We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the modern business scenario, the art and science of Production Management have taken center stage as a pivotal force in ensuring operational excellence. It encompasses a spectrum of activities, from meticulous planning to seamless execution, from resource allocation to process optimization. Understanding the intricacies of product manager roles and responsibilities is integral to achieving success in Production Management. Product managers play a crucial role in the planning, development, and implementation of products throughout their lifecycle, contributing significantly to the overall operational efficiency of a business.
Amid the myriad complexities that define the global marketplace, the objectives of Production Management have emerged as guiding stars, offering direction and purpose to businesses striving for success. In this blog, we will discuss what are the main Objectives of Production Management to optimize operations through effective planning and control.
Furthermore, as businesses navigate the dynamic landscape of the market, the principles of product management play a crucial role in aligning production objectives with overall business strategy. Examining the intersection of production management and product management provides a holistic view of how organizations can streamline processes and enhance their competitive edge in today's dynamic business environment.
Table of Contents
1) What is Production Management?
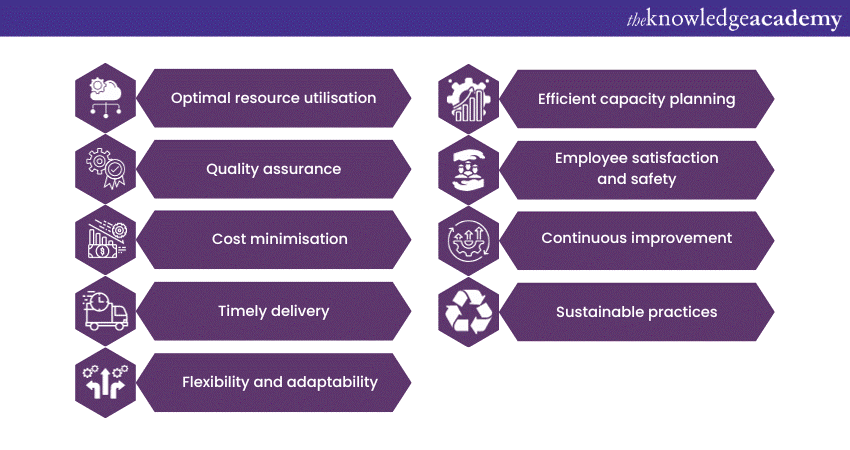
2) Objectives of Production Management
a) Optimal resource utilisation
b) Quality assurance
c) Cost minimisation
d) Timely delivery
e) Flexibility and adaptability
f) Efficient capacity planning
g) Employee satisfaction and safety
h) Continuous improvement
i) Sustainable practices
3) Conclusion
What is Production Management?
Production Management is a critical aspect of any business that involves the creation of goods and services. It is the process of planning, organising, controlling, and coordinating resources to achieve the desired output efficiently and effectively.
From the towering skyscrapers of metropolis factories to the intricate workings of automobile workshops, the objectives of Production Management serve as the compass, navigating enterprises through the seas of competition and innovation.
Learn more about Product Management Training Course today!
Objectives of Production Management
These objectives, ranging from optimising resource allocation and ensuring top-notch quality to managing costs and adhering to deadlines, form the foundation of a robust strategy that breathes life into the production process. So, let's begin to understand how Production Management plays a pivotal role in driving a company's success.
Optimal resource utilisation
One of the primary objectives of Production Management is to ensure the efficient utilisation of resources. This includes managing raw materials, labour, equipment, and time in a way that minimises waste and maximises output. In the process of optimising resource allocation, a business can reduce costs and enhance overall productivity.
Example: In the energy sector, optimising resources means generating maximum power while minimising waste. Renewable energy sources like solar panels are strategically placed to capture the most sunlight, thus optimising energy production.
Quality assurance
Maintaining product quality is a key objective of Production Management. Ensuring that products meet or exceed established standards is vital for customer satisfaction and long-term success. Product Managers must implement quality control measures, monitor production processes, and address any issues that could compromise the final product's quality.
Example: Imagine the bustling floor of an automotive assembly plant. From scheduling the arrival of raw materials, such as metal sheets and engine parts, to coordinating the assembly line workforce, Production Management ensures that the manufacturing process flows smoothly.
Cost minimisation
Controlling production costs is a critical objective that directly impacts a company's profitability. Product Managers strive to identify and eliminate inefficiencies in processes, reduce wastage, and streamline operations to produce goods and services at the lowest possible cost without compromising quality.
Example: Let's take the example of the fashion industry, where they ensure that the manufacturing process aligns with the latest trends and seasonal demands. The objective here is to strike a balance between creativity, timely production, and cost-effectiveness, ultimately delivering stylish garments to consumers.
Timely delivery
Meeting delivery schedules is essential for maintaining customer trust and fulfilling market demand. Production Management aims to create realistic production timelines and ensure that goods and services are produced and delivered on time. This objective involves effective coordination of various stages of production and efficient scheduling.
Example: Food and beverage manufacturing plant. Here, Production Management ensures that ingredients are sourced, processed, and packaged efficiently to create a range of consumable products.
Join our renowned Train the Trainer course and gain the expertise you need to inspire and educate others effectively.
Flexibility and adaptability
In today's rapidly changing business environment, the ability to adapt to market fluctuations and shifts in demand is crucial. Production Management objectives include establishing flexible production processes that can quickly adjust to changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and market trends.
Example: Smartphones, laptops, or other electronic devices, the process involves managing the procurement of electronic components, coordinating assembly lines, and testing products for functionality and quality. Production Managers here strive to balance technological advancements with efficient production, all while adhering to stringent quality control measures.
Efficient capacity planning
Production Managers are tasked with determining the optimal production capacity to meet current and future demands. Overproduction can lead to unnecessary costs, while underproduction can result in missed opportunities. Striking the right balance through effective capacity planning is a key objective to ensure smooth operations.
Example: Let's take the example of the pharmaceutical industry, where They oversee the entire process, from raw material sourcing and formulation to packaging and distribution, ensuring that life-saving medications reach those in need.
Employee satisfaction and safety
A productive workforce is the basis of successful Production Management. This objective encompasses creating a safe and conducive work environment, providing training and skill development opportunities, and ensuring employee satisfaction. Content and motivated employees are inclined to make constructive contributions to production processes.
Example: In the construction domain, Production Management coordinates various trades, schedules, and resources to ensure projects are completed on time and within budget. They manage labour, materials, and equipment, striving to strike a balance between construction speed, safety, and quality.
Continuous improvement
Production Management objectives also include fostering a culture of continuous improvement. This involves regularly evaluating production processes, identifying bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and implementing enhancements to optimise operations over time. Continuous improvement leads to increased efficiency and competitiveness.
Example: The concept of lean principles is a prime example of continuous improvement. Toyota, for instance, pioneered this approach, focusing on minimising waste and maximising efficiency. Through methods like Kaizen (continuous improvement) events, production managers and workers collaborate to identify and eliminate inefficiencies in processes, leading to streamlined production, reduced costs, and enhanced product quality.
Sustainable practices
Modern Production Management recognises the importance of sustainability. Businesses aim to minimise their environmental footprint by adopting eco-friendly production methods, reducing waste generation, and conserving resources. Implementing sustainable practices enhances a favorable brand image and aligns with evolving consumer preferences.
Example: For example, manufacturing companies might invest in more energy-efficient equipment, monitor resource consumption, and implement eco-friendly practices. Over time, these incremental changes contribute to reduced environmental impact and a greener footprint.
Conclusion
Optimal resource utilisation transcends industry boundaries, uniting them in a common pursuit of efficiency. After handling raw materials, human capital, energy, or time, effective Production Management ensures that resources are channelled towards achieving the greatest output with minimal waste. These examples underscore the versatility and importance of Production Management across industries. It's the invisible hand that guides the transformation of ideas into tangible products, embracing creativity, precision, and efficiency.
Try out our Agile Product Management Training Course for a successful career
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Product Management Training
Product Management Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


