We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Problem Management is one of the 34 practices in ITIL 4. It is a process that undertakes the life cycle management of underlying problems or incidents. There is a cause-and-effect relationship between an incident and a problem. Accordingly, the ITIL defines a problem as the cause of one or more incidents. For instance, if a user reports that they cannot access an application, that is an incident.
However, when the cause of this incident is further investigated, it is discovered that the application was not accessible due to a technical error or server overload, which is defined as the problem that caused the incident. This distinction between problem and incident will help you better understand ITIL Problem Management and how you can use this approach to improve your company's performance.
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL Problem Management?
2) Objectives of Problem Management in ITIL
3) What are the types of ITIL Problem Management?
4) Process flow for Problem Management
5) Problem Management roles and responsibilities
6) Benefits of Problem Management in ITIL
7) Fundamental challenges of ITIL Problem Management
8) Conclusion
What is ITIL Problem Management?
Problem Management is a critical process within IT service management, focusing on the life cycle management of “Problems.” Its effectiveness is measured by its ability to swiftly identify and implement solutions or temporary fixes, thereby reducing organisational impact and preventing future occurrences. This process involves pinpointing the faults within the IT infrastructure that lead to problems and, consequently, to user-reported Incidents. ITIL outlines key definitions pertinent to this process:
a) Problem: The origin of one or more Incidents, typically unidentified when initially recording the Problem.
b) Error: A defect or malfunction failing IT services or other configuration items.
c) Known error: A Problem with an established root cause and a documented workaround.
d) Root cause: The fundamental reason behind an incident or problem.
These definitions are foundational for understanding and executing Problem Management effectively.
Objectives of Problem Management in ITIL
Problem Management has three key objectives:
a) To identify and prevent problems (and resulting incidents) from happening
b) To eliminate repetitive Incidents and have control over problems
c) To minimise the impact of Incidents that cannot be prevented
What are the types of ITIL Problem Management?
Organisations can benefit from the ITIL Problem Management process in two ways:
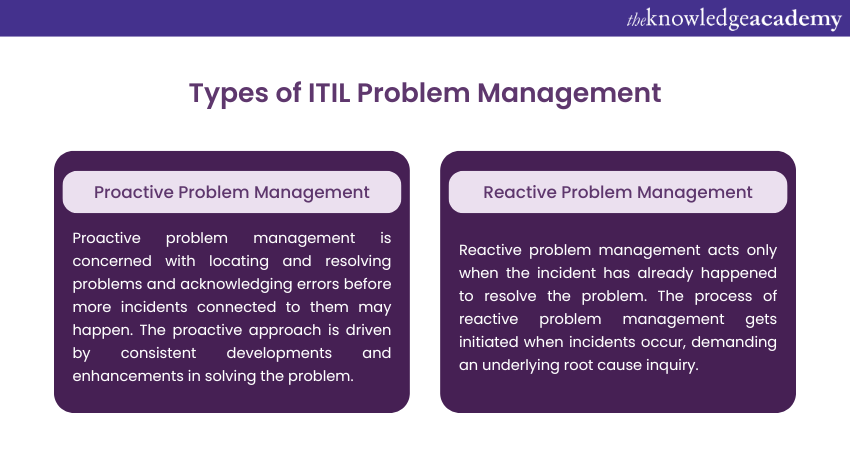
Proactive Problem Management
The task of the Proactive Problem Management process is to identify risks and prevent any potential future incidents from occurring in your organisation. Proactive Problem Management, according to ITIL, is concerned with locating and resolving problems and acknowledging errors before more incidents connected to them may happen. The proactive approach is driven by consistent developments and enhancements in solving the problem.
The proactive team investigates and identifies risks lurking around the organisation instead of waiting for problems or incidents to occur. Any errors or warning signs that could trigger or start a major problem are flagged and rectified immediately to avoid any impact on your business.
Instead of solving issues, Proactive Problem Management stops incidents from happening again. As a result, proactive issue-solving might be challenging. If you spend too much time attempting to repress problems from happening in the future, you can wind up messing with resource availability, risk mitigation, Capacity Management, and Change Management.
It is necessary to do a cost-benefit analysis of the Proactive Problem Management procedure.For instance, the security warnings identified in your business software could lead you to identify more incidents. By keeping your software updated and fixing the identified threats, your security structure enhances and helps you minimise incidents and problems in future.
Elevate your career: Join our ITIL Certification Course and learn more!
Reactive Problem Management
Reactive Problem Management acts only when the incident has already happened. It focuses on resolving the problem. The process of Reactive Problem Management is initiated when incidents occur, demanding an underlying root cause inquiry.
The team identifies the underlying problems related to the incidents and sets to resolve them at the earliest. Further, with the results derived from the Root Cause Analysis, the team investigates the incident to identify the underlying causes and tries to find ways to fix the problem completely.
For instance, the swarming technique is accustomed by multiple businesses for Reactive Problem Management. This technique helps many team members to collectively direct their attention and skillset on the incident and focus on identifying the root cause that could have led to the problem.
From the discussion above, you can see that both Proactive and Reactive Problem Management seem different, but they are closely related to each other. We can say that both approaches are two sides of the same coin. This process is not authoritative in nature and can be customised to fit the needs of your services.
The practitioners managing the IT-enabled operations and digital services and products can benefit from ITIL® 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support Certification Course!
Process flow for Problem Management
Image Description: Process flow for Problem Management
The first step of the ITIL Problem Management process starts with identifying the problem and concludes with the team taking preventive measures to avoid a similar problem in the future. Here's a complete breakdown of the ITIL Problem Management lifecycle stages:

Preparation
The first response stage to an incident is planning and preparation. This time should be utilised meticulously to plan, prioritise, assign, and delegate roles and responsibilities for the team.
Setting up a response plan and implementing an effective strategy is the key to ensuring a consistent and timely response to any possible incidents. It is critical to be prepared for each day to handle any new threats and vulnerabilities, such as ransomware updates, new viruses, and other attacks emerging unexpectedly.
Problem identification
The second stage in ITIL Problem Management is crucial: it involves identifying and detecting problems. The team aims to recognise issues early to manage, scrutinise, and eliminate potential threats. Incidents that recur or complaints from end-users often highlight these problems.
The team can ascertain if similar problems have occurred by consulting their issue logs. Organising these threats into categories helps prioritise them based on their criticality and frequency, setting the stage for subsequent resolution phases.
Problem logging and threat containment
To effectively maintain a complete historical record of all incidents and problems, it’s essential to log pertinent details such as user information, timestamps, descriptions, related incidents, and resolution data. This comprehensive logging serves two key purposes:
a) Categorisation: By categorising each entry, teams can efficiently monitor, assign, and systematically escalate issues.
b) Prioritisation: Prioritising issues is vital for staff to comprehend and establish a resolution hierarchy.
Multiple issues often arise simultaneously, so prioritisation based on impact and urgency ensures that the most critical problems are addressed first. This strategy guarantees that the IT support team is organised and focused on high-priority issues, facilitating swift resolutions and segregating urgent matters.
Threat containment
You must prioritise and immediately contain the incident based on the severity of critical threats. The foremost goal of containment is to isolate the hazard to minimise and prevent further damage to your system.
The antivirus can only quarantine the pre-defined threats. But other severe threats, such as data breaches, malicious malware, and undefined viruses, would require a sophisticated approach to handle.
Problem analysis
Discovering the underlying root cause of an issue at this step in the ITIL Problem Management process is essential to repairing your system and preventing any such future attacks. To tackle the problem as quickly as possible, your team needs to plan the best course of action. You may enhance the overall availability of services and achieve better outcomes at this point by proactively detecting similar incidents that may influence business operations.
Resolving the problem
Resolving the problem is one of the most crucial stages of the actual work. You need to initiate the most appropriate solution once you have identified the root cause of the problem.
After it has been resolved and tagged as closed, the problem no longer continues and cannot result in more incidents. You must confirm that the pertinent description of the issue and the measures your team took to fix it are included in your problem record.
Recovery
The recovery phase begins with post-incident analysis and threat neutralisation. The extent of damage dictates the duration of the recovery effort. For data breaches, deploying patches or replacing compromised servers is essential. If the incident involved unauthorised access, updating passwords is a straightforward fix.
Understanding the incident’s nature aids in preventing future issues and enhances incident response strategies, ensuring thorough and effective recovery. This process restores operations and strengthens security measures against potential future incidents, contributing to a resilient organisational infrastructure.
Problem prevention and testing
Problem prevention and testing are the final and most crucial steps in the ITIL Problem Management lifecycle. Your team will have a deeper understanding of the issue and be working nonstop to solve it. The foremost goal is to prevent similar issues or occurrences from happening again.
You may also write knowledge-based articles about specific problems and publish them as best practices for Problem Management so that others can learn and benefit from them. Understanding the differences between ITSM vs ITIL can guide you more on that.
Advance your IT career with our ITIL Courses. Learn essential skills and excel in IT management. Register today!
Problem Management roles and responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of a Problem Management team are directly related to the organisation's current structure. Factors such as the organisation's age, culture, technology, and presence among the worldwide nations matter and affect the formation and setup of the Problem Management team.
a) Should be aware of the organisation's general process and strategies to form a strong team.
b) Should be familiar with the organisation's resources available or allotted for the Problem Management team.
c) Acquire knowledge and maintain accountability towards the organisation's growth and fall life scale.
d) Own up to the responsibility to perform effectively and increase the efficiency of the entire team and process.
e) Organisations should be prepared to grow and mature along with their developments and evolution.
Benefits of Problem Management in ITIL
Now let us list out the benefits of Problem Management in ITIL:
a) Prepares you to tackle the anticipated attack incidents that might affect you.
b) Encourages consistent improvement and prevents incidents.
c) Can save time as you are pre-prepared to react and initiate countermeasures in case of an incident or attack.
d) Increases overall productivity and efficiently boosts the value of the organisation.
e) Avoids unnecessary costs, time, and effort by avoiding incidents of attacks.
Maintaining stability and preventing incidents will enhance the quality and performance of the service provided.
Fundamental Challenges of ITIL Problem Management
The challenges in problem-solving include the following:
1) It is very time-consuming and labour-intensive.
2) The problems in ITIL Problem Management are never measured, resulting in the management being strenuous and demanding at times.
Upgrade your skills with ITIL® 4 Foundation Bridge Training – streamline IT services and enhance career opportunities. Register Now!
Conclusion
In this blog on ITIL Problem Management we discussed how Reactive Problem Management is well-designed in most businesses. However, Proactive Problem Management is something many organisations lack. This understanding will help the qualified ITIL Problem Management professionals to establish their presence in the organisation and expect better career growth.
For those who wish to be involved in understanding the diagnosis problems, you can join our Root Cause Analysis Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Professionals can find reputable resources or guidance to master ITIL Problem Management practices from the following:
1) Official ITIL Certification Courses
2) Specialised training programs
3) Industry conferences
4) Online forums and communities
5) By following webinars and books

There are some tools like ServiceNow, JIRA, Zendesk, etc., are commonly use in Problem Management. These tools help in issue tracking, root cause analysis, and incident management. They also facilitate software solutions by streamlining communication, providing data analytics, etc.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL® Certification Training, including ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Course, ITIL 4 Specialist: Create Deliver and Support CDS, and ITIL 4 Specialist: Drive, Plan and Improve DPI. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ITIL 4 Guiding Principles.
Our IT Service Management blogs covers a range of topics related to ITIL 4, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 13th Mar 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


