We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The Cost of Sales (CoS) is essentially the heartbeat of any business's profitability. It’s the price you pay to turn ideas into tangible products or services. CoS represents the direct costs involved in producing goods or services sold by a company, including materials, labour, and overhead directly tied to production.
In short, CoS is the formula for successful Pricing, budgeting, and growth. This blog will take you through the key concepts and calculations behind COS. So read on and drive your business' profitability like never before!
Table of Contents
1) What is Cost of Sales?
2) Components Included in Cost of Sales
3) Importance of Cost of Sales
4) How to Calculate the Cost of Sales?
5) How to Calculate Cost of Sales in Different Industries
6) Cost of Sales vs Cost of Goods Sold
7) How to Manage and Reduce the Cost of Sales?
8) Cost of Sales Examples
9) Does Cost of Sales Include VAT?
10) Conclusion
What is Cost of Sales?
Cost of Sales, also known as Cost of Goods Sold (CoGS), refers to the direct costs incurred by a business to produce the goods or services it sells during a specific period. These costs are directly tied to the production process and include expenses related to raw materials, labour, and manufacturing overhead. Cost of Sales is a fundamental aspect of a company's income statement and plays a crucial role in determining gross profit.
Components Included in Cost of Sales
The Cost of Sales is a multi-faceted metric that encapsulates various direct expenses associated with producing goods or services. Each component contributes significantly to shaping the comprehensive cost framework of a company's products or services.
Let's delve deeper into these components to understand what comprises the Cost of Sales:

1) Direct Materials
Direct materials are the foundational elements required to create a product. They encompass all the essential components that go into the manufacturing process.
Consider the following:
a) Direct materials include raw resources like metals, plastics, and textiles, as well as semi-finished components.
b) The cost of direct materials goes beyond the initial purchase price.
c) It includes acquisition, transportation, storage, and handling expenses.
d) Effective Inventory Management is essential for a smooth production process.
e) A shortage of materials can cause production delays.
f) Excess inventory can tie up capital and increase storage costs.
2) Direct Labour
Direct labour costs represent the compensation paid to employees who are directly engaged in the production process. These individuals use their skills and labour to transform raw materials into finished goods. Here are some important points about direct labour:
a) Direct labour includes assembly line workers, machine operators, and artisans.
b) Direct labour costs include wages, salaries, benefits, and overtime pay.
c) Accurate tracking of time and tasks is essential for attributing labour costs to specific products.
d) Efficient Management of direct labour helps optimise productivity and maintain product quality.
Learn how to build trust with callers by signing up for our Telephone Sales Training now!
3) Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing overhead, also known as indirect manufacturing costs, encompasses various expenses that indirectly contribute to the production process. These costs do not directly relate to specific units of production but are essential for the overall manufacturing environment to function smoothly.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses such as:
a) Utilities: Costs associated with electricity, water, and gas required for running production machinery and maintaining the manufacturing facility.
b) Rent and Depreciation: The cost of leasing or owning the production space, as well as the gradual reduction in the value of machinery and equipment over time.
c) Maintenance: Expenses incurred for the upkeep and repair of machinery and equipment.
d) Indirect Labour: Compensation for employees who support production indirectly, such as maintenance workers, supervisors, and quality control personnel.
It's important to note that manufacturing overhead costs are not always easy to allocate to specific products, as they benefit the overall production process rather than individual units.
Supercharge your sales career with our industry-leading Sales Training Courses. Discover proven strategies to improve sales outcomes and increase your earning potential.
Importance of Cost of Sales
The Cost of Sales (CoS) is a pivotal financial metric that holds significant importance for businesses across industries. Its influence extends beyond the realm of Accounting and finance, impacting various aspects of operational decision-making and strategic planning. Let's delve into why the Cost of Sales is so crucial and the reasons it commands attention from business leaders and financial professionals.
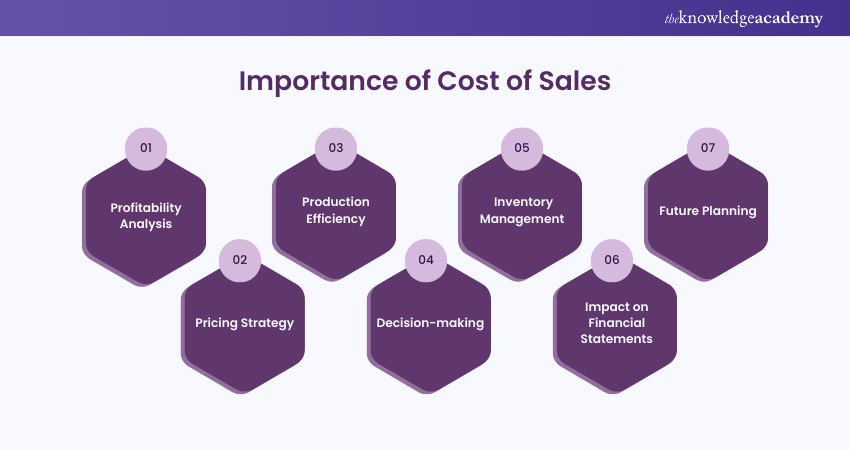
Profitability Analysis
One of the primary reasons for calculating and understanding the Cost of Sales is its direct link to profitability analysis. By deducting CoS from the total revenue, a company arrives at its Gross Profit. This figure indicates the amount of money a business retains after accounting for the direct costs of producing goods or services. A healthy Gross Profit margin suggests that a company is efficiently managing its production costs and generating substantial revenue.
Pricing Strategy
Cost of Sales plays a vital role in shaping a company's pricing strategy. Businesses must strike a delicate balance between setting prices that cover production costs and pricing their products competitively. Accurate CoS data enables companies to calculate a minimum acceptable selling price that ensures they don't sell products at a loss while remaining competitive within their market.
Production Efficiency
Monitoring and analysing the Cost of Sales can help identify inefficiencies within the production process. High CoS relative to Revenue may indicate that the production process is not as efficient as it could be. This insight prompts businesses to focus on optimising their processes, reducing wastage, and streamlining operations to improve overall efficiency.
Decision-making
Cost of Sales data aids decision-making across various domains. From Inventory Management to outsourcing decisions, understanding the direct costs involved in producing goods or services provides a foundation for informed choices. For instance, if CoS is disproportionately high, a company might explore outsourcing certain components to reduce costs and enhance profitability.
Inventory Management
Effective Inventory Management is intricately tied to CoS. By tracking CoS and comparing it with inventory turnover rates, companies can make informed decisions about stock levels. Striking the right balance between maintaining sufficient inventory to meet demand and minimising carrying costs is crucial for optimal financial health.

Impact on Financial Statements
The Cost of Sales has a significant impact on a company's financial statements, particularly the Income statement and the Balance sheet.
a) Income Statement: CoS is subtracted from the total revenue to calculate Gross Profit. This Gross Profit figure influences the Net Income by further deducting operating expenses, interest, taxes, and other costs.
b) Balance Sheet: The Cost of Sales indirectly affects the Balance Sheet by influencing the value of ending inventory. Unsold products from the previous period become the beginning inventory of the next, shaping the financial health of the company.
Future Planning
Accurate knowledge of CoS is essential for long-term planning. Businesses can evaluate whether their production methods are maintained or not. Furthermore, they need to explore initiatives for cost-saving opportunities.
Elevate your Sales Management expertise with our Sales Management Training – join now!
How to Calculate the Cost of Sales?
As stated before, the CoS metric serves as a pillar for evaluating a company's profitability, setting prices, and making strategic decisions. To better grasp its significance, let's dive into the details of calculating the Cost of Sales. The formula to calculate CoS is simple:
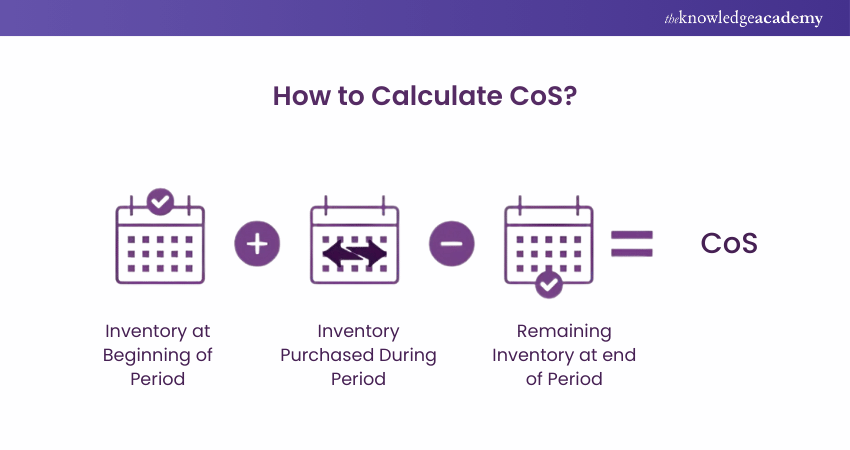
Here's a breakdown of each component:
a) Beginning Inventory: This is the value of inventory at the start of the accounting period. It includes all the products that were not sold during the previous period and have been carried over.
b) Purchases: This refers to the value of additional inventory acquired during the current accounting period. It includes both direct materials and finished products that are purchased for resale.
c) Ending Inventory: This represents the value of inventory remaining at the end of the accounting period. It includes products that have not been sold yet and will be carried over to the next period.
The CoS formula essentially calculates the total cost of all products that were sold during the period, which is why the value of ending inventory is subtracted. This is because these unsold products are still part of the inventory and have not contributed to generating revenue.
To illustrate this concept, let's consider a hypothetical example:
a) Beginning Inventory: £50,000
b) Purchases: £100,000
c) Ending Inventory: £30,000
Using the CoS formula:
CoS = £50,000 + £100,000 - $30,000 = £120,000
This means that the company's total Cost of Goods Sold for the period is £120,000. In other words, it cost the company £120,000 to produce the products that were sold during this time frame.
Transform data into sales strategies with our Sales Analytics Training – Join today to drive exponential growth!
How to Calculate Cost of Sales in Different Industries
The Cost of Sales equation may need adjustment based on your business type to achieve the most accurate result. Below are the example equations for service businesses, retailers, and manufacturers.
Cost of Sales Example Formula for Service Businesses
Service businesses tend to count all their input costs, including the Employees who offer services and the facilities where they are based. Back-office employees are excluded from the Cost of Sales. In some cases, travel and equipment costs might not be relevant, such as a freelancer working at home. Here’s the formula:

Cost of Sales Example Formula for Retailers
Retailers can use the following Cost of Sales formula for inventory accounting. An e-commerce business may choose to add shipping and transaction fees, which are common for retail sales.

Cost of Sales Example Formula for Manufacturing
Manufacturers keep raw materials and production costs in consideration for their Cost of Sales calculations. A manufacturer may choose not to include freight or warehousing if they see these as operating expenses. Here’s the formula:

Cost of Sales Vs Cost of Goods Sold
The Cost of Sales and Cost of Goods Sold keep a record of the cost of production of services and goods. The costs might cover raw materials, labour, and overhead costs.
Cost of Sales
Cost of Sales, also known as cost of revenue, determines how many goods or services a company sells. For example, an IT company must include Cost of Sales for direct expenses of travel in it.
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold track record of cost that is directly tied to goods produced by the company. For example, labor and material used to create a product. However, indirect costs like Sales, distribution and marketing costs are excluded.
Acquire advanced selling skills to become a better sales professional in our Outbound Sales Training - Sign up now!
How to Manage and Reduce the Cost of Sales?
Managing and reducing the Cost of Sales is a crucial aspect of business operations. Companies can enhance their profitability, competitiveness, and overall financial health by implementing effective strategies. Here are some strategies that businesses can utilise to achieve these goals:
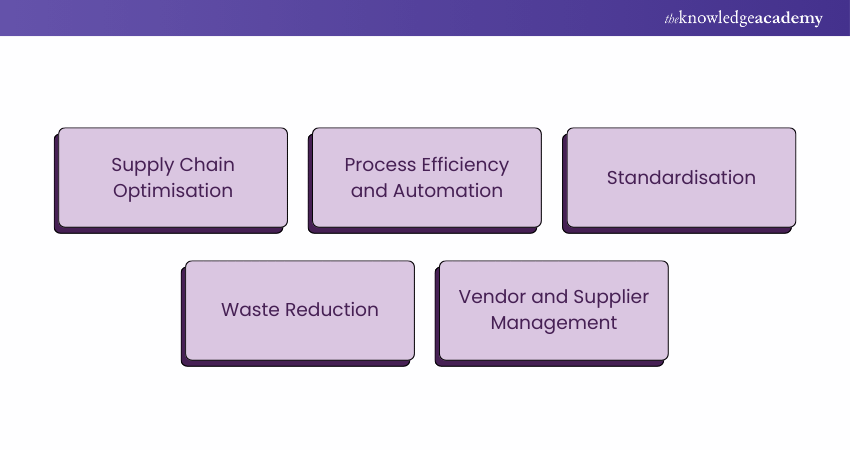
1) Supply Chain Optimisation
A well-optimised supply chain can significantly impact the Cost of Sales. By building strong relationships with suppliers and negotiating favourable terms, businesses can secure better prices for raw materials and components. Just-in-time Inventory Management and demand forecasting can also minimise excess inventory and associated carrying costs.
2) Process Efficiency and Automation
Streamlining production processes through automation and lean manufacturing principles can lead to substantial cost savings. Automation reduces labour costs and enhances production speed and accuracy. By identifying and removing bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the production process, companies can lower their overall Cost of Sales.
3) Standardisation
Standardising product designs, materials, and production processes can simplify operations and reduce costs. When components and processes are consistent across products, companies can achieve economies of scale and negotiate bulk discounts on materials. This approach also facilitates training and reduces the likelihood of errors, further cutting costs.
4) Waste Reduction
Minimising waste in both material and energy consumption is an effective way to lower the Cost of Sales. Sustainable practices not only reduce costs but also align with environmental and social responsibilities. Adopting techniques like recycling, reusing, and energy-efficient manufacturing can lead to substantial savings over time.
5) Vendor and Supplier
Close collaboration with vendors and suppliers is essential. Developing long-term partnerships and sharing information can lead to cost-sharing arrangements, volume discounts, and improved delivery schedules. Regularly reviewing supplier contracts and performance can help identify areas for cost reduction and improvement.

Cost of Sales Examples
The following examples illustrate if an expense counts as CoS:
1) If you pay your team commission, you can either factor it into the cost of delivering your product or service or treat it as an operating expense.
2) When repairing or maintaining equipment used in production, you may choose to classify this as a CoS or an operating expense.
Does Cost of Sales Include VAT?
The Cost of Sales doesn't include VAT incurred on purchasing the goods or services because this portion belongs to the tax authority.
Conclusion
Cost of Sales is a critical metric that provides insights into a company's production efficiency and profitability. By grasping its components, calculation methods, and impact, businesses can make smart decisions that contribute to their financial success. Effective management of CoS, along with a focus on optimising processes, positions companies for sustained growth and improved competitiveness in the market.
Empower your sales journey with our comprehensive Online Sales Training. Sign up now and achieve remarkable results!
Frequently Asked Questions

There are plenty of ways to reduce Cost of Sales, such as:
a) Negotiating with suppliers for better prices or terms.
b) Shopping for better deals on stock or raw materials.
c) Increasing production efficiency with new technology.
d) Improving Inventory Management.
e) Outsourcing specific skills so you don’t need to hire staff.

The Cost of Sales directly impacts your profitability. If there isn’t much difference between the CoS and your product's retail price, your business won’t profit much. A higher Cost of Sales also impacts gross profit margins and overall net profit.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Sales Training, including the Sales Bootcamp Training, Telephone Sales Training, and Closing Sales Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Sales Analytics.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Sales, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Sales skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Sales Bootcamp
Sales Bootcamp
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


