We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the expansive world of computer networks, communication is key. Whether sending an email, streaming a video, or browsing a website, data needs to travel smoothly and efficiently from one point to another. This is where Network Protocols come into play. They are the unsung heroes of the digital world, facilitating the exchange of information across interconnected devices. But what exactly are Network Protocols, and how do they function? Let's delve into a comprehensive exploration of this vital aspect of Networking.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Network Protocol?
2) Types of Network Protocols
3) How do Network Protocols work?
4) Network Protocols examples
5) Conclusion
What is a Network Protocol?
A Network protocol is a set of rules or standards governing how data is exchanged between devices in a network. Think of it as a language that devices use to communicate with each other effectively. These Protocols define various aspects of communication, including the format of data packets, the order of transmission, error handling, and more. These standardised Protocols are necessary for devices to understand each other, leading to chaos in the digital realm.
One of the fundamental aspects of Network Protocols is their role in defining the format and structure of data packets. When transmitted over a network, data is broken down into smaller units called packets. These packets contain the actual data being transmitted and crucial information such as source and destination addresses, sequence numbers, and error-checking codes. Network Protocols dictate how these packets are formatted, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different platforms and devices.
Furthermore, Network Protocols specify the rules and procedures governing the transmission of these data packets. This includes determining the order in which packets are sent and received, handling errors and retransmissions, and managing flow control to prevent congestion within the network. By establishing clear guidelines for data transmission, Network Protocols help optimise the efficiency and reliability of communication between devices.
Types of Network Protocols
Network Protocols are the cornerstone of modern communication, providing the framework for data exchange across interconnected devices. Understanding the different types of Network Protocols is essential for comprehending how information flows within a network infrastructure.
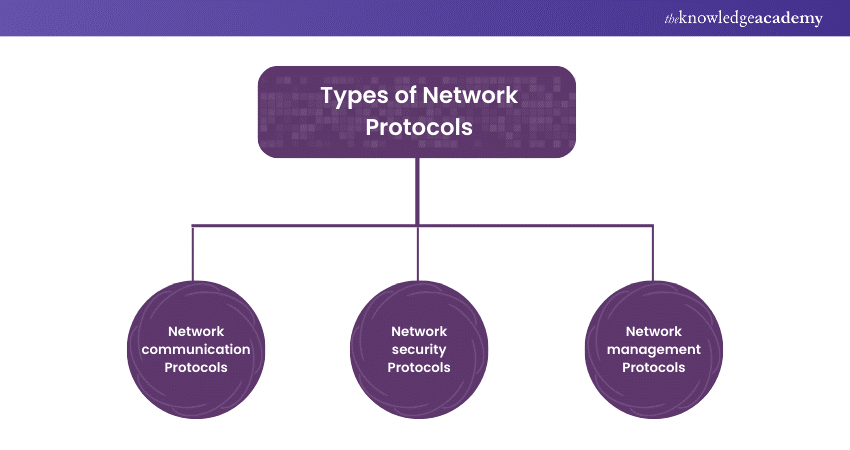
1) Network communication Protocols
Communication Protocols form the backbone of Networking by dictating how data is transmitted between devices. They encompass a range of functions, including addressing, routing, and delivering data packets. Examples of communication Protocols include TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, UDP or User Datagram Protocol, HTTP or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, and SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
These Protocols ensure data travels efficiently and reliably across the network, enabling seamless communication between devices. One of the primary functions of communication Protocols is addressing. They establish rules for identifying the source and destination of data packets, enabling devices to communicate effectively. Through mechanisms like IP addressing, communication Protocols facilitate the routing of packets through the network, directing them along the most efficient path to their destination.
2) Network security Protocols
Network security Protocols constitute a critical aspect of modern Networking infrastructure, primarily dedicated to fortifying Networks against a plethora of cyber threats. With the proliferation of interconnected devices and the increasing dependency on digital communication, the importance of robust security measures cannot be overstated.
These Protocols encompass diverse mechanisms designed to safeguard sensitive data, prevent unauthorised access, and mitigate potential security breaches. Encryption Protocols, such as SSL/TLS and IPsec, play a pivotal role in securing data transmissions by encoding information so that only authorised parties can decipher it, ensuring confidentiality.
3) Network management Protocols
Managing a complex network infrastructure requires meticulous oversight and control, which is where network management Protocols come into play. These Protocols facilitate device configuration, monitoring, troubleshooting, and performance optimisation. Examples of network management Protocols include SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
By providing administrators with the tools they need to manage network resources efficiently, these Protocols ensure the smooth operation of the network infrastructure. Network management Protocols serve as the administrative backbone of complex Network infrastructures, facilitating efficient oversight, control, and optimisation of network resources. These Protocols are essential for ensuring the smooth operation of networks by enabling administrators to perform a wide range of tasks remotely.
Unlock the realm of VPN with our VPN Training – Sign up today!
How do Network Protocols work?
Understanding how Network Protocols function is crucial to grasping the intricacies of communication in modern computer networks. Let's explore deeper into the inner workings of Network Protocols to gain a comprehensive understanding of their operation.
1) Standardisation and Protocols: Network Protocols rely on standardised rules and conventions to ensure seamless communication between devices. These standards are established by organisations like the Internet Engineering Task Force or IETF and the Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers/ IEEE. By adhering to these standards, different devices from various manufacturers can communicate effectively, regardless of their underlying hardware or software differences.
2) Packetisation: One of the fundamental concepts of Network Protocols is packetisation. Data is fragmented into smaller chunks called packets before transmission. Each packet contains the actual data and control information, such as source and destination addresses, sequence numbers, and error-checking codes. Packetisation allows for more efficient transmission over the Network, as it enables data to be sent in smaller chunks rather than as a continuous stream.
3) Addressing and routing: Network Protocols handle addressing and routing to ensure that packets reach their intended destination. Each device in a specific network is assigned a unique identifier, like an IP address, which is used to route packets. Routing Protocols, like the Border Gateway Protocol or the BGP and the Open Shortest Path First or the OSPF protocol, determine the optimal path for packet transmission based on network topology, congestion levels, and quality of service requirements.
4)Transmission control: Transmission control is another crucial aspect of Network Protocols. Protocols like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) provide reliable, connection-oriented communication by implementing acknowledgement, retransmission, and flow control mechanisms. These mechanisms ensure that data is transmitted accurately and in the correct order, even in the face of network errors or congestion.
5) Error detection and correction: Network Protocols incorporate error detection and correction mechanisms to maintain data integrity during transmission. For example, Protocols like TCP use checksums to detect errors in transmitted data packets. If an error is found, the protocol can request retransmission of the corrupted packet to ensure the data arrives intact.
6) Protocol stack: Network Protocols are often organised in a hierarchical structure known as a protocol stack. The most commonly used protocol stack in modern Networking is the TCP/IP stack, which consists of multiple layers, including the application, transport, network, and link layers. Each layer is responsible for specific tasks, such as data encapsulation, addressing, and routing, with higher layers building upon the services provided by lower layers.
7) Interoperability and compatibility: Interoperability and compatibility are essential considerations in Network Protocol design. Protocols must be interoperable with existing infrastructure and compatible with various devices to ensure seamless communication across heterogeneous networks. Standardisation efforts help address these concerns by establishing Protocols and ensuring widespread adoption.
8) Evolution and adaptation: Network Protocols continuously evolve to meet the changing demands of modern Networking environments. New Protocols are developed to address emerging technologies and challenges, while existing Protocols are updated to incorporate improvements and address vulnerabilities. This evolution ensures Network Protocols remain robust, efficient, and secure despite threats and technological advancements.
Explore the skills needed for CloudFare with our CloudFare Training – Sign up today!
Network Protocols examples
Network Protocols are the unsung heroes of modern communication, enabling seamless data exchange and facilitating the smooth operation of interconnected devices. Let's delve deeper into some prominent examples of Network Protocols and explore their roles and applications in the digital realm.
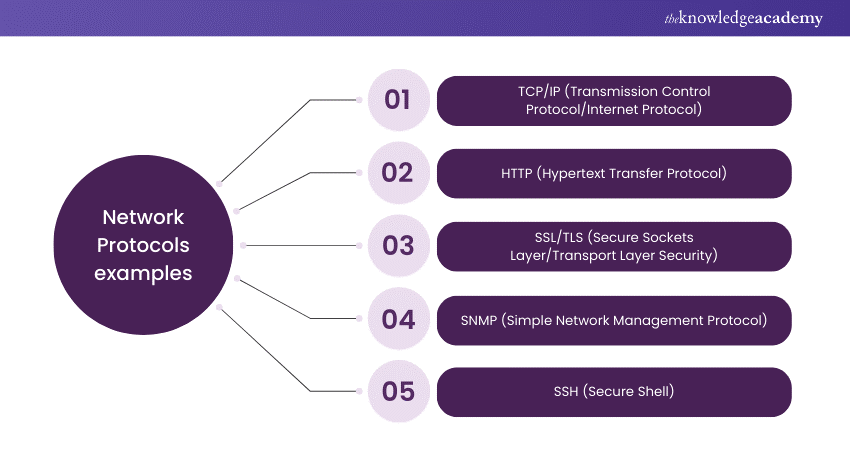
1) TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol):
TCP/IP stands as the cornerstone of modern Networking, serving as the primary protocol suite for transmitting data across the Internet. It comprises two main Protocols: TCP and IP. TCP ensures the trustworthy delivery of data by establishing connections, breaking data into packets, and reassembling them at the destination.
2) HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol):
As the protocol behind the World Wide Web, HTTP facilitates the retrieval and display of web pages in browsers. It works on a client-server model, where a client, which can be a web server, sends requests to a server (hosting a website), and the server responds with the requested content. HTTP dictates the format of these requests and responses, enabling seamless browsing experiences for users worldwide.
3) SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security):
SSL/TLS Protocols are instrumental in securing communications over the Internet. They establish encrypted connections between clients and servers, safeguarding sensitive data from eavesdropping and tampering. SSL/TLS Protocols are commonly used in secure browsing (HTTPS), email encryption (SMTPS, POP3S, IMAPS), and virtual private Networks (VPN).
4) SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol):
SNMP facilitates the remote management and monitoring of network devices. It allows Network administrators to gather information about the status and performance of routers, switches, servers, and other network components. SNMP operates on a manager-agent model, where a central management station (manager) communicates with network devices (agents) to retrieve data, configure settings, and detect faults.
5) SSH (Secure Shell):
SSH or Secure Shell is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure and remote access to network devices and servers. It provides a secure alternative to traditional remote login methods (e.g., Telnet) by encrypting communication sessions between clients and servers. SSH supports various authentication methods, including passwords, public-key cryptography, and multi-factor authentication, ensuring secure access to sensitive systems and data.
Stay at the forefront of IT skills and fundamentals with our IT Fundamentals Training – Join today!
Conclusion
Network Protocols have become the foundation of modern communication systems, enabling seamless data exchange across interconnected devices. Whether facilitating communication, ensuring security, or streamlining network management, these Protocols are pivotal in shaping the digital landscape. By adhering to standardised rules and conventions, Network Protocols ensure interoperability and reliability, laying the groundwork for today's interconnected world.
Gain insights into Networking with our Introduction to Networking Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three significant Network Protocols are TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, UDP short for User Datagram Protocol, and HTTP short for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. Understanding the different types of Network Protocols is essential for comprehending how information flows within a network infrastructure.

Protocol standards are rules and guidelines that ensure compatibility, interoperability, and reliability in communication Protocols. They define the format, syntax, semantics, and data exchange synchronisation, facilitating seamless interaction between devices and systems.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various IT support and solution training including VPN Training, Snort Training, and IT Fundamentals training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Escalation Matrix.
Our IT Infrastructure and Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to IT Businesses, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


