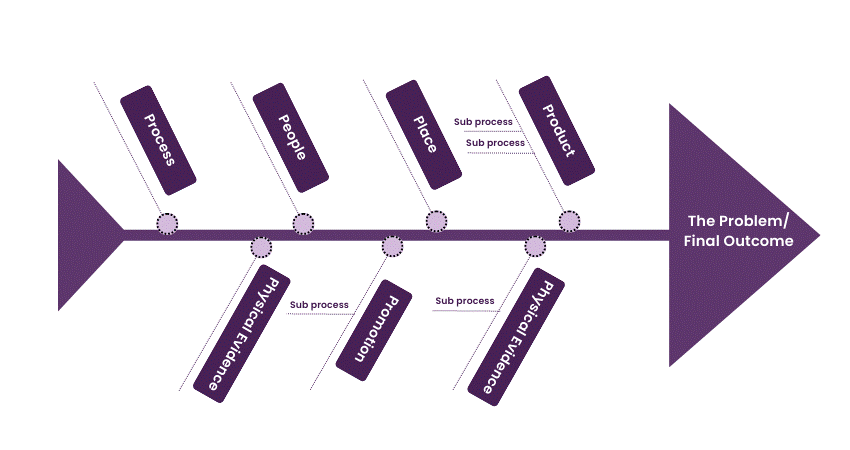
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
The Fishbone Diagram for Root Cause Analysis is like a map that helps you find out why problems happen. Imagine a fish’s skeleton: the head is the problem you’re trying to solve, and the bones are all the possible reasons for the problem. It helps you look at everything that could be causing trouble, like the people involved, how things are done, the stuff you use, the equipment, and where it all happens.
Pareto Analysis
It is popularly known as the 80/20 rule, which prioritises causes based on frequency or impact. Pareto helps identify the vital few causes that contribute the most to the problem. Therefore, teams can allocate resources more effectively and achieve maximum impact in resolving the issue.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is a proactive method to identify potential failure modes and their effects. It assesses the severity, likelihood of occurrence, and detectability of failure modes to prioritise actions.
Change Analysis
Change Analysis examines the impact of recent changes or events on the occurrence of a problem. It investigates whether any modifications, process changes, or external factors contributed to the issue.
Data Analysis
This means looking at the information you have about a problem to spot any patterns or connections. You can use math tricks like checking if things change together or predicting what might happen. This helps you figure out the real reasons behind a problem by looking at the facts and numbers.
Brainstorming and team discussions
Brainstorming is like a group of friends getting together to solve a puzzle. Everyone shares their different ideas and thoughts. This way, the group can come up with new and better ways to solve problems that one person might not think of alone.
Gain in-depth knowledge of the responsibilities of an IT Service Manager with our Certified IT Service Manager CITSM Course.
Process of conducting Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is a way to find out the main reasons why a problem happened. To do this, you follow certain steps that help you look closely and carefully at the problem. This helps companies figure out the real reasons for the problem and then, they can fix it properly.
1) Define the problem
Defining the problem is the first step in Root Cause Analysis. A well-defined problem statement sets the foundation for a focused RCA. It involves the following activities:
a) Begin by clearly defining the problem or incident that requires analysis.
b) Describe the issue in specific terms
c) Include information on its impact, frequency, and any relevant background information
2) Gather information
Collect all available data and information related to the problem. The goal is to understand the problem and its context comprehensively. This may include the following:
a) Incident reports
b) Documentation
c) Data logs
d) Witness statements
e) Any other relevant sources
3) Identify possible causes
This step includes conducting the following activities:
a) Brainstorming and generating a list of potential causes that could contribute to the problem.
b) Encouraging diverse individuals with different perspectives to participate in this ste
c) Consider using the Five Whys, Fishbone Diagrams, or Data Analysis to identify and explore potential causes.
4) Analyse and prioritise causes
Evaluate the potential causes identified in the previous step. Further, assess their likelihood of occurrence, impact on the problem, and available evidence supporting each cause. Additionally, prioritise the causes based on their significance and likelihood of being the Root Cause.
5) Implement solutions
This is one of the crucial steps in conducting the Root Cause Analysis. This step involves the following:
a) Putting the corrective actions into practice.
b) Assigning responsibilities
c) Establishing timelines
d) Allocating necessary resources to implement the solutions effectively
Further, communication and collaboration are also crucial during this stage. This ensures everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities.
Ready to become an expert in Root Cause Analysis? Register for our Root Cause Analysis Course now!
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis offers several benefits to organisations in their problem-solving and improvement efforts. Here are the key Benefits of Conducting RCA:
a) Prevents problem recurrence by addressing the underlying cause
b) Drives continuous improvement and enhances operational efficiency
c) Facilitates informed decision-making based on a comprehensive understanding
d) Reduces costs and minimises waste through process optimisation
e) Improves product and service quality by resolving Root Causes
f) Enhances risk management by identifying and mitigating potential issues
g) Fosters a proactive approach to problem-solving and prevention
h) Increases customer satisfaction through better problem resolutio
i) Empowers employees by involving them in problem-solving processes
Tips for performing effective Root Cause Analysis
Here are some tips that you can follow to perform effective Root Cause Analysis:
a) Work together with your team: It’s important to work well with your team to come up with new ideas and views about the issue you’re dealing with. With everyone’s different thoughts on the problem, you can solve even the toughest issues quickly.
b) Prepare for more Root Cause Analysis: Keep asking lots of questions to find the best way to do things for you. Write down the Root Cause Analysis methods that might be useful for you in the future.
c) Use RCA when things go right: Root Cause Analysis isn’t just for fixing problems; it’s also good for understanding why things went well. Knowing what made you successful in one area can help you do well in other areas too.
Conclusion
After reading this blog, we hope you understood What is Root Cause Analysis. This blog also discussed that RCA goes beyond simply treating the symptoms of a problem. It focuses on uncovering the fundamental reasons behind the issue. By implementing corrective actions and preventive measures, businesses can reduce costs, enhance product and service quality, and improve customer satisfaction.
Enhance your IT Service Management skills with our comprehensive ITIL® Certification Training.
Frequently Asked Questions

Root Cause Analysis (RCA) enhances career development by improving problem-solving skills, promoting a deep understanding of systems, and fostering a proactive mindset.

Root Cause Analysis (RCA) contributes to effective problem resolution within organisations by identifying the fundamental causes of issues and preventing recurrence.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training, including Root Cause Analysis, ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support CDS Course, and ITIL® 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve DPI Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into on Root Cause Analysis Templates.
Our IT Service Management blogs cover a range of topics related to Root Cause Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your RCA skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


