We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever found yourself stuck between options, unsure of the best path forward? Navigating the complexities of Decision-making can often feel like a daunting task. Whether you’re steering a business, managing a team, or making personal choices, understanding the Decision Making Process is essential.
From breaking down the seven key steps of the Decision Making Process to exploring various models and tools, this blog covers everything you need to know. Ready to enhance your Decision Making Skills and face challenges with assurance? Let’s dive in and master the art and science of making impactful decisions.
Table of contents
1) What is the Decision Making Process?
2) Why is Implementing a Decision Making Process Important?
3) Seven key Decision Making Process
4) Tools for Better Decision Making Processes
5) What are the Different Types of Decision Making Models?
6) When to Use Decision Making Models?
7) Challenges in the Decision Making Process
8) Conclusion
What is the Decision Making Process?
The Decision Making Process is a structured approach to identifying and solving problems by evaluating alternatives and choosing the best course of action.
It typically involves seven steps:
a) Identifying the problem
b) Gathering relevant information
c) Exploring available options
d) Evaluating the potential outcomes
e) Making the decision
f) Implementing the decision
g) Reviewing the outcomes
This process helps ensure that decisions are logical, well-informed, and aligned with goals. By following these steps, individuals or organisations can minimise risks, optimise outcomes, and ensure efficient problem-solving. The process may vary in complexity depending on the situation but is essential for making sound decisions.
Why is Implementing a Decision Making Process Important?
Implementing a Decision Making Process is important for several reasons:
a) Improves clarity: A structured process helps clearly define the problem and objectives, ensuring everyone understands the issue at hand.
b) Increases efficiency: By following steps, the Decision Making Process becomes more organised, reducing wasted time and resources.
c) Enhances decision quality: Collecting information and weighing options leads to more informed, well-thought-out decisions.
d) Reduces risks: Evaluating alternatives and potential outcomes minimises the chances of making poor choices.
e) Promotes accountability: A clear process ensures all stakeholders are involved and responsible for their roles in the decision.
f) Encourages consistency: Implementing a structured approach ensures consistency across decisions, leading to better long-term results.
Seven Key Steps in Decision Making Process
The process of Decision Making typically consists of seven essential steps that assist individuals or groups in reaching informed and effective decisions. Let's explore each of these steps:
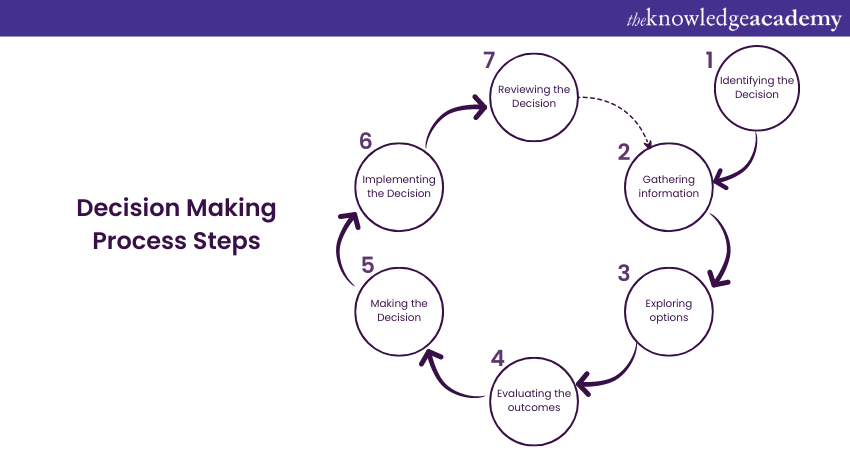
1) Identifying the Decision
1) Clearly define the decision or problem at hand.
2) Ask key questions:
a) What problem are you solving?
b) What goals do you aim to achieve?
c) How will you measure success?
3) Use these questions as part of goal setting to assist you toward an optimal solution.
2) Gathering Information
1) Collect accurate and necessary data for informed Decision-making.
2) Review past data or previous efforts to solve the issue.
3) Expand research beyond internal sources to include:
a) Market research
b) Industry consultants
c) Peers or colleagues in similar roles with relevant experience
4) Use external insights to uncover additional solutions and perspectives.
3) Exploring Options
a) Brainstorm multiple solutions to address the problem.
b) Explore various options to meet different stakeholder needs.
c) Consider how different teams or departments may have unique priorities (e.g., design team vs. development team).
d) Ensure that by evaluating multiple alternatives, you can make a more inclusive and well-rounded decision.
4) Evaluating the Outcomes
1) Analyse each solution by determining how well it addresses the problem.
2) Assess the pros and cons of each option to narrow down choices.
3) Eliminate less effective alternatives.
4) Use common evaluation tools such as:
a) Pros and cons lists
b) SWOT Analysis
c) Decision matrices
5) Making the Decision
a) Make the final decision using the information gathered.
b) Consider the impact of each alternative on all stakeholders.
c) Be open to blending several alternatives for a more effective solution.
d) Use creative problem-solving, avoiding limitations to conventional options.
6) Implementing the Decision
a) Develop a clear implementation plan to align everyone on the next steps.
b) Ensure all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
c) Begin executing the plan.
d) Continuously monitor progress to evaluate if the decision is delivering the expected outcomes.
7) Reviewing the decision
1) Revisit the success criteria defined in Step 1.
2) Evaluate if the decision effectively solved the problem.
3) Assess both the positive and negative impacts of the decision.
4) Gather feedback from stakeholders on their response to the decision.
5) If necessary, adopt an iterative approach to refine and improve outcomes using available resources.
Transform your Leadership skills with our Agile Leadership Training today for success!
Tools for Better Decision Making Processes
Here are some powerful tools that enhance the Decision Making Process to achieve better results.
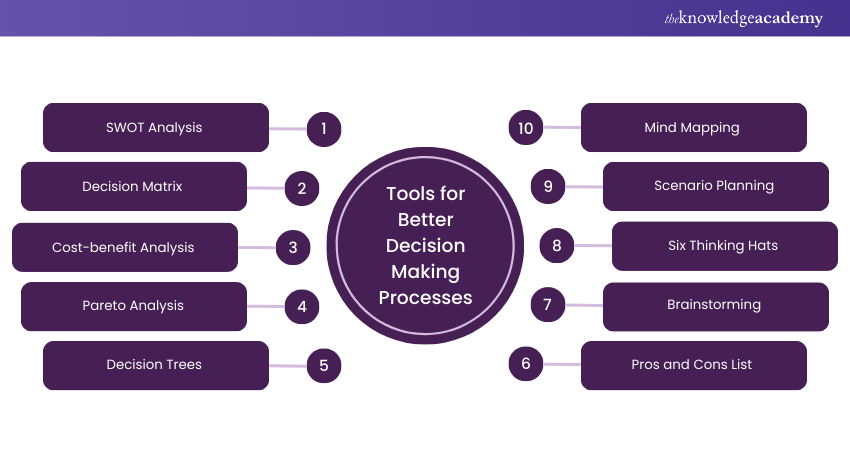
1) SWOT Analysis
1) Assesses your situation by identifying four key areas:
a) Strengths (internal positive factors)
b) Weaknesses (internal negative factors)
c) Opportunities (external positive factors)
d) Threats (external negative factors)
2) Helps in evaluating a company’s position in the market.
3) Commonly used in strategic planning and Decision-making.
4) Guides you in making informed decisions by analysing internal and external factors.
2) Decision Matrix
1) Compares multiple options by evaluating them against predefined criteria.
2) Scores each option based on how well it meets each criterion.
3) Helps determine the most suitable choice systematically.
4) Useful for making objective, data-driven decisions.
3) Cost-benefit Analysis
1) Compares the monetary costs and benefits of different solutions.
2) Assesses whether the benefits of a decision outweigh the costs.
3) Determines the economic viability of a solution.
4) Aids in making financially informed decisions.
4) Pareto Analysis
1) Based on the 80/20 rule, where 80% of problems are caused by 20% of the factors.
2) Identifies the few critical factors that contribute to the majority of problems.
3) Helps prioritise key issues that, when addressed, have the greatest impact.
4) Focuses on solving the most significant issues with minimal effort.
5) Aims to improve efficiency by targeting high-impact areas first.
5) Decision Trees
1) Visual tools that map out different decision paths and possible outcomes.
2) Helps you anticipate the results of various choices.
3) Clearly lays out the consequences of each decision.
4) Aids in making more calculated and informed decisions.
5) Useful for complex decisions with multiple outcomes or factors to consider.
6) Pros and Cons List
1) Simple tool for listing the positive (pros) and negative (cons) aspects of each option.
2) Provides a quick overview of the benefits and drawbacks of each choice.
3) Helps in comparing alternatives side by side.
4) Facilitates making a balanced, informed decision based on advantages and disadvantages.
5) Easy to use for straightforward Decision-making scenarios.
7) Brainstorming
1) Encourages creativity by generating ideas from individuals or groups.
2) No immediate judgment or criticism is allowed during the process.
3) Useful for producing a wide variety of solutions.
4) Particularly effective for addressing complex problems.
5) Promotes open, collaborative thinking.
8) Six Thinking Hats
1) Assigns different “hats” or thinking styles to individuals (logical, emotional, optimistic, pessimistic, creative, etc.).
2) Encourages looking at decisions from multiple perspectives.
3) Ensures a more comprehensive approach to Decision-making.
4) Helps balance objective analysis with subjective insights.
5) Ideal for group discussions to ensure all angles are considered.
9) Scenario Planning
1) Involves envisioning different future scenarios based on possible variables.
2) Helps teams prepare for a range of potential challenges and opportunities.
3) Ensures decisions are flexible and robust enough to handle various outcomes.
4) Encourages proactive thinking and long-term planning.
5) Useful for dealing with uncertainty and complex situations.
10) Mind Mapping
1) Visually organises ideas and thoughts.
2) Highlights connections and relationships between concepts.
3) Useful for brainstorming and problem-solving.
4) Helps identify links that may not be immediately obvious.
5) Facilitates clearer thinking and structured idea generation.
Master the strategies to lead high-performing teams for exceptional success with our High Performing Teams Training – join now!
What are the Different Types of Decision Making Models?
Decision Making models provide structured approaches to analyzing and solving problems using various Decision Making Techniques. Here’s a list of different types of Decision Making models:
1) Rational Model:
a) Based on logical, structured, and step-by-step processes.
b) Involves identifying the problem, gathering information, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the best solution.
c) Often used in business and strategic Decision-making.
2) Bounded Rationality Model:
a) Recognises the limitations of Decision-makers in terms of time, information, and cognitive capacity.
b) Decision-makers opt for a solution that is "good enough" rather than optimal.
c) Often used when time or resources are limited.
3) Intuitive Model:
a) Relies on gut feelings, instincts, or subconscious reasoning.
b) Decision-makers draw on experience and intuition to make quick decisions.
c) Often used in fast-paced or uncertain environments.
4) Creative Model:
a) Involves generating innovative and out-of-the-box solutions to problems.
b) Focuses on brainstorming, lateral thinking, and exploring alternatives beyond traditional approaches.
c) Used when decisions require new, novel solutions.
5) Collaborative Decision Making Model:
a) Involves group input and consensus-building.
b) Encourages collaboration and collective input from different stakeholders or team members.
c) Often used in team or organisational settings where different perspectives are valued.
6) Vroom-Yetton Decision Making Model:
a) A situational model that adjusts Decision-making styles based on the situation's requirements.
b) Outlines different Leadership styles (autocratic, consultative, and group-based) depending on the complexity and the need for team involvement.
7) Incremental Decision Making Model:
a) It focuses on making small, gradual decisions instead of big, comprehensive decisions all at once.
b) Decisions are made step by step, often revising or improving on previous steps.
c) Used when long-term decisions require continuous adjustments.
8) Analytical Decision Making Model:
a) Focuses on using data, facts, and logical reasoning to guide decisions.
b) Involves in-depth analysis of all available information before reaching a conclusion.
c) Ideal for solving complex issues that require careful consideration of multiple variables.
d) Used in Business strategy, finance, engineering, and other fields where precision and detailed evaluation are essential.
9) Heuristic Decision Making Model:
a) Uses mental shortcuts or rules of thumb to simplify Decision-making.
b) Helps Decision-makers make quick, efficient choices, especially when faced with complex situations.
c) Often used when time is of the essence or when there's a lack of complete information.
10) Satisficing Decision Making Model:
a) Decision-makers choose the first satisfactory solution rather than seeking the best possible one.
b) Similar to the bounded rationality model, this model focuses on "good enough" choices.
Elevate your Leadership skills to lead with confidence and empower your team with our Leadership Skills Training - sign up now!
When to Use Decision Making Models?
Decision-making models are helpful in various situations, particularly when:
a) Complexity is High: When faced with complex decisions involving multiple variables, models like the Analytical or Rational models help structure the process.
b) Uncertainty Exists: When outcomes are uncertain, models such as Scenario Planning or Decision Trees are ideal for exploring potential futures and outcomes.
c) Need for Structured Decisions: Models like SWOT Analysis or Decision Matrices are useful when a structured, methodical approach is needed.
d) Group Decision Making: For team-based decisions, models like Collaborative or Six Thinking Hats help gather diverse perspectives and build consensus.
e) Limited Time or Resources: Models like Heuristic or Intuitive Decision-making are useful for making quick decisions when time and information are limited.
f) Incremental Improvements: The Incremental Decision-Making model is suitable when small, gradual changes are preferred over large, sweeping decisions.
Transform your business strategies with cutting-edge innovation techniques in this Business Model Innovation Training – register now!
Challenges in the Decision Making Process
Here are a few common challenges faced during the Decision-making Process:
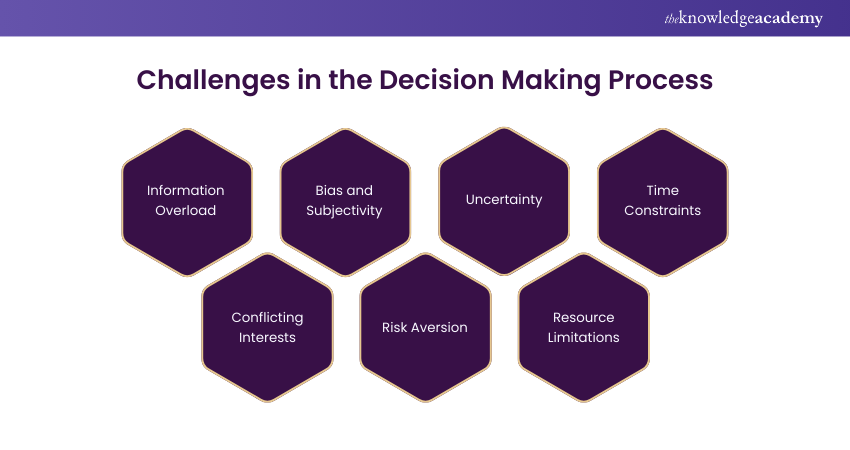
a) Information Overload: Too much data can overwhelm Decision-makers and lead to analysis paralysis, delaying the decision process.
b) Bias and Subjectivity: Personal biases, assumptions, or emotions can influence the Decision-making Process, leading to less rational or objective choices.
c) Uncertainty: Incomplete information or unpredictable future outcomes can make it difficult to choose the best course of action.
d) Time Constraints: Urgent decisions may require quick action, limiting the ability to thoroughly analyse all options and outcomes.
e) Conflicting Interests: In group Decision-making, differing opinions or priorities among stakeholders can create conflicts, slowing down or complicating the process.
f) Risk Aversion: Fear of failure or negative outcomes can lead to indecision or overly cautious choices, potentially missing out on valuable opportunities.
g) Resource Limitations: Lack of necessary resources, such as time, money, or expertise, can hinder the ability to fully explore alternatives or implement decisions effectively.
Learn how to make important decisions effectively with our Decision Making Course now!
Conclusion
Mastering the Decision Making Process empowers you to tackle challenges with confidence and clarity. By applying these structured steps, you can transform uncertainty into opportunity, make smarter choices, and drive better outcomes. Start implementing these strategies today for lasting success!
Take the next step in developing your Leadership skills by registering for our Leadership Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Individuals Reduce Cognitive Bias in Decision Making?

Individuals can reduce cognitive bias in Decision-making by:
a) Seek Diverse Perspectives
b) Use Data and Evidence
c) Apply Structured Decision Making Tools
d) Practice Self-awareness
e) Reflect on Past Decisions
How Can Individuals Adapt Their Decision Making Process to Accommodate Uncertainty or Dynamic Environments, Ensuring Agility and Adaptability?

To adapt Decision-making in uncertain or dynamic environments, individuals can:
a) Embrace Flexible Strategies
b) Make Incremental Decisions
c) Foster Continuous Feedback
d) Encourage Team Collaboration
e) Prioritise Agility
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses, including Decision Making Course, Leadership Skills Training, Creative And Analytical Thinking Training and Agile Leadership Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Delegating Leadership Style.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Decision Making, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Decision Making skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


