We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Power BI Gateway is an application that helps developers access data located within an on-premises network. The developers can choose from both cloud-based and on-premises locations when requesting their data.
According to Statista Power BI has a 7.1 per cent market share amongst all Business Intelligence and Data Analytics platforms. This share is constantly on the up and owing to the wide suite of features it offers. Power BI Gateway is a powerful tool for integrating on-premises data with Power BI. Learn how to use Power BI Gateway to securely connect to data sources.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Power BI Gateway
2) Benefits of Power BI Gateway
3) Types of Power BI Gateway
4) Power BI Gateway Architecture
5) Power BI Gateway Setup
6) Important Things to Consider Before Installing the Gateway
7) Managing and Monitoring the Power BI Gateway
8) Conclusion
Understanding Power BI Gateway
The Power BI Gateway tool is a software application that helps users access the required data residing in an on-premises network. The tool acts as a gatekeeper for the source of data, and any requests made by users to access the data from a cloud or web-based application go through this gateway. Users are granted access depending on their authentication and data needs.
It's important to note that the tool does not transfer any data from the on-location source to the user's platforms. Instead, the tool connects the data source to the platform directly, and the user or client can then access their data for creating reports and analysing data. The Power BI Gateway tool is also designed to establish connections between the data source(s) and the source on-location.
Companies can utilise this tool to connect to sources like databases, local systems, servers, and so on, which provide them with essential data that needs to be further analysed. Users can access data directly from the on-location source without the need to move the data to the cloud. Generally, when an organisation expands its business, it needs multiple connections to create one Power BI report.
Power BI typically supports more than 50 native connectors to generate valuable reports. However, it is a tedious task to connect with the on-location source, which is where the tool comes in handy.

Benefits of Power BI Gateway
Some key benefits of Power BI Gateway include:
1) Companies can maintain connections to on-location data sources and update their dashboards and data reports by utilising the Power BI Gateway tool.
2) Companies can directly access data without the need to move large volumes of it to an online Cloud Storage, reducing the risk of data loss.
3) Companies can be assured of a secure and reliable connection established between the local data sources and Power BI. The safe connection protects the on-location data.
For instance, a company may require a Gateway to access data from an SQL Server database residing on their local domain.
Types of Power BI Gateway
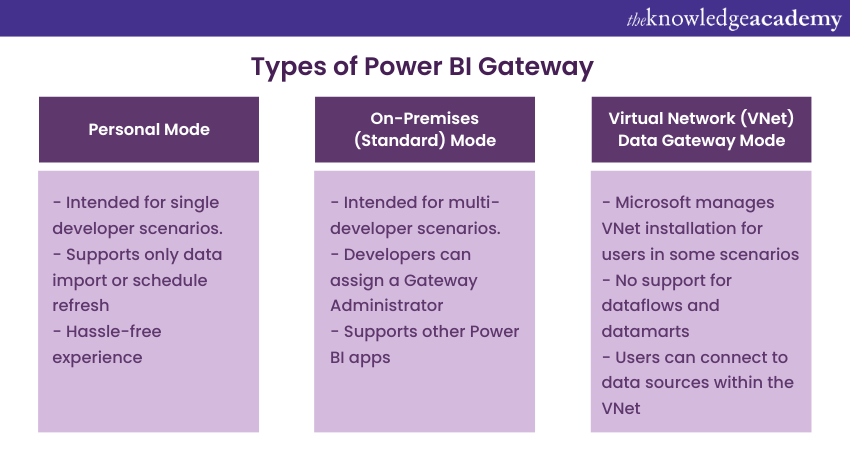
The Power BI Gateway comprises three modes, depending on how the tool is to be used. Here are the descriptions of the modes in detail:
The Power BI Gateway comprises three modes, depending on how the tool is to be used. Here are the descriptions of the modes in detail:
Personal Mode
The Personal Mode of the Power BI Gateway service is installed only if a user intends to utilise it for themselves. They can connect it to the local data sources, including Microsoft SQL Server, Excel, and other similar sources. Users should note that the Personal Mode of the Power BI Gateway only supports one connection type, i.e., import data or schedule refresh.
However, since the service is in Personal Mode, users cannot use it for team development scenarios. This drawback of the Personal Mode can be a possible disadvantage for multiple developers because they would not be able to use the gateway simultaneously. Users can utilise the Personal Mode to create their reports and connect to it. They can also share it with multiple users. However, users must note that the Gateway can only be used by one developer at a time.
The above-mentioned factors explain why the mode is personal. Moreover, users will find it easier to install and configure the Personal Mode than the on-location gateway. The reason is that the Personal Mode installation does not include the option to configure the data sources. Users will not need to perform any configurations after the installation. The Personal Mode is intended for Business Analysts who want a hassle-free experience publishing and refreshing their data reports.
It is best suited for Business Analysts who want to publish their Power BI reports and schedule them to refresh easily. The minimalist and user-friendly characteristics of the Personal Mode make it ideal for single-developer scenarios.
On-premises Standard Mode
The On-premises gateway mode enables multiple developers to connect with each other on various on-premises data sources. With a single installation, developers can use all of its supported services. This mode is best suited for situations that involve multiple developers with access to several sources of data.
Additionally, the On-Premises Gateway Mode allows developers to have a Gateway administrator who can use the central configuration section of the service to add more data sources and control them. Moreover, this mode supports many other apps, such as Microsoft Flow, Azure Logic Apps, and PowerApps, which are cloud-based technologies from Microsoft.
The On-Premises Gateway mode also supports all kinds of connections from Power BI, including DirectQuery and Live Connection, apart from importing data and scheduled refreshes. This mode is intended for enterprise usage of the Power BI tool, and it is beneficial in situations where Power BI is used with other applications like PowerApps.
Furthermore, the Gateway administrator has the authority to allow multiple developers to use the same Gateway. This type of gateway offers more centralised control and monitoring features.
Step into the future of analytics gaining skills to analuse and visualise data with ease with our Business Intelligence Analyst Course, Sign Now!
Virtual Network Data Gateway
The Virtual Network Data Gateway allows users to connect to various sources of data through secure and reliable Virtual Networks without the need to install a gateway since Microsoft manages it. This type of Gateway is most suitable for complex scenarios where many users need access to multiple sources of data.
Microsoft designed the VNet Data Gateway to allow users to connect their Azure data services with Microsoft cloud services within a Virtual Network securely. The VNet Data Gateway establishes a secure communication between the VNet and the data source, enabling query execution and result transmission back to the service.
However, the VNet Data Gateway is only available to datasets in Power BI, Power Platform dataflows, and paginated reports in Power BI. It does not support Power BI dataflows and datamarts, and cloud architectures designed and built to offer data users access in compliance with local laws and regulations.
Limitations in Azure AD, such as activating the service endpoint for Azure AD on the delegated VNet and activating conditional access policies for the tenant, can cause possible failures for users. Users can only set their regional information and subscription details for the VNet once during the initial VNet Gateway creation.
Learn to manage data and turn it into powerful insights to make better-informed business decisions with our Microsoft Power BI Training now!
Power BI Gateway Architecture
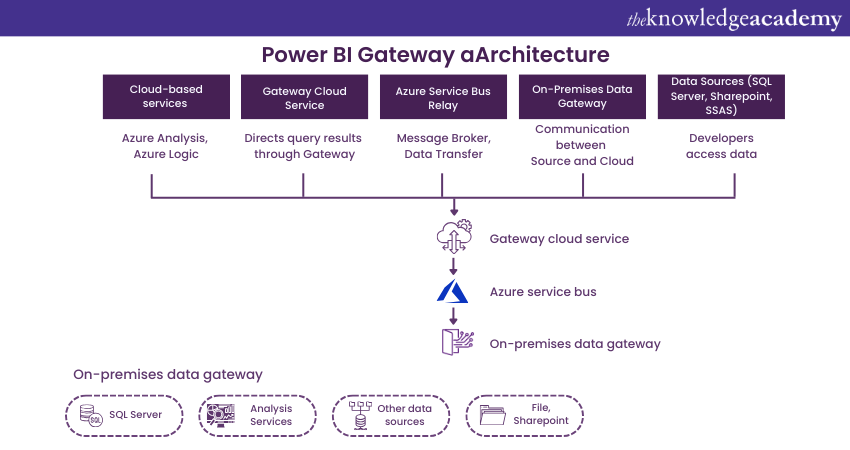
Users may find it difficult to understand the architecture of the on-premises Gateway. Here is a simplified description of how the Gateway works:
1) The On-premises Power BI Data Gateway typically has three components: Cloud Services, Gateway Services, and On-Premises Data Sources.
2) The cloud-based Power BI service creates an access query that requests data from an on-premises data source.
3) The Power BI Gateway Cloud service processes and analyses the request, and then sends it to the Azure Service Bus (ASB). Additionally, the service manages the Azure Service Bus by default.
4) All data access requests sent to the on-premises data gateway are handled by the Azure Service Bus. The credentials are decrypted for the data source and the user is connected to the data source with the help of the ASB service.
5) Additionally, the On-Premises Data Gateway sends the data access query to the on-premises data source from the cloud service.
6) The data query is executed at the source, which can be SQL Server, SharePoint, SSAS, and so on.
7) The result of the executed Data query is returned by the data source(s) to the on-premises Data Gateway. Furthermore, the On-Premises Data Gateway sends the result back to the cloud service via the Azure Service Bus.
Regarding data requests pulled by the Azure Service Bus, the Gateway pulls the ASB to check for pending data requests. Although the ASB cannot trigger the data gateway, this protocol is in place to ensure the architecture's security.
In a scenario where the Data Gateway can be triggered by the ASB, the security ports for inbound requests will have to be kept open. Keeping inbound security ports open puts the architecture's security at risk. Therefore, by using only outbound security ports, the data gateway's connection is kept very secure.
Enhance your knowledge of Power BI learning new techniques with our DAX Training– Register now!
Power BI Gateway Setup
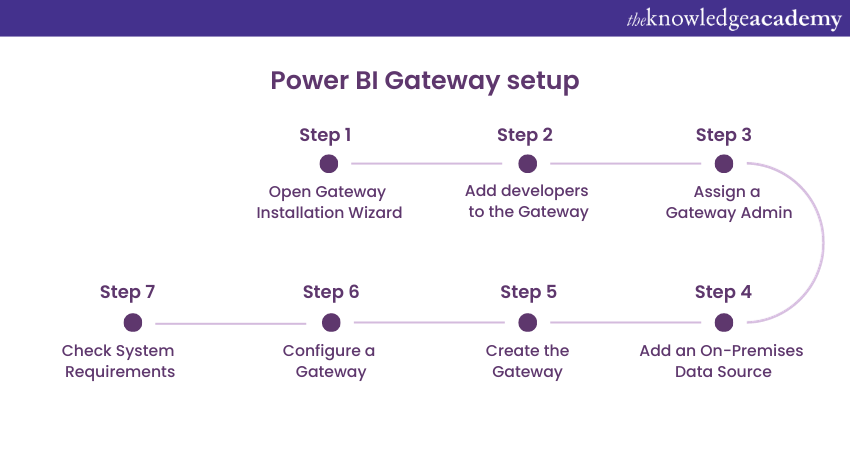
To start using the Data Gateway in Power BI, developers can follow these four steps:
1) Install the Data Gateway on their systems.
2) Add other developers to the Data Gateway, giving them access to on-premises data sources.
3) Use data from on-premises sources to analyse and generate reports.
4) Utilise the Power BI Gateway service to refresh data on-premises, ensuring that reports and dashboards are updated.
Important Things to Consider Before Installing the Gateway
The Power BI Gateway can be installed on any machine within the on-premises domain, but it is not recommended that it be installed directly on the Domain Controller. Below are the requirements for installing the gateway:
Minimum Requirements:
a) .NET Framework: Version 4.7.2 (for December 2020 or earlier releases) or 4.8 (for February 2021 or later releases).
b) Operating System: 64-bit version of Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 R2 with TLS 1.2 and supported cipher suites.
c) Disk Space: At least 4 GB for performance monitoring logs (default configuration).
Recommended Specifications:
a) Processor: 8-core CPU.
b) Memory: 8 GB RAM.
c) Operating System: 64-bit version of Windows Server 2012 R2 or later.
d) Storage: Solid-state drive (SSD) for better spooling performance.
How Many Gateways are Required?
A single gateway is sufficient for most scenarios. However, in some cases, using multiple gateways can improve performance. For instance, if one gateway handles both scheduled data refreshes and Live Connections, the Live Connection may experience slow performance during a refresh. In this situation, using separate gateways for Live Connections and scheduled refreshes is advisable.
a) The gateway can only be installed on 64-bit Windows operating systems.
b) Choose the appropriate gateway version carefully. For servers, it is strongly recommended to install an on-premises standard gateway instead of a personal gateway.
c) The machine hosting the gateway must always remain operational to handle data refresh requests effectively.
d) Avoid installing the gateway on a machine connected via a wireless network, as this can significantly reduce performance.
e) The gateway requires certain outbound ports to be open: TCP 443 (default), 5671, 5672, and 9350–9354. No inbound ports are needed.
Managing and Monitoring the Power BI Gateway
Effectively managing and monitoring the Power BI Gateway is essential for optimal performance. Here are vital considerations for this process:
Manage Gateways
Familiarise yourself with the Power Platform admin centre to manage On-premises Data Gateways efficiently. Once installed, manage Gateways based on specific requirements. The management options may vary depending on how each service integrates Gateways. Administrators can add or remove Gateway administrators in the management dashboard, configure settings, and manage security roles and permissions.
Troubleshooting
Monitoring the On-premises Data Gateway's performance is crucial. Instead of manually monitoring performance counters, Power BI provides query logging and a Gateway Performance PBI template file for visualising results. When troubleshooting, verify the Gateway software version, check logs for errors, and consult the Power BI community forum for solutions.
High Availability
Prioritise high availability for datasets and reports in Power BI. Design a well-architected On-premises Data Gateway setup with failover and redundancy. Cluster multiple Gateway instances, monitor each instance's health, and regularly test failover strategies. This ensures efficient, reliable data access, minimising downtime and operational challenges.
Conclusion
The Power BI Gateway establishes a connection between the dataset on the cloud-based service and the source of data on-premises. It is important for developers to know that the Gateway is necessary only for accessing data sources on-premises data sources.
Take your data analytics skill to the next level gaining new techniques to visualise and monitor data with ease with our Grafana Training, Sign Now!
Frequently Asked Questions

a) OS: 64-bit Windows 8/10 or Server 2012 R2 or later.
b) .NET Framework: 4.7.2 or 4.8.
c) Specs: 8-core CPU, 8 GB RAM (recommended), SSD storage.
d) Network: Open outbound ports (TCP 443, 5671, 5672, 9350-9354).
e) Always-on machine for uninterrupted service.

a) Only available on 64-bit Windows OS.
b) Does not support wireless connections (slower performance).
c) Requires separate gateways for high workloads like simultaneous Live Connections and data refreshes.
d) Limited to outbound ports; no inbound connections allowed.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Intelligence Reporting, including Business Intelligence Analyst Course, Microsoft Power BI Course and Tableau Desktop Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Power BI Alternatives.
Our Office Applications Blogs cover a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Power BI skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


