We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
As businesses grow, so do their data needs. Handling vast amounts of information efficiently and extracting valuable insights can be challenging. That’s where AWS Redshift comes in. But What is AWS Redshift? It is a fully managed cloud Data Warehouse designed to power fast and secure Data Analytics at any scale. With its robust architecture and real-time processing, AWS Redshift can help businesses harness their data like never before.
In this blog, we’ll dive into what is AWS Redshift, exploring its key features and how it optimises Data Analytics. Discover how this powerful tool transforms the way organisations manage and process large datasets, providing faster insights and more efficient data handling.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is AWS Redshift
2) What Makes AWS Redshift Unique?
3) Difference Between AWS Redshift and Traditional Data Warehouses
4) Benefits of Using AWS Redshift
5) Limitations of Using AWS Redshift
6) Exploring the Amazon Redshift Architecture
7) Data Transfer in Amazon Redshift
8) AWS Redshift Pricing Model
9) Amazon Redshift Best Practices
10) Conclusion
Understanding What is AWS Redshift
AWS Redshift is a Cloud-based Data Warehousing Service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). Launched in 2012, it uses Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) to distribute data across multiple nodes, enabling quick data processing and analytics.
Redshift employs Columnar Storage technology for better data compression and query performance, handling large datasets efficiently. It integrates easily with various data sources and supports SQL, making it simple to transition from traditional databases.
Scalability is a key feature of AWS Redshift. You can begin with a single node and expand as needed. For security, Redshift offers Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), SSL/TLS for data in transit, and encryption for data at rest. This makes it a secure and flexible solution for businesses of all sizes.
What Makes AWS Redshift Unique?
Redshift is an OLAP-style (Online Analytical Processing) column-oriented database based on PostgreSQL version 8.0.2. This allows the use of regular SQL queries with Redshift. However, what sets it apart is its ability to quickly process queries on large databases with exabytes of data.
This fast querying is enabled by Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) technology developed by ParAccel. MPP allows many computer processors to work in parallel to perform computations. Sometimes, processors across multiple servers are used for this purpose.
Unlike most MPP vendors, ParAccel does not sell MPP hardware. Instead, their software can be used on any hardware to leverage multiple processors. AWS Redshift uses ParAccel’s MPP technology. Redshift was initiated after AWS invested in ParAccel and adopted its MPP technology. ParAccel is now part of Actian.
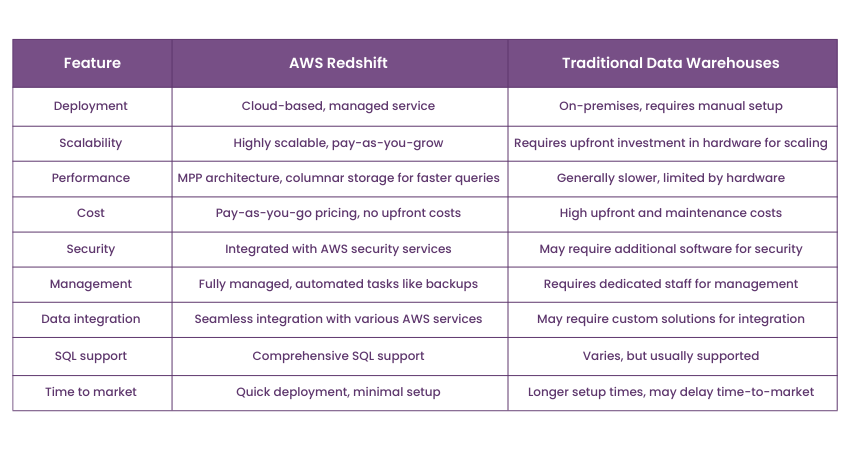
Difference Between AWS Redshift and Traditional Data Warehouses
AWS Redshift and Traditional Data Warehouses differ fundamentally in deployment, scalability, performance, and cost. Here are the differences highlighted between the two:
Benefits of Using AWS Redshift
Here are the various points highlighting the important facets of AWS Redshift:
1) Scalability: One of the most crucial aspects of AWS Redshift is its ability to scale according to the data storage needs of a business. Companies can start with a single node and seamlessly transition to multi-node clusters as data volume grows, ensuring that they don't over-invest upfront.
2) Performance: The Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) architecture and Columnar Storage allow Redshift to deliver high-speed data processing. This performance level is vital for businesses requiring real-time analytics and fast query returns to make quicker decision-making.
3) Cost-effectiveness: AWS Redshift has a pay-as-you-go pricing model and no need for specialised hardware. Therefore, it lowers the total cost of ownership compared to traditional Data Warehouse solutions. This makes Data Warehousing accessible even for smaller businesses with tighter budgets.
4) Security: In an era where data breaches are common, robust security measures for data transit are indispensable. Some of the security measures offered by Redshift includes Virtual Private Clouds (VPC), Data Encryption, and SSL/TLS. This layered security approach ensures that sensitive information remains protected.
5) SQL Support: AWS Redshift's SQL support ensures that the transition from traditional databases is smooth. This allows businesses to use existing skills and tools, reducing the learning curve and speeding up integration.
6) Simplified Management: As a fully managed service, Redshift automates many administrative tasks like backups, patch management, and fault tolerance. This frees up human resources and allows businesses to focus more on Data Analysis rather than infrastructure management.
7) Data Integration: Redshift's has compatibility with a variety of data formats. It also has integration with other AWS services like S3 and DynamoDB. This makes it a versatile solution for varied data storage needs.
8) Business Agility: The rapid query capabilities and real-time analytics options provide businesses with the agility to adapt to market changes swiftly. This agility is important for staying competitive in today's fast-paced business environment.
Build, deploy and manage your applications by signing up for our AWS Cloud Practitioner Training now!
Limitations of Using AWS Redshift
Redshift isn’t perfect. It has its drawbacks, including:
1) Potentially Costly Migration: Organisations with petabytes of data may face high costs when moving data to AWS cloud facilities, especially if they have bandwidth limits.
2) Parallel Upload Limitations: Redshift supports parallel uploads from Amazon S3, DynamoDB, and EMR databases. For other sources, separate scripts are needed to upload data.
3) Uniqueness Limits: Redshift lacks tools to ensure data uniqueness, which can lead to redundant data points.
4) OLAP Limitations: As an OLAP database, Redshift is optimised for analytical queries on large datasets. However, it is less efficient than traditional OLTP databases for basic tasks like insert, update, and delete operations.
Exploring the Amazon Redshift Architecture
Amazon Redshift’s architecture is built for robust Data Warehousing, focusing on speed, scalability, and manageability. Its key components include:
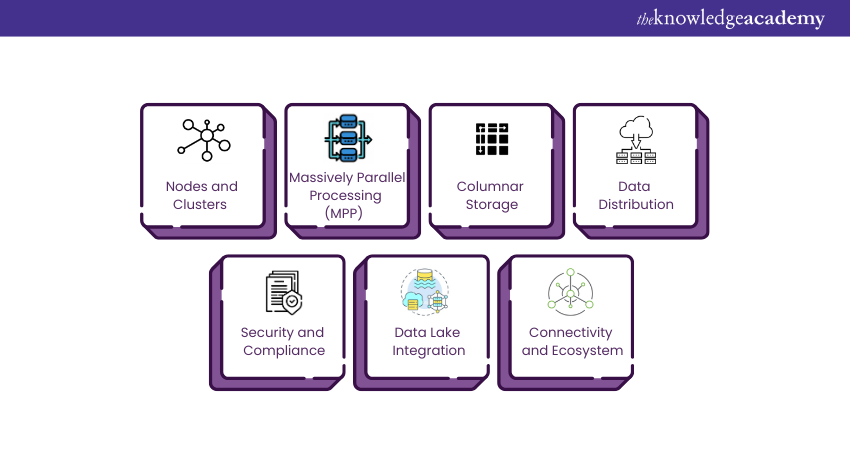
1) Nodes and Clusters
The basic building block of Amazon Redshift architecture is a node, which is essentially a computing resource featuring CPU, RAM, and storage. Nodes are grouped into clusters, with a single leader node coordinating the activities of the remaining compute nodes. Users interact primarily with the leader node when submitting SQL queries. The leader node compiles the query and develops an execution plan. This is then distributed among the compute nodes for parallel execution.
2) Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
MPP architecture is one of the most important features of Redshift Architecture. This means that data is distributed across multiple nodes. Each node works on its subset of data in parallel with the others. This dramatically speeds up data processing and analytics tasks, making it suitable for handling large datasets efficiently.
3) Columnar Storage
Another distinctive feature is the Columnar Storage of data, as opposed to traditional row-based storage. In a Columnar Storage model, data is stored in a column-by-column layout rather than row-by-row. This leads to better compression rates and, subsequently, quicker query performance. Since most queries focus on a subset of columns rather than entire rows, Columnar Storage significantly speeds up data retrieval times.
4) Data Distribution
Data distribution is crucial in Redshift architecture. Redshift offers several ways to distribute data across nodes: key distribution, even distribution, or condition-based distribution. The choice of distribution method significantly affects query performance. Therefore, it should be selected based on specific query patterns and data access methods.
5) Security and Compliance
Amazon Redshift integrates with Amazon’s Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to isolate the Data Warehouse cluster in a private network space. It supports SSL for data in transit and offers encryption options for data at rest. This multi-layered security approach ensures sensitive data is well-protected.
6) Data Lake Integration
Amazon Redshift also offers native integration with Amazon S3 Data Lakes, enabling SQL queries across structured and unstructured data. This seamless interaction between a high-performance Data Warehouse and a scalable Data Lake makes Redshift particularly flexible and powerful for complex analytics tasks.
7) Connectivity and Ecosystem
Redshift supports many client tools and provides JDBC and ODBC drivers. This allows easy integration with popular reporting and analytics tools.
Build a Data Lake efficiently, by signing up for the Building Data Lakes on AWS Training now!
Data Transfer in Amazon Redshift
Data transfer in Amazon Redshift is crucial. Efficient Data Ingestion and export can greatly impact the performance and usability of a Data Warehouse. Redshift offers multiple ways to load and extract data, meeting various data workflows and organisational needs. Here’s a detailed look into how data transfer occurs in Amazon Redshift:
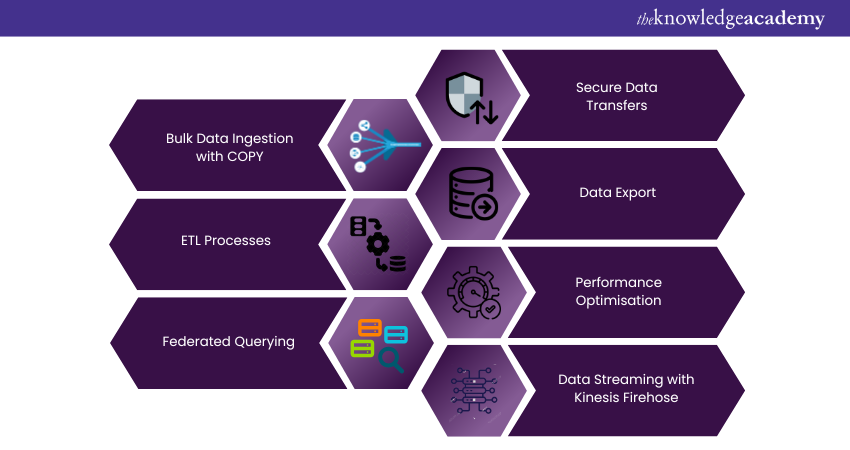
1) Bulk Data Ingestion with COPY
Amazon Redshift’s COPY command is designed for fast bulk Data Ingestion. It lets users to load large amounts of data in parallel from sources like Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, and remote hosts via SSH. This parallel loading speeds up Data Ingestion by using Redshift’s Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) architecture.
2) ETL Processes
Many organisations use ETL processes to move data into Redshift. Several third-party ETL solutions work with Redshift, and AWS offers its own AWS Glue service. These ETL processes clean, transform, and reliably move data from various sources into Redshift, enabling more complex data workflows.
3) Federated Querying
Amazon Redshift supports federated queries. It allows you to query and transfer data across different AWS services without first loading it into Redshift. This feature can access data in Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and other Redshift clusters, making it easy to combine data from various sources.
4) Secure Data Transfers
Security is crucial during data transfers, and Amazon Redshift provides several features to ensure data safety. All data transfers can use SSL, and the service offers options to encrypt data at rest. When used within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), data transfers happen in an isolated environment, adding another layer of security.
5) Data Export
Exporting data from Amazon Redshift is also made straightforward with commands like UNLOAD, which allows you to export query results to Amazon S3. From there, the data can be moved to other AWS services or downloaded for local analysis.
6) Performance Optimisation
Redshift provides several ways to optimise data transfers for performance. For example, the use of compression algorithms before ingestion can speed up the loading process. Likewise, specifying distribution styles and sort keys can optimise how the data is stored and accessed. This influences the speed of future data transfers within the cluster.
7) Data Streaming with Kinesis Firehose
For real-time Data Ingestion needs, Amazon Redshift can directly integrate with Amazon Kinesis Firehose. This allows you to stream data in real-time into a Redshift cluster, enabling analytics on fresh data. It is mostly useful for businesses that rely on up-to-the-minute data for decision-making.
Set up and troubleshoot Kinesis video streams by signing up for our Amazon Kinesis Training now!
AWS Redshift Pricing Model
AWS Redshift offers flexible pricing starting at £0.19 per hour for a terabyte of data. You need to choose the node type based on your needs. There are three types of nodes:
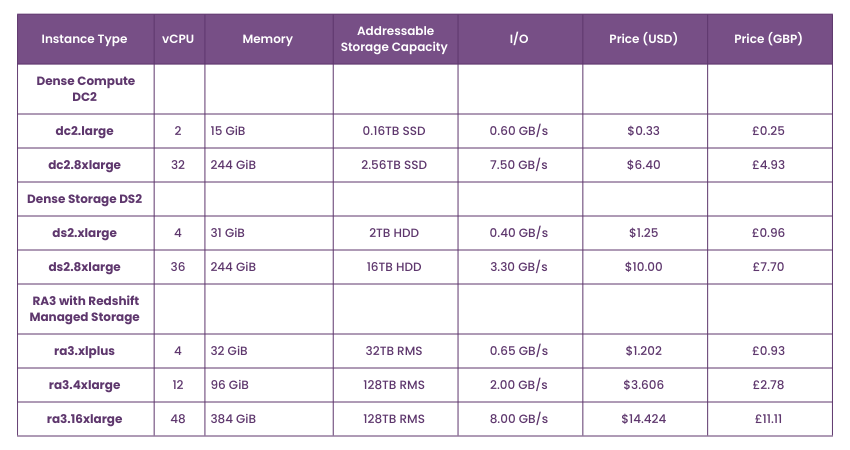
1) RA3 Nodes with Managed Storage: Choose based on the performance level you need. Managed Storage is billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. The number of RA3 clusters depends on the daily data processed.
2) DC2 Nodes: Ideal for high performance with local SSD storage. Add more nodes as data size grows. Best for small data sets needing high performance.
3) DS2 Nodes: Suitable for large data sets with HDD storage. It has a slower performance but is cheaper.
Redshift also has a pay-as-you-go model:
1) Redshift Spectrum Pricing: Run SQL queries on large datasets in an S3 Data Lake. Pay based on the data scanned, priced at £3.82 per terabyte.
2) Concurrency Scaling Pricing: Dynamically allocate resources based on demand. Pay for usage, with one free scaling credit per cluster daily, covering 97% of customers’ needs.
3) Redshift Managed Storage Pricing: Separates computing and storage costs for RA3 nodes. No need to add more nodes as data grows, but RA3 storage is costlier than separate Managed Storage.
4) Redshift ML: Train ML models using SQL queries. Use Amazon Sagemaker free credits before paying for ML models.
For detailed pricing, you can visit the AWS Redshift pricing page.
Launch AWS Redshift clusters and implement Data Warehouses by signing up for our Data Warehousing Training on AWS now!
Amazon Redshift Best Practices
Ensuring optimal performance, security, and manageability in an Amazon Redshift Data Warehouse involves following a set of best practices. Adhering to these guidelines can significantly improve your Redshift experience. Below are some key best practices to consider:
1) Schema Design
1) Distribution Style: Choose an appropriate distribution style based on your query patterns. This will help optimise data distribution across nodes, thus improving query performance. For example, use the "Key" distribution when joining large tables on a common column.
2) Sort Keys: Pick sort keys that align with your query predicates. This will allow Redshift to perform range-restricted scans instead of full table scans, speeding up your queries.
2) Performance Tuning
1) Vacuum and Analyse: Run the VACUUM command often to free up storage from deleted rows and keep data sorted. Use the ANALYZE command to update statistics, which helps the query optimiser create better execution plans.
2) Column Encoding: Allow Redshift to automatically select the best compression methods for columns during the first data load. This minimises I/O and enhances query performance.
3) Data Loading and Unloading
1) Batch Operations: Use bulk operations like the COPY command for ingesting data into Redshift whenever possible. Bulk operations are faster than inserting one row at a time.
2) Parallel Load: Use the COPY command’s parallel load feature to load data from multiple files at the same time. This takes advantage of Redshift’s MPP architecture for faster Data Ingestion.
4) Query Optimisation
1) Use Workload Management (WLM): Properly configure WLM queues to manage query priorities and allocate resources according to business needs.
2) Avoid Using SELECT *: Only query the columns you need. Unnecessary columns consume extra resources and could slow down query execution.
5) Security Measures
1) Encryption: Use SSL for data in transit and enable encryption for data at rest. Amazon Redshift supports AES-256 encryption for enhanced security.
2) VPC Configuration: Deploy your Redshift cluster within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for network isolation.
3) Least Privilege Access: Grant the least amount of privilege necessary for users to perform their tasks. Make use of roles and schema-level permissions to control access.
Conclusion
Understanding What is AWS Redshift is important for businesses that want to use Big Data Analytics. Its strong architecture, performance optimisation, and best practices make it a top choice for companies seeking efficient, scalable, and secure Data Warehousing solutions.
Store data securely on cloud infrastructures by signing up for our AWS Certification Courses now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Amazon Redshift is fully managed, reducing the need for manual setup and maintenance. It offers automatic backups, scaling, and optimisations. Redshift also integrates with other AWS services, providing a seamless and efficient data warehousing solution.

Amazon Redshift secures data with encryption at rest and in transit. It uses AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for Key Management. Redshift also supports network isolation with VPC and offers auditing and logging to monitor access and usage.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various AWS Certification Training, including the Amazon Redshift Training, AWS Professional DevOps Engineer Training, and Systems Operations on AWS - Associate Certification. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into AWS Careers.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to AWS, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 AWS RoboMaker Training
AWS RoboMaker Training
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


